Resource breakdown structure
(→Application) |
(→Abstract) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
This article will explain the resource breakdown structure RBS, a tool that can be used in project management. The target audience for this article is students new to courses of project management. | This article will explain the resource breakdown structure RBS, a tool that can be used in project management. The target audience for this article is students new to courses of project management. | ||
| − | Resource breakdown structure is a hierarchical model used to provide information about which resources are needed in a project and necessary data about the resources. Each level down the hierarchy gives more detailed information about the specific resource than the one above. The needed level of details of resources can be different in all projects and the RBS can therefore be adjusted to fit the specific project. It is often the project manager who | + | Resource breakdown structure is a hierarchical model used to provide information about which resources are needed in a project and necessary data about the resources. Each level down the hierarchy gives more detailed information about the specific resource than the one above. The needed level of details of resources can be different in all projects and the RBS can therefore be adjusted to fit the specific project. The RBS can be used in all types of projects and should be set up in the beginning of the project. It is often the project manager who makes the model, with input from the rest of the team. |
| + | The article presents benefits and limitations of using RBS. It also explains how to set up the model and different types of the RBS, called organizational and geographical RBS. Organizational is the most common one and the geographical is used less frequently. The resources in the hierarchy are divided into several parts, for example types and categories and the article explains related terms to the RBS. | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 21:55, 4 March 2019
Contents |
Abstract
This article will explain the resource breakdown structure RBS, a tool that can be used in project management. The target audience for this article is students new to courses of project management.
Resource breakdown structure is a hierarchical model used to provide information about which resources are needed in a project and necessary data about the resources. Each level down the hierarchy gives more detailed information about the specific resource than the one above. The needed level of details of resources can be different in all projects and the RBS can therefore be adjusted to fit the specific project. The RBS can be used in all types of projects and should be set up in the beginning of the project. It is often the project manager who makes the model, with input from the rest of the team.
The article presents benefits and limitations of using RBS. It also explains how to set up the model and different types of the RBS, called organizational and geographical RBS. Organizational is the most common one and the geographical is used less frequently. The resources in the hierarchy are divided into several parts, for example types and categories and the article explains related terms to the RBS.
Big idea
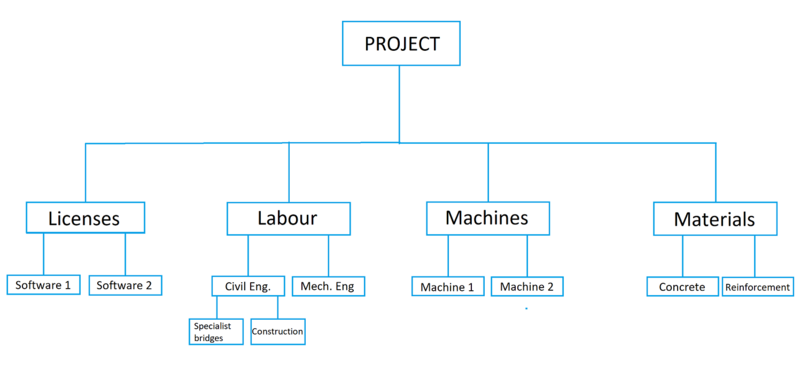
The resource breakdown structure RBS is a tool that can be used within project management. It is a hierarchical model that shows the resources that are needed to complete a specific project. A resource is everything needed to implement a project and having a cost. Examples of resources are licenses, taxes and labour. Money is not defined as a resource for the RBS. [2] The purpose of the tool is to plan, manage and control project work. The resource breakdown structure is related to the more known work breakdown structure WBS. Briefly explained is WBS a model that breaks up necessary project work into smaller and concrete tasks. WBS and RBS can be connected together, where the resources are accompanying a specific task. [1]
The benefits of using this model are several. As stated, the model is made to give an overview of which resources are needed in a project. The side effect of this is that it can be easier to give a price estimate. It is no secret that money is important in a project and the model can highlight the prices of the resources. The benefit of this, is that if it is necessary to cut expenses, it will be easier to see which of the resources could be changed to better solution regarding money. An example of this can be that you need license. If the license is very expensive and there needs to be saved money, one can look at the requirements of the software and try to find another software that can do the necessary operations for the specific project. Here it is important to distinguish between a long-term view and short-term view. For a small company with relatively few projects it can be beneficial to make an investment and buy the license for the expensive program that can do more than the specialized program. This is because it can be more expensive to buy two licenses instead of one, when they have the next project.
Also, as the model points out required properties of the resource, it is easy to find out which resource replace the resource when necessary. Cases of this can be if a resource gets broken, for example a machine. All required properties about the machine can be found in the model and from there it is possible to evaluate whether it is best to fix the machine, get a new similar one or another machine. Lastly a good template can be used for more than one project. This saves time and consequently money. Comparable projects often require similar resources and the template can be used as a starting point. Models should be sorted after similar type of project and can then be easily found back to.
Application
Usually it is the project manager who sets up the model with input from the team. The model does not have a set template for all, as the needed level of detailing is varying in different projects, but as stated in Big Idea, there can be used a template as a starting point. A good rule is to continue to fill in information until estimators and schedulers have sufficient information about the resource. [2]
RBS can be divided into two main groups, organizational and geographical, which are ways of building up the model. The organizational is the most common one and divides the resources after organizational groups.[3] An example of this can be that it is divided to for example to construction department, architectural and economy. The benefit of this model is that it is easy to divide the responsibility of who should provide the resource. The geographical model is a bit more infrequent. This model considers the location of the resources and has more of a physical control over them. [3]. It implies that the resources are divided across categories concerning organization. In other words, the resources are presented in a category independent of which department their needed at. [3] This can be illustrated with an example. If the category is licenses, all licenses are presented below this category. It does not matter if it is a software for a calculation program for a civil engineer or a license for a truck driver. The benefit of using the geographical model is that it creates a very good impression of what is needed in all categories.
The model can be set up two ways, graphically and schematically. The decision on whether to go for one or the other is purely out of preference. An example, set up with both models, are sketched below.
When it is chosen between organizational/geographical and graphically/schematically the model can be set up. The resources are firstly divided into categories. The most used ones are labour, fees/licenses, materials, tools and machines, but it is not limited to these categories. For the first level of the resource, the structure should be divided in 3 to 9 categories. [2] Dividing it in categories creates a clear model and the resources can easily be found, when in need of information about a specific resource.
Labour separates from the other categories and are also referred to as human resources. The other resources are signified as physical resources. This includes teams or persons working on the project. Labour can be changed throughout the process, as some expertise might be needed in some time of the process or less people are needed towards the end. Some personnel or teams can have a full-time position throughout the project, meanwhile others have part-time. These factors should be taken into consideration and updated throughout the process. [1]
Limitations
There are not many obvious disadvantages about the resource breakdown structure, but there are a few things that should be kept in mind when using the tool. As mentioned in Big Idea, it is easy to know how to replace a resource when needed because all necessary information is given in the model. The downside of this is that it can prevent new thinking. Instead of exploring other alternatives for the resource one will go directly for the same resource as used previously. Consequences of this could be missing out on cheaper or even more fitted resources, when the previous resource did not work out.
Related to this there is another factor that should be taken into consideration. The model always needs to be up to date. In this it lies that that costs are always updated, and the most beneficial version of the equipment. For example, it is often desired the newest version of a software, which may demand a license.
The last factor, which concerns almost all projects: time. The point of using the RBS is to save time, costs, create overview and so on, so it is important to not use too much time setting up the model. It may be impossible to set up the entire model in the start of the project, so it should be a matter of judgment how much of the model it is beneficial to set up in the beginning of a project. A predefined model can also be used to save time, but the team should be aware that the model could need some slight changes to have all resources covered.
Annotated bibliography
[1] Project Management Institute. Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge. Pennsylvania: Project Management Institute, 2017.
This is a standard regarding project management, which means that it has been approved by a recognized body. Chapter 9 has been the main source of information, addressing Project Resource Management.
[2] Rad, Parviz F. Project Estimating and Cost Management. Virginia: Management Concepts, Inc. 2002
The book presents tools within project management, such as the RBS and how to apply them. Chapter 3 has been the main source of information, explaining the resource breakdown structure.
[3] Stoy. RBS or Resource Breakdown Structure – What Is This and How You Can Use it In Project Management, Stoy, Ada. Bright Hub, Inc. 11.02.2019 https://www.brighthubpm.com/resource-management/32864-what-is-a-resource-breakdown-structure-rbs/
The article mainly concerns types of resource breakdown structure. The website is owned by a media company called Bright Hub, Inc. The articles are written by and for project managers.