SWOT Analysis
Developed by Henning Duwe
SWOT is a commonly used method that helps to systematically analyze a topic by dividing it into the four categories “Strengths”, “Weaknesses”, “Opportunities” and “Threats” to examine their influence [1] and how these attributes interact with each other. It can be described as a planning technique for Situation [2] or Data Analysis [3]or as a tool for “identifying, relating, and making performance improvement decisions within context.”[1] The results can then be used as a foundation to formulate goals and to search for solutions.[2]
SWOT is used on many occasions. Three situations, in which the method particularly applicable are shown below:
- When analyzing performance. The effects of the internal and external dimensions are being surveyed and how they have an influence on the output of the group. The effectiveness of the group could be another dimension of the survey.
- When executing cause analysis. SWOT can examine which practices, tools or methods should still be used in the future and which should be dropped.
- As a part of a continuous improvement process, by regularly checking and updating the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and strengths when new influences arise.[1]
Contents |
Description of the Tool
The Role of SWOT in Project, Program and Portfolio Management
Due to its basal approach to analyze a problem, SWOT can be used in various applications. In terms of Project, Program and Portfolio Management it is commonly used in the planning process to analyze the future situation of the Project, Program or Portfolio with its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Being a method for situation analysis, it is used at the beginning of the Problem Solving Cycle (PSC).[2]
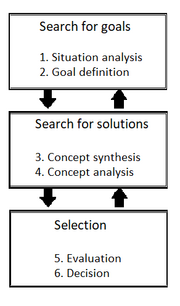
The PSC is a procedure that aims to solve problems and create the best possible solution. According to Rainer Züst and Peter Troxler it can be divided into three major and six minor steps (see Figure 1):
- The search for goals, consisting of the situation analysis and the goal definition,
- the search for solutions, consisting of the concept synthesis and concept analysis and
- the selection, consisting of the evaluation and decision.[2]
These steps are not definite. In fact, the later steps can have effects on the earlier steps and reassessments may be necessary.[2]
A core question during the situation analysis is "What do we want to achieve?"[2] To successfully aim at the desired future state, it is necessary to take all uncertainties into account. SWOT helps project, program and portfolio managers to systematically consider these uncertainties and to anticipate changes in the environment surrounding the project, program or portfolio.[2] By executing a SWOT-Analysis a better prediction of external factors and future developments is possible and great knowledge of internal factors and the situation is gained. This makes it a powerful tool for the first step in the Problem Solving Cycle.
Conventional SWOT-Analysis
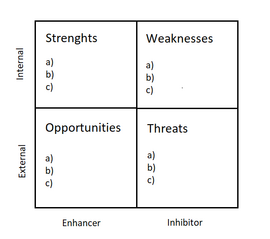
SWOT can be executed in different ways, but they all share the view on internal and external enhancers and inhibitors of organizational performance.[1] At the beginning of the analysis, strengths and weaknesses of the specific organization, project or the whole business area are identified. The next step is detecting which opportunities and which threats result from this.[3] Claire Capon, Professor of the Staffordshire University; defines the four dimensions of the analysis as follows:
- Strength: an internal enhancer of competence, a valuable resource, or attribute
- Weakness: an internal inhibitor of the competence, resources, or attributes necessary for success
- Opportunity: an external enhancer of performance that can be pursued or exploited to gain benefit
- Threat: an external inhibitor of performance that has the potential to reduce accomplishments [1]
The SWOT-Analysis is often being executed without examining the interdependencies between these attributes.[1] Still, in this “Conventional SWOT” the two dimensions “Strengths” and “Weaknesses” are categorized as internal factors and “Opportunities” and “Threats” as external factors. For the SWOT, a 2-by-2 matrix is commonly used as a structure (see Figure 2).
The advantages of this simplified analysis are that each factor can be examined individually with still having a broad view on the matter. Additionally, this way of executing SWOT is faster and easier than the way the SWOT will be executed in the following chapters.[1] On the other hand, the analysis is less broad and deep and the interdependencies and synergies are getting ignored.
Advanced SWOT-Analysis
In the literature, there is no such thing as "Advanced SWOT-Analysis". This term is made up by the author to distinguish between the conventional SWOT and the more detalized SWOT shown in this chapter.
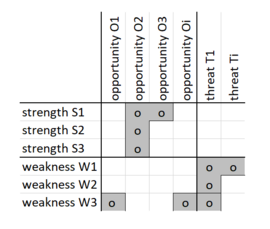
The advanced SWOT-Analysis structures the different causes of the strengths, weaknesses etc. especially due to their urgency for action.[2] But it also examines to which degree the strengths of the organization could offset the threats and determines if the weaknesses possibly restrain the opportunities.[3]
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats which have the same cause can be put into groups since they probably need the same or similar actions. For each of the four fields in the matrix a basic approach can be defined:
- Strengths/opportunities: build on strengths and use opportunities
- Strengths/threats: build on strengths and minimalize threats
- Weaknesses/opportunities: repair weaknesses and use opportunities
- Weaknesses/threats: repair weaknesses and minimalize threats[2]
For each of these segments, an own evaluation is made. The ultimate goal is to have an overview of the issue from the most important perspectives and therefore have a basis for upcoming decisions under uncertainty. One of the strengths of SWOT is that it raises attention to the context, in which the results of the decision will be implemented. In a traditional SWOT-Analysis, contextual factors like an increasing market fragmentation categorized as a threat are classified and discussed by the participants. By doing so, a better understanding of the context can be accomplished. [1]
Application: Advanced SWOT-Analysis on Coal Energy
A concrete example of a full SWOT-Analysis on the use of coal energy compared to other fossil fuels in Thailand based on this paper [4] shall be executed here.
Strengths
Costs
Coal is a comparably cheap source for electricity production. The high availability and accessibility are reasons for this. In distinction to oil or natural gas, it does not need pipelines as an infrastructure. The prices are not fluctuating as much as those from oil. According to R. Prurapark and P. Asavaritikrai, the costs of coal are low compared to nuclear power and solar power in that region.
Availability
Compared to other fossil fuels like natural gas and oil, there are significantly higher reservoirs of coal in Thailand. The reserve to production ratio (R/P ratio), which expresses the length of times in years, a fossil fuel can be used with the current known reserves and the current production rate [5] is by factors higher than those of its competitors. With the current usage, coal has a R/P ratio of 63 years, while the R/P ratio of natural gas and oil is 5 and 2 years.
Safety in Transportation (Overseas)
The transportation of coal is said to be safer and easier than the transportation of oil and natural gas. While leaks of coal overseas are unfortunate, a leak of oil is disastrous. Transporting natural gas is also highly complicated since it has to be cooled down to liquified natural gas due to efficiency reasons.
Weaknesses
Air Pollutants from Coal
One of the biggest weaknesses of using coal as a source for energy production is air pollution. Even in comparison with oil and natural gas, the emission figures are quite high. In regards to carbon dioxide, one of the main drivers of climate change, producing one unit of energy using coal emits 40 % more carbon dioxide than oil respectively 88 % more carbon dioxide than natural gas. But it also has the highest carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulates and mercury emissions, which makes coal an unfavorable source for energy production.
Cost of Coal Transportation
Due to the amounts of coal needed for energy production and the fact, that coal can not be packed as tightly as oil or gas, the cost of coal transportation is high. This issue can be met by having short distances from the coal mines to the power plants, but since the distance of transferring energy should also be kept as short as possible, this requires the coal mines to be close to the cities, which is not always the term.
Opportunities
According to Pinyo Meechumna, professor and specialist regarding coal and sustainable energy, the population and economy in Germany have reached a plateau and this leads to a state of electric saturation. This means that there will be little change of the centralized electricity production such as nuclear power, coal et cetera and decentral, renewable energy like solar plants are built. In contrast, growing countries such as Thailand are not electrically saturated and offer therefore the opportunity of rising demand for the usage of coal. The International Energy Agency estimates that despite the decreasing usage of coal in some modern states, the need for coal will grow by 3 % from 2020 until 2022, due to its low costs and high accessibility.
Threats
Public Mistrust of Coal Energy
Since the usage of coal comes with air pollution and emitting greenhouse gas, its usage is questioned by the public which hinders the further use of this source of energy.
Ambiguity in Laws, Regulations, and Controls from the Government
Even though the use of coal as a source of energy is today clearly allowed in Thailand, different trends still lead to uncertainty regarding laws and regulations. Diverse sectors are responsible for coal usage which leads to unclear competencies. There is a lack of specific regulations that lower the trust in long-term stable conditions for burning coal. Furthermore, global warming and the pollution of the environment are factors, which are questioning energy production with the usage of coal in the future.
Discussion and Limitations
- External vs internal
- Prioritization of the SWOTs
- What can it do, what can it not do?
Annotated Bibliography
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Watkins, Ryan and Leigh, Doug. Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, 2010, Pfeiffer.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Zuest, Rainer and Troxler, Peter. No More Muddling Through, 2006, Springer.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Project Management Institute. Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, 2017, Project Management Institute.
- ↑ R. Prurapark and P. Asavaritikrai. Assessing Coal Use in Thailand: Current and Future Trends, 2020, Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
- ↑ Wikipedia, 23.02.2021, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reserves-to-production_ratio.