Monte Carlo Simulation of Risk
Contents |
Abstract
”To dare is to lose one’s footing momentarily. To not dare is to lose oneself” - Søren Kierkegaard
Staying dynamic is a means of survival in today’s modern society, thus the expression the burning platform. In order for companies to stay competitive and sustain their businesses, they have to either become cost leaders or product leaders i.e. innovative. In order to realize this, companies have to dive into new areas of business, explore new possibilities in terms of evolving their products and/or processes. During the process of exploring and maintaining dynamism, uncertainty is inevitable due to the respective volatile nature of the markets within which the diverse companies operate in. Companies can’t foresee the future, hence don’t know how their respective markets will react to their new ways of doing business, new products or on the other hand if they are resilient enough to sustain unexpected drawbacks when exploring new paths. Thus it can be concluded that risk is incorporated in the DNA of any project, program or portfolio management, therefore “Risk Management” is a necessity for companies to continuously embark when exploring new dimensions in order to mitigate risk and suppress their corresponding consequences. There are several ways in which risk management can be conducted. This article provides a profound description of how to conduct a quantitative risk assessment by means of utilizing Monte Carlo simulations. Risk is random since its uncertain thus Monte Carlo Simulations are utilized to simulate it by means of a probability distribution.
- not complete*
Risk
It is basically inevitable not to associate risk and uncertainty to any human activity[1] although they can vary from activity to activity, depending on what’s at stake. In literature, risk in management has been defined as the probability (chance) of an event occurring, which could eventually result (uncertainty) into a negative impact (consequence) on a particular project in context[2][3] thus risk is an expected loss over time.
Risk = Probability of risk occurring ×Impact of risk occurring
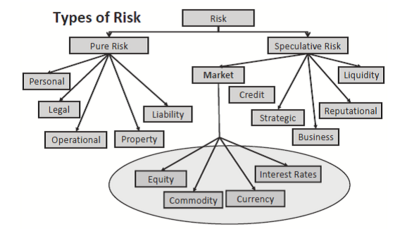
Risk can be categorized as either pure or speculative [4] [5] , as depicted in Figure 1.1 Regarding pure risk, there is no benefit or gain pertained to it, thus loss is the only possible outcome e.g. companies exposed to fraud or damage of assets etc. On the other hand, speculative risk can result into an uncertain degree of loss or gain e.g. a company can either gain or lose on investing in a new product, since there is a risk of market rejection. In this article emphasis is laid on speculative risk.
Risk Management
When dealing with project, program or portfolio management it is crucial to understand that a lot of uncertainties (risks) are pertained to them, since their eventual benefits are projected into the future (vision/goal). These uncertainties occur randomly within the lifecycle of the different categorize of management, thus eventually resulting into delays, budget overruns and eventually terminations, if not managed hence the importance of risk management. According to ISO 31000 (Danish Standards, 2009) risk management is the coordination of activities to direct and control an organization with regards to risk. In literature (Nemuth, 2008), (Danish Standards, 2009) risk management can be decomposed into four continuous phases i.e. risk - Identification, Analysis, Evaluation and Monitoring as depicted in Figure 2 1 and elaborated below. Before embarking on a risk management course, it is crucial to commence with a risk management plan. Risk management planning is the structuring and detailing of how the risk management process is going to be conducted throughout the lifecycle of a project (Tysiak & Sereseanu, 2010). Subjects such as methodology, practices, roles and responsibilities, sequence and timing of activities are pertained to risk management planning (Danish Standards, 2009).
- Risk management planning:
This phase involves the structuring and the detailing of how risk management should be conducted during the course of the particular project in context. Subjects such as methodology, roles and responsibilities, time span and risk categories are pertained to risk management planning.
- Risk identification :
This phase involves the pinpointing of potential risks that might eventually affect a particular project in context and their causes.
- Qualitative risk analysis:
This phase involves prioritizing and evaluating the initially identified risks in the previous phase, since risk can have different severity degrees (fig-risk matrix). Furthermore, a description of the different consequences pertained to the different risks and means by which they can be mitigated is given.
- Quantitative risk analysis:
This phase involves the utilization of probability distributions to model the individual risks
- Risk response planning:
- Risk monitoring and control:
Monte Carlo Simulation
Methodology
Data source
Data fitting
Probability Distribution
Random Variable
Discrete or continuous
Bounded or non-bounded
Parametric or non-parametric
Simulation
Tools (software)
@Risk
Latin Hyper cube (LHC)
comparison
Example
Strengths and weaknesses
- ↑ Hertz David B. & Thomas Howard,Risk analysis and its application 1983
- ↑ WANG, Xing-xia; HUANG, Jian-wen,Risk analysis of construction schedule based on Monte Carlo simulation,International Symposium on Computer Network and Multimedia Technology (CNMT 2009)
- ↑ Nemuth, Dr.-Ing. Tilo,Practical Use of Monte Carlo Simulation for Risk Management within the International Construction Industry,6th International Probabilistic Workshop 2008
- ↑ Hertz David B. & Thomas Howard,Risk analysis and its application 1983
- ↑ Gupta, Aparna,Risk Management and Simulation 2013
- ↑ Gupta, Aparna,Risk Management and Simulation 2013