Project Execution Model (PEM)
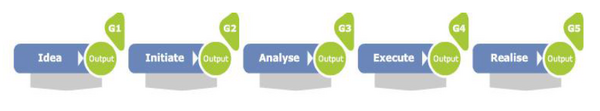
The sale in Novo Nordisk was steady increasing, which resulted that Novo Nordisk was forces to continuously hire new employees to keep up the increasing demand. The consequence was, that the company experienced, that the diversity of the way project managers handled project was huge. Therefore did the management of the area Product Supply in Novo Nordisk in 2001 decide to initiated a project which purpose was to make a global standardized way to handling projects based on best practice. The idea was based on Novo Nordisk has working with projects in many years and obtained a lot of know how about how to handling projects to secure the best output, but also obtained a lot of know how, of what NOT to do. All the knowledge should be used to develop one global model. One year later in October 2002, the first version of Novo Nordisk Project Execution Model(PEM) was established (source). Afterward Novo Nordisk obtained more know how, and today the 5th version of the Project Execution Model is developed as the newest model, that project managers use. PEM is a stage-gate project model that consist of five phases, which guiding project managers to successful completion of each project phase. The five phases are: idea-, initiate-, analyse-, execute and realisephase. Figure 1 shows the 5 phases in the model. The main focus of PEM is investment projects, but can easily be adopted for non-investment projects as well. The procedure establishes a framework to ensure that projects are identified, captured, scoped, planned, executed and closed in a standardized and efficient manner according to the model.
Each phase in the PEM model has a gate, where line management, portfolio manager, project owner, steering group and project sponsor evaluate and review the project by either approve or reject the project to continue to next phase. In the following, each phase will be described. Beside the phases, the roles & responsibilities plus an discussion about Novo Nordisk PEM compared to other project model will be presented:
Contents |
PEM - a five gate model
Phase 1
The first phase is characteristic of the idea phase. When the idea for a project is identified, the project manager need to find an owner project owner in which the idea is funded. The idea is described in collaboration with Line of Business(LoB) with the project objectives in a brief – this is to secure ownership from the beginning. In phase 1 the project manager should also create a one-pager which describes:
- Background for starting the project and top level objectives
- Scope of the project.
- Level 0 time plan – just a rough time plan that don’t need to be too detailed. Only top 10 milestones of the project which include gate approval dates
- A rough estimate of manning needs, quality strategy, risk list, environment health and safty screening (safty first is essential in Novo Nordisk project)
- Cost estimate: The project manager should make a pre-estimate of the cost budget. There is only a expectation of about 20 % contingency of the estimate.
As mentioned in the beginning the idea are either an investment or a non-investment project. It is required to make a preliminary stakeholder analysis together with top-level project requirements. The communication to the stakeholders is more than just passing information. It is about making a message understandable, about listening to the reactions from the stakeholders the project manager communicate with and engage in a dialogue. The stakeholder analysis involves a 4 step-process, which are described bellow:
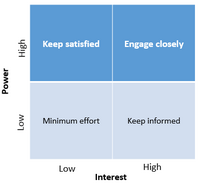
1. Identify stakeholder:
The process of identifying all people or organizations who are impacted by the project and documenting relevant information regarding their interest involvement and impact on project success. Bellow there is a grid to get a overview of how important the difference stakeholders are to the project
2. Scope the communication task:
The Project Manager need to know the size of the communication task and make it clear what the different stakeholders expect from the project manager. Before the Project Manager plan anything, the following questions need to be answered to get a better idea of how to plan the communication:
- What to communicate?
- To whom? (more specific contact person)
- Why is it necessary and relevant to communicate?
- When to communicate?
- What to achieve?
- By which channel, which media?
- How to communicate?
Knowing the needs is crucial to planning successful communication and to get there the Project Manager must ask the right question about the stakeholders.
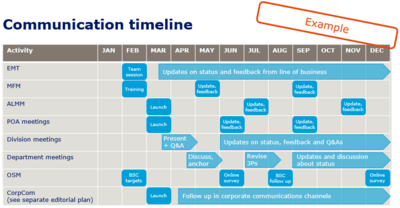
3. Do the plan for communication with stakeholder
The process of making relevant information available to project stakeholders as planned. A key part of this involves planning and manage both current and new project information arriving. Here the project it is also important to plan how to communicate to stakeholder. When the questions from step 2 is answered, the project manager need to make a plan of Who, When and What to communicate. This is a on-going process, which can change through the project. A example of the final result of a communication plan is showed in figure 2.
4. Measure the impact:
As the project manager roll out the planned communication, the PM should start measuring the impact it has and to what extend the communication objectives have been achieved. Til will help the PM to optimise the communication and evaluate the impact of the communication later on.
Overall this phase is just to give a estimated overview of the project, to get an idea of the project. Normally there are only a contingency of 20% in this phase. Prior to gate the gate 1 approval, the idea is subjected to minimum the Corporate Vice President portfolio review. If the idea is also approved during Line of Business and if prioritizations and deliverables that are required at gate 1 are fulfilled, it enters the project portfolio as an accepted project, and go to phase 2.
Phase 2
Phase 2 is the Initiate phase. During the immediate start of phase 2, the project manager and project owner must establish a steering group. The role of the steering group during this phase is to help the project manager elaborate all business objectives and to evaluate and give direction on the project scope and scope alternatives.
The main deliverables in phase 2 for the project manager are:
- Resource allocation: When starting phase 2 work, key Novo Nordisk project manning must be available and prioritized by LoB resource managers. Here it is recommended to make a brief organizational diagram with manning requirement and any increased headcount.
- Level 1 schedule: a more detailed project plan with 30-50 lines with deliverables and activity duration including milestones for 3rd phase.
- Environment, health and safety (EHS) assessment
- Cost estimate: The project manager should make a more detailed estimate of the cost. It is expected that the cost estimate have a contingency of 80% - which means that changes in the budget is not expected.
- The main deliverable for phase 2 is a clear scope recommendation for the project based on main scope and alternative scope.
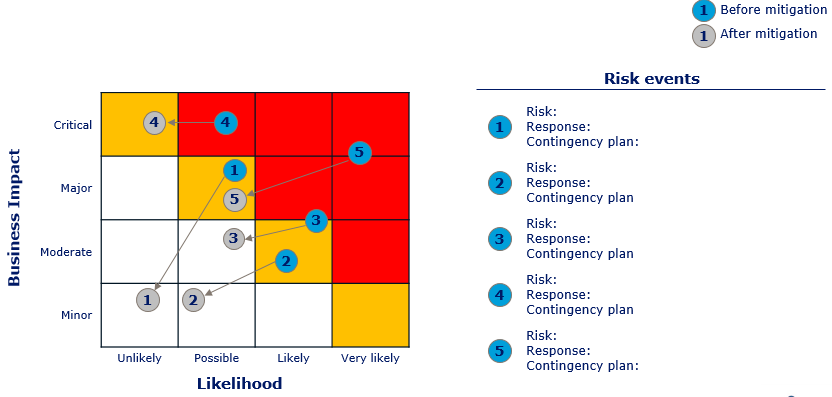
A last key deliverable is the risk management. Here the top 10 risk are identified in a grid. The risk management process consist of a 6 step process which help to ensure that the risks of the project are identified and a response and monitoring are performed.
1. Plan risk management:
This is act of actively deciding and documenting in the project how risks shall be addressed. The risk management plan may state to what extent the project is willing to accept risks and plan how the continuing risk management shall be performed.
2. Identify risk:
First step in documenting risks in the project is to produce a list of identified risks for the project.
3. Perform qualitative risk analysis:
Categories each risk into a grid with business impact and likelihood.
4. Perform quantitative risk analysis:
Calculate the resulting risk costs, cost of mitigating and presumed costs of all known risks.
5. Plan risk response:
Decide on the appropriate response type for the top 10 risks and plan the actual work needed to bed one to mitigate transfer or avoid the risks.
6. Monitor and control risks:
Typical monthly review on known risks and bi annual reviews to identify new risks. Reporting status of key risks to steering group.
The steering group decide if the project manager have secure that all of above are in place. It that is the case and the project manager gets the approval the project can continue to phase 3.
Phase 3
Phase 3 of the project is known as the analyse phase. Before upstart of phase 3, it is essential that the key project manning for phases 3 and 4 is in place and approved by the project owner and project sponsor. If key manning is not in place, upstart of phase 3 should be postponed. In this phase of the project are the main planning of the project done by the project manager and key project team are in place based on the scope from phase 2. The main purpose of this phase is to analyse and describe a detailed solution. Furthermore includes the content of phase 3:
- A Work breakdown structure (WBS) (make a link to wikiarticle)
- If necessary small adjustments to the project plan
- Ensure stakeholder commitment, maybe the needs for communication have changed – it is needed to consider this in this phase.
- Risk analysis is further developed along with mitigating actions.
- Make a first draft of the training needs in LoB
- Final cost budget
At gate 3, the agreement and supporting document are subject to review and approval by steering group. Prior the final approval, the project manager must also seek local IT approval for the automations and IT solutions.
Phase 4
Phase 4 is the executing phase. In this phase, most of the project work is carried out, constructed or purchased. The project manager manages the project and project team within the limits defined in the agreement. The purpose of this phase is to develop, implement and roll-out the solution and secure a smooth transition from project phase to daily operation. The project manager is responsible for the following tasks:
- Direct and manage project
- Distribute information
- Manage stakeholder’s expectations
- Conduct procurement – Need to close all purchase orders and contracts, and report supplier performance.
- Ensure good EHS practice
In the implantation of the new business processes in the LoB, the organizational set up and competencies are updated, if needed. Also necessary training and organizational change management activtites are performed. The project manager also work on a package report with project learnings to steering group.
In order to pass gate 4, a project completion review are prepared by the project manager. The main purpose of the review is to gain final acceptance of the project deliverables and to collect learning point from the project planning and execution phase.
When all above is approved by the steering group, the project manager formally hands over the project deliverables to the project owner who then has the responsibility of realizing the benefits of the project.
Phase 5
During phase 5, the project owner realizes the project benefits. The project owner typically maximize realization of benefits by tracking KPIs. This is to ensure the solution is anchored in the organization. During this period, LoB is responsible for following up on supplier guarantees on equipment or buildings in due time before any guarantees expire, e.g. one year review on equipment or five year review on building parts.
After 6-24 month when benefits of the project have been shown a benefit review is prepared by the project owner for the project sponsor approval. The benefit review is mandatory for all projects.
Roles and responsibilities
In the following the roles and their responsibilities of the persons that are involved in the project, will be described.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Project owner
On small projects the project sponsor is the same person as the project owner |
|
| Project manager |
|
| Steering group (StG) |
|
| Project sponsor
On small projects, the project sponsor is the same person as the project owner |
|
| Project team |
|
| Line of Business (LoB) |
|
Maybe describe what the different are - maybe it can be confusing what a steering group are?
Discussion of Novo Nordisk's Project Execution Model compared to other project models
Conclusion
Pros and cons
Skriv nogle linjer om refferancerne.
Skriv noget om hvor i project management life cycle dette befinder sig