Prince2
Contents |
Abstract
Many major projects fail due to complexity and poor management. The use of standardized project management methodologies is in many cases a necessity in order to achieve desired progress and results. PRINCE2 is a widely used project management methodology and is to be considered as a solution for managing advanced projects. It is designed to drive projects with focus on benefits in each stage of the project. The essence of PRINCE2 is to break the project down into smaller stages which simplifies the project's process. The following article will describe the method, compare it to other methodologies and come with a critical evaluation of it. The article will also discuss PRINCE2’s suitability in relation to a variety of project scales.[1]
History
According to the Cambridge dictionary a project is defined as “a temporary organization that is created for the purpose of delivering one or more business products according to an agreed business case.” [2]
1975 PROMPT
1989 PRINCE
1996 PRINCE2
2009 revision
2017 revision
Overview
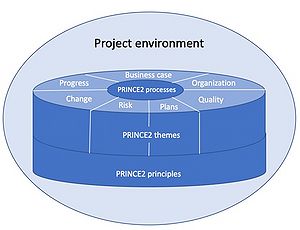
PRINCE2 is a project management methodology and stands for projects in controlled environments. It is used globally and based on experience from professionals within a variety of different professions and industries. It is generic and can be applied to projects of different art, regardless of project scale, type, organization, geography or culture.
The method can be described with four integrated elements: principles, themes, processes and project environment.[4]
PRINCE2 principles
The PRINCE2 principles are important to be familiar with when determining whether a project should be managed with PRINCE2 or not. There are seven principles that must all be fulfilled for a project to be appropriately managed by the use of PRINCE2.
The seven PRINCE2 principles are:
- Continued business justification
- There must be an approved justified reason for initiating the project. The justification will have to continue throughout the life of the project.
- Learn from experience
- Project’s team members learn from experience. One shall review previous projects so that lessons are learned before initiating a project. One shall continue the learning process throughout the project so that improvements can be incorporated during the life span of the project. Experience and lessons learned from the project shall be passed on.
- Defined roles and responsibilities
- Established roles and responsibilities within the structure of the organization which involves the stakeholder interest for those involved.
- Manage by stages
- A project must be managed stage-by-stage. The PRINCE2 project is required to have a minimum of two stages: the initiation stage and an additional management stage.
- Manage by exception
- Responsibilities for directing, managing and delivering projects are clearly defined so that accountability is maintained on all levels. Accountability is secured by delegation of authority from one management level to the next by defining performance tolerances by: cost, time, quality, scope, benefits and risk. Exceeded tolerances are defined as an exception and upper management will have to decide on how to handle the issue.
- Focus on products
- Quality requirements are important in PRINCE2 as projects with this focus tend to be successful
- Tailor to suit the project
- PRINCE2 universal nature towards managing projects is retained because of its design to be tailored. As a consequence, it can fulfill required needs.
PRINCE2 themes
The themes address what is critical to address when it comes to project management. This is an ongoing progress throughout the project’s lifetime.[4]
| Theme | Description | Answers |
|---|---|---|
| Business case | Justification for undertaking the project | Why? |
| Organization | Roles and responsibilities | Who? |
| Quality | Quality of the deliverables (products) | What? |
| Plans | Distription of how to make/modify the project’s products. Time and money required. When to perform activities | How? How much? When? |
| Risk | Plans on how to manage risk | What if? |
| Change | Management of change and impact general change | Impact? |
| Progress | Viability of the project's plans | Status? Direction? Continue? |
PRINCE2 processes
The processes describe the project’s progress during its lifetime. From before initiating project activities to the closure of the project. The process based methodology in PRINCE2 provides checklists with recommended activities, products and respective responsibilities.[4]
The project environment
Many organizations desire consistency in their project management approach. By means of tailoring PRINCE2 the organization are able to make a unique project management method and way of working.
PRINCE2 in relation to other project management methodologies
Critical Evaluation
PRINCE2 is a powerful project management method, but it has some constraints, and the use of it does not guarantee for a project succeeding. It can be considered unsuitable for smaller projects, or for projects where requirements are dynamic. This can be explained by work intensive procedures related to document control, logging and similar. Using PRINCE2 for the smallest projects may simply be unnecessary in relation to the gains achieved. It can in some cases lead to a pointless production of different management related documents with no or minor substance. This can contribute to a situation where the focus on management is unbalanced with the actually work being done. The extra documentation time required is simply not justifiable.
On the other side, one can argue that PRINCE2 can be scaled and tailored to meet the concerns about an excessive focus on the management part of a project. However, by using the stated argument it is hard deny whether PRINCE2 is appropriate as a project management tool as any confrontational problem can be characterized as an improper use of PRINCE2. This reasoning will not accuse the PRINCE2 methodology as a reason to the problem itself, but rather the application of it.
Generally speaking, three different categories are to be recognized as omitted from the PRINCE2 scope: [4]
Specialist aspects
Its generic nature makes it less suitable for activities that are specified for unique activities within different industries. Agile methods, specific techniques including change management or procurement and project lifecycles which all are seen as specific activities, can although be used along with PRINCE2.
Detailed techniques
Well known techniques in planning and control, such as critical path analysis, are not described in detail in PRINCE2. Only techniques that are unique to PRINCE2 or specifically recommended for a certain planning and control setting are described in detail. An example is the PRINCE2 quality review technique.
Capability for leadership
It is not possible to methodize a leadership style that works in every single situation. This is important to empathize as leadership, motivational skills and similar are vastly critical in project management. One cannot simply set a fixed method for leadership, as one leadership style may work well in a given situation and completely unsuitable in another.
Suitability
References
- ↑ Paul D. Gardiner. 2005. Project management - a strategic approach. New York: Palgrave Macmillan
- ↑ Cambridge. 2019. "Project." Accessed February 21, 2019. https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/project
- ↑ Add reference
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Nigel Bennett, Robert Buttrick, Phil Stanton. 2017. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2, 6th ed. Norwich: AXELOS Limited