Project Management Reporting
Developed by Dana Rut Gunnarsdóttir
Contents |
Abstract
Proper communication is one of the key components of successful project management. It helps to make sure vital information are exchanged properly and that tasks are being controlled and monitored proactively. Project reporting is one way to ensure effective communication is maintained throughout all project phases and to keep the project stakeholders as well as the internal project board informed of the project status at regular intervals. [1] Many different methods exist in the project management field, but one of the most widely used method and the one that will be used as a guideline in the article, is the PRINCE2. [2] The article will discuss the importance of having consistent communication in project management. Moreover, how a project manager can use reporting as a tool to ensure good communication through out all project's processes. Finally applications on different types of reporting will follow, which can be use to ensure high-quality management throughout the project.
Project management
In recent years, organizations have been realizing the value of project management. Researches have proven that companies that are committed to project management practices waste 28 times less money because of their efficient strategy and that 80% of “high-performing” projects are directed by a project manager. Project managers exists in most organization, but their position can vary from one project to another. A project manager is responsible for the whole project scope, team, resources etc. Thus, they must act greatly under pressure and be comfortable in the dynamic environment they work in. [3] Regardless of the subject matter area involved, every project manager has to fulfil a common set of responsibilities and duties as the project success lies on their shoulders. These duties can be presented in relation to the Four Function of Management framework and are as follows:
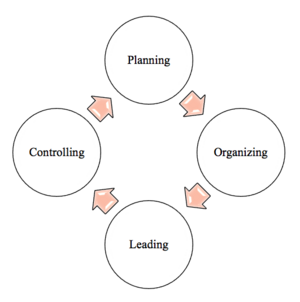
- Planning
- In the planning phase the project manager defines:
- 1. What needs to be done
- 2. By whom
- 3. When it has to be done
- This is an iterative process and is ongoing throughout the lifespan of the project.
- Organizing
- In the organizing phase, the project team structure is analyzed as well as roles and positions are identified.
- Leading
- The leading phase is ongoing throughout the project. This task can be challenging for new project managers, as it involves a lot of intercommunication skills. The key duties for successfully leading a project includes:
- 1. Directing the project team
- 2. Coordinating activities
- 3. Assigning team members to tasks
- 4. Motivating the team
- Controlling
- The controlling phase is all about making sure the project is running according to the plan. This step is very important and has to be well monitored. One of the key controlling duties performed by the project manager is ensuring that stakeholders and relevant parties receive a project status report in addition to delivering their expectations.
Project Manager vs. Program Manager
What separates a project from a program is that a project has a defined beginning and end, while a program is an ongoing operation. A project is launched to establish, adapt or simply improve a product or service and is constrained with several factors such as resources, time, scope etc. [6] Despite that a project manager and program manager have a different role within an organization, they use similar tools and techniques in their management. The main difference is that the program manager is in charge of several projects and project teams that may include the project manager and ensures successful program deliverables. While the project manager is responsible for a specific project and team. [3]
Importance of communication in project management
Communication management is by many believed to be one of the most important skill in project management, but very complex one at the same time. Communications can be affected by several factors, such as stakeholders, environment, team members and company structure. By having an effective communication when working on a project, it can be ensured that team members, stakeholders and the project board are all well informed about the project status. This can help to face arising challenges, identify risks and issues beforehand, as well as prevent misunderstandings.[7] According to PMI’s Pulse study, the most critical success factor is an effective communication to all stakeholders. Their study also showed that ineffective communication can have a huge impact of project’s outcome and even contribute to a project failure. This implies on the importance for organizations to take ownership of this problem and improve their communication to prevent unnecessary project failures. Four ways can be used to improve communication:
- Close the communication cap: By improving communication in the company structure, projects become more successful.
- Tailor the communication form to different stakeholders: It is important to align the communication to various stakeholders’ groups, to ensure that everyone is speaking the same language.
- Acknowledge the value of communication: Many organizations underestimate communication in a project management, which results in bad project’s outcome. It is important to recognize the value of an effective communication, to be able to improve this knowledge skill within the firm.
- Standardize project communication practices: It can be attained with a formal communication plan which must be adaptable to different stakeholders. This can, for example, be done via frequent reporting.
Reporting according to PRINCE2 standards
According to PRINCE2, each project consists of seven processes that have to be well managed to achieve a success in a project. A visual explanation on the processes can be seen on the figure to the right, but the processes are the following[2] :
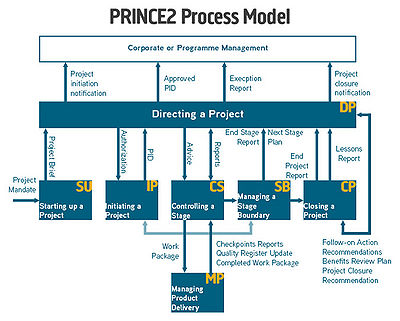
- Starting up a project
- Initiating a project
- Directing a project
- Controlling a stage
- Managing a stage boundary
- Managing product delivery
- Closing a project.
The figure to the right, shows how a project follows the predefined processes.
PRINCE2 breaks each project down to a so-called management stage. During the project’s lifecycle each management stage is reviewed, and further project plan and risks discussed to decide whether next stage should be followed to continue with the project. Appropriate management stages for a project depends on the size and complexity of the project, decisions and control points required during the project’s lifecycle, organization policies etc. The PRINCE2 method is based on experiences of projects all over the world and can thus be applied on any kind of projects, regardless of their complexity or size. The experiences have proven that a project must have a minumum two stages; initiation stage and at least one other management stage. It is important that every stage has predefined tasks right from the beginning. This makes sure that the project is properly initiated beforehand. It is known that all projects face uncertainty when seeking to achieve their objectives. Thus, encouraging an effective communicating is essential to face new risks that might arise in the project. In PRINCE2 information related to threats/opportunity are discussed though the following products:
- Checkpoint report
- Highlights report
- End stage report
- End project report
- Exception report
A project has six types of tolerance; time, cost, quality, scope, benefit and risk. These factors have to be monitored and reported throughout the project. To maintain a desired level of progress, weekly checkpoint reports have to be carried out. To control a stage a project manager has to make a regular review on the progress through the checkpoint reports. By reviewing the reports, the project manager can update the stage plan with actual progress achieved. The frequency of reporting can vary between projects, but in projects where the project team is inexperienced the project manager might need to increase the frequency of reporting.
In addition to report throughout the project, it is vital to learn from previous experiences. Thus, it is highly recommended to spent time making a detailed end project report and a lessons report, that highlight what was learned during the lifespan of the project. This can help to improve the estimation in costs, resources, time etc. for upcoming projects. Before making those reports several things has to be reviewed, such as baseline of the project and approved changes throughout the project.
When the project manager prepares the End project report, he has to go through how the project was performed and how it accomplished compared to planned target and tolerances. The results of the project compared to the expected benefit in the business case, the team performance and a review of the project’s product and a brief summary of recommended actions taken, if appropriate. If the project was brought to a premature closure, the end project report should contain documented reasons for the decision.[10]
The lessons report identifies lessons that can be learned from in upcoming projects. The report includes a review what went well and what could have been done better and any abnormal events that the project team was facing in the lifespan of the project that occur a deviation from the scheduled plan. The report should also include useful measurements such as, required effort from the project team, how the quality management approach was designed and developed and statistics on risks and issues.[10]
Application
As mentioned in this article, it is vital to conduct a good communication between all involved in the project. As a project manager, several reports have to be written throughout the project process. When organization is performing according to PRINCE2 standards, the following reports have to be made by the project manager.
Checkpoint report
Used to report status of the work package, written at a frequency which is defined in the work packages. Includes [10]:
- Date of checkpoints
- What period is being followed and what products/activities are being developed by the project team
- Completed products
- Quality management activities that are being carried out and lessons learned.
- Outstanding items from previous reports, actions completed and unresolved issues.
- What is the next step for the following reporting period, what products are planned to be completed prior end of that period.
- Where the project stands compared to the tolerance, such as cost, time, baseline, scope etc.
- Updated risks and issues the project is facing
As people tend to be more motivated when seeing their accomplishment more visually, as well as how far from goals and milestones they are. One way a project manager can do to motivate his project team is to conduct a status report template. According to Template Lab, the following benefits can be attained [11]:
- Focus point more clear: All involved focus on same issues each and every week.
- Clarifies activities of the project: Projects can have several complexities and having a visual template can help to clarifies these things and bring them forward. In the report template, milestones can be highlighted so team members are all aware what they are aiming for in their work, which accomplishments they have achieved etc. Any concerns regarding issues and delays that can affect the project budget can also be involved in the project template, to keep everyone informed.
- Keeps projects progress documented: Even though the project manager is not around, the project does not have to go on hold, as the team members can use the report as a reference.
- The big picture: By seeing the bigger picture of the project, all the process and what needs to be done can be seen more clearly. This leads to better decision making for the success of the whole project.
- Keeps all involved updated: One of the most important in successful project management, is to keep everyone updated.
- Enforces regular analysis of the project’s performance: Makes the project manager perform a regular analysis of the project’s performance and what actions need to be taken.
- Motivational: The status report template is motivating and inspiring for the project participants. By seeing the milestones and accomplishments gives the team a motivation to keep on working on the project.
End stage report
Gives the status of the project and a sufficient information for the project board to decide which actions should be taken in the project, such as:
- Authorize next stage
- Modify the next stage
- Put a closure on the project.
The End stage report can take different formats, depending on the project. It can be be done via presentation to the project board, in a document or email issued to the project board or simply included in a project management tool. [10]
Exception report
Used when a stage plan is forecast to exceed the predefined tolerance level. It includes description of the cause of a deviation and what consequences it can affect the project if it is not addressed properly. The exception report is used to inform the project board of the situation, so they can plan which actions should be taken. [10]
Highlight report
Used to provide the project board and other stakeholders a summary of the management stage status of the project
- How it stands
- What is completed
- Which actions will be taken in the next stage
This report is given with regular frequency that can be different from one project to another.[10]
End project report
Purpose? Used to review how the project performed, compared to the plan. The information are used to evaluate the project and authorize a project closure. The report can take various formats as the End stage report. However, the following topics should be covered in the report[10]:
- What can be learned from the project
- Details of unfinished work and ongoing risks in the project
- Project manager‘s report about the project‘ s performance
- Review of the benefits and deviations from the approved business case
- Review of how the project performed against the planned goals and tolerance for project objectives
- Review of the team performance
- A review of what can be learned from, what went well and what could be done better next time
Issue report
An issue report is needed when arisen issues need to be handled systematically. The report includes a description of the issue, impact assessment and recommendation for the problem. The report is created when the issue is arising and is updated when the issue has been verified and closed. According to PRINCE2 standard, the issue report consist of[10]:
- Issue identifier
- Issue type
- Date on which issue was raised
- Name of the individual/team who raised the issue
- Issue report author
- Description of the causes and impacts of the issue
- Impact analysis
- Recommendation
- Priority
- Severity
- Which decision have been taken, by whom and when
- What date the issue was closed
Lessons report
The lessons report can be very helpful when starting a new project. The main purpose of the report is to provoke actions within the organization, so the project team is able to learn from previous mistakes/success on future projects.[10]
Limitation
By having consistent reporting, proactive actions can be taken to an unexpected risk and issues that can affect the project health such as cost, time schedule, resources etc. A documented history of the project can help organizations to establish lesson learned in their future projects by reviewing and evaluating old projects and see where they succeeded and which difficulties the project team was facing. However, status reports are only a formal document that summarize the progress of the project and should not replace ongoing project communications between project manager, project teams and other relevant parties.[1]
Annotated Bibliography
AXELOS, AXELOS. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition. The book presents one of the world’s most practised method for project management. The method consists of seven themes, principles and processes which are used to manage successful projects. In this article, a general introduction to the PRINCE2 method is presented and the seven processes a project has to follow, where the main focus is on the project stages. The processes are only briefly discussed in the article, but deeper understanding can be attained by reading chapters 13 – 20 in the book. The book provides good guidance which a project manager/management team should follow to achieve a successful project.
PMI. THE HIGH COST OF LOW PERFORMANCE: THE ESSENTIAL ROLE OF COMMUNICATIONS This is an in-depth report that provides a detailed analysis of how poor communication can affect projects’ outcome. The report is based on many studies and researches that all imply on that effective communication is one of the most crucial factors in project management. In this Wikipedia article, the report was used to gain deeper understanding of the importance of communication and what strategies project managers can take to improve it in their projects.
Karolina Muszynska. Project communication management patterns. This article discusses the importance of communication in project management. Eleven different communication management patterns are introduced. The patterns are separated into four categories and are the following; Informational-, Strategic-, Emotional- and Practical Communication Management Patterns. The topic is well explained in the article and can be helpful for project managers who are implementing communication management practices.
Knowledgehut. Project Manager - An Ultimate Guide: This article emphasis on the increasing need for a project managers all over the world. It is a great introductory article with good explanations of what defines a project manager, what they do, different types of project manager and how to become one.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006) "Project Status Reporting" https://www2.cdc.gov/cdcup/library/practices_guides/CDC_UP_Project_Status_Reporting_Practices_Guide.pdf
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 ILX Group. (2019) "PRINCE2 Processes" https://www.prince2.com/eur/prince2-processes
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Knowledgehut. "Project Manager - An Ultimate Guide" https://www.knowledgehut.com/blog/project-management/how-to-become-a-project-manager-ultimate-guide Retrieved 28-02-2019.
- ↑ G. Jones and J. George. "Essentials of Contemporary Management." McGraw-Hill, 2007. ISBN9780073011226.
- ↑ Michael A. Martinez. "A Framework for Understanding Project Manager Duties" https://www.project-management-skills.com/project-manager-duties.html Retrieved 22-02-2019.
- ↑ U.S. OFFICE OF PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT. (2003) "Interpretive Guidance for Project Manager Positions" https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/classification-qualifications/reference-materials/projectmanager.pdf
- ↑ Karolina Muszynska. "Project communication management patterns" 2016 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS) https://ieeexplore-ieee-org.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/document/7733398 Retrieved 28-02-2019.
- ↑ PMI. "THE HIGH COST OF LOW PERFORMANCE: THE ESSENTIAL ROLE OF COMMUNICATIONS", May 2013. https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/learning/thought-leadership/pulse/the-essential-role-of-communications.pdf Retrieved 28-02-2019.
- ↑ Andy Trainer. "PRINCE2 Process Diagrams" Silicon Beach, 2013. https://www.siliconbeachtraining.co.uk/blog/prince2-process-diagrams
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 10.8 AXELOS, AXELOS. "Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition". London: The Stationery Office Ltd, 2017
- ↑ TemplateLAB. "Project Status Report Templates" http://templatelab.com/status-report/#Benefits_of_Making_a_Status_Report_Template Retrieved 20-02-2019.