Resources loading, leveling and crashing
(→Abstract) |
(→Resource planning in the project management lifecycle) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
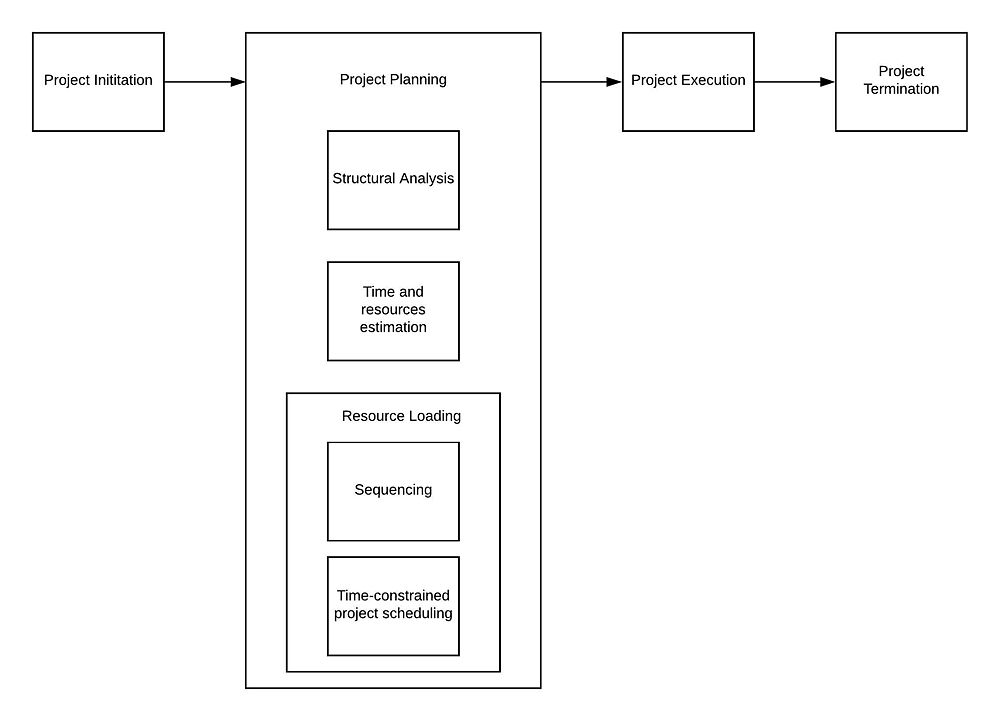
Project planning at first decomposes the projects tasks into the order list of activities that are defined by structural analysis of the project such as [[Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)]]. Each of the activities is later collated together with the time duration and resources requirements. Together they forms the project representation as a network modelling activities with the preceding activities before them. Based on resource availability and activities slack time, the initial starting time and deadlines are provided. Finally, the last step of project planning process consists of allocating the optimal resources over time for the successful activity execution. This is the most complex step in the project planning, which is why it became the common topic for many of the researches. | Project planning at first decomposes the projects tasks into the order list of activities that are defined by structural analysis of the project such as [[Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)]]. Each of the activities is later collated together with the time duration and resources requirements. Together they forms the project representation as a network modelling activities with the preceding activities before them. Based on resource availability and activities slack time, the initial starting time and deadlines are provided. Finally, the last step of project planning process consists of allocating the optimal resources over time for the successful activity execution. This is the most complex step in the project planning, which is why it became the common topic for many of the researches. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Basic [[Scheduling techniques in Project Management]] such as CPM or PERT assume the unlimited resource availability in the project network. In reality, both the time and resource requirements need to be properly allocated while developing network schedules. Projects are subjected to three major constraints: | ||
| + | * Time limitation | ||
| + | * Resource availability | ||
| + | * Performance requirements | ||
| + | |||
| + | Satisfying all three criteria at the same time are difficult to perform without reade-offs. That has risen a need for project progress control methods that could deal with these inconsistencies in a project schedule. | ||
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
Revision as of 12:15, 23 February 2018
Contents |
Abstract
The current business trends aim to achieve the operational excellence by maximizing the profit while minimizing the cost at the time. This has a profound impact on project managers forcing them to operate more and more efficiently. However, most of the project management systems used today tend to limit the efficiency due to the lack of data consistency and reliability. In consequence companies spend substantial amount of resources trying to standardize and integrate processes. As resources are needed by activities, activities produce products, products constitute projects, and projects make up organizations. Thus, resource management can be viewed as a basic component of the management of any organization. Integrating resources with schedule systems through resource loading, leveling or crashing allows to better utilize the assets and therefore help to predict the final outcome of the project more accurately.
Resource planning in the project management lifecycle
The lifecycle of the project consists of the 4 established stages: project initiation, project planning, project execution and closure(referene here?) Each phase in the project life cycle requires specific project management techniques.
Project planning at first decomposes the projects tasks into the order list of activities that are defined by structural analysis of the project such as Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Each of the activities is later collated together with the time duration and resources requirements. Together they forms the project representation as a network modelling activities with the preceding activities before them. Based on resource availability and activities slack time, the initial starting time and deadlines are provided. Finally, the last step of project planning process consists of allocating the optimal resources over time for the successful activity execution. This is the most complex step in the project planning, which is why it became the common topic for many of the researches.
Basic Scheduling techniques in Project Management such as CPM or PERT assume the unlimited resource availability in the project network. In reality, both the time and resource requirements need to be properly allocated while developing network schedules. Projects are subjected to three major constraints:
- Time limitation
- Resource availability
- Performance requirements
Satisfying all three criteria at the same time are difficult to perform without reade-offs. That has risen a need for project progress control methods that could deal with these inconsistencies in a project schedule.
Definitions
Resource loading or resources allocation identifies the amount of project resources required over the project lifecycle. It is often represented as the graphical representation of resource allocation over time. That provides a convenient information for budgeting and planning.
Resource leveling is the optimization technique used to adjust the schedule model to the demand and supply fluctuations. adapt the start ad finish dates based on the resource constraints with the goal of balancing demand for resources with the available supply. The method can be used when the required resources are available only during certain period or in limited quantity or. It is also used to balance the resource consumption level. [1]
Crashing is a method used to analyze and choose the most cost-efficient measurements of compressing the project duration.[2] Crashing is a schedule compression technique used to meet schedule constraints, dates and other objectives without compromising the project scope. This can be done by utilizing extra resources like: approving overtime hours, bringing the additional resources or expediting delivery of activities to the reach the critical path.