SWOT Analysis Management
Developed by Helená Evin Cinar
Contents |
Abstract
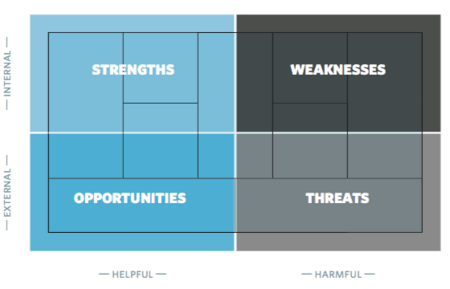
The article will shed light on the analysis tool SWOT model.The SWOT analysis is a frequently used method in strategy development in both private and public organizations. A SWOT analysis is an analytical tool when it comes to value-based management and strategy formulation to define strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats for a given company. [1]
Strengths and weaknesses can be characterized as internal value-creating (or destructive) factors such as. assets, skills or resources that a company has at its disposal according to its competitors. The factors for the organization's strengths and weaknesses can be measured using internal assessments or by external benchmarking. Opportunities and threats are characterized as external value-creating (or destructive) conditions over which an organization has no direct influence, but instead emerge from the competitive dynamic connections of industry / market or from demographic, economic, technical, social or legal factors. Typically, you will be able to use the SWOT analysis in connection with any organization that intends to create a fit with its external environment.
The SWOT table is an effective tool for analyzing the (internal) strengths and weaknesses of a company and the (external) opportunities and threats. However, this analysis will only be a single link of many when it comes to analysis at an organizational level. In fact, the creation of the adaptation will be a contradictory work to embark on, as the reality behind the SWOT analysis will most often point in contradictory directions, leaving strategists with the paradox of creating adaptation either from the outside (market-driven strategy) or from within. -out (resource-based strategy). [2]
Introduction
The SWOT analysis is a simple and compliant technique. The tool can be used to formulate strategies and working methods for administrators.The SWOT analysis can be approached in many ways, the classic way of setting up models is as illustrated in the 2 by 2 matrix: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities , Threats as illustrated in the abstract. The main purpose of the following article is to illustrate how SWOT can be used by administrators to process, analyze and initiate reflective perspectives within the management area.[3]
History of SWOT analysis
The SWOT analysis was initiated by mangament consultant Albert Humphrey in the 1960s at the Stanford Research Institute. At that time, business planning did not debut as much as it does today, and the method was therefore not considered until companies began to lack a method for planning long-term planning strategies that were executable and compliant. In addition, Humphrey and his research team advised that the SWOT model would be an obvious tool for maintaining accountability and objectivity in the planning phase, since then the SWOT model has been popular with many companies.[4]
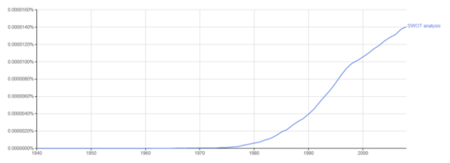
According to Albert Humphrey, the idea of the analysis was specifically aimed at criteria such as products, process, customers, distribution, finance and administration. SWOT analysis has over time had some success as it has only grown in popularity since its inception, which is also evident in the Google Books Ngram search[5]How to use SWOT as a tool
When the company is going to fill in the quadrants, there are a number of issues that need to be considered and taken into account. In most cases, one will start by filling in strengths and weaknesses as the internal characteristics are typically easier to notice. Her husband can consider factors such as:
Experience: What do you know in advance? Do you have a special impression of the circumstances, customers or processing company?
Economic status: Is the economy harmonizing? Are there alternative sources of income?
Resources: Employees, volunteers, managers, or customers. How do they contribute? Are they at ticket price for the company?
Material resources: What is on offer? Is there a lack / need for something?
In addition, you will be able to work further with opportunities and threats which are described as the external elements. This category focuses exclusively on factors outside the company. Hers, a large budget, for example, will be considered an option, whether it's sense of god economic sense can be considered as being than strength. As a rule, one should be realistic and specific when considering these options. If you are in doubt about what factors to add, you should consider the following points:
Financial status: Are your customers willing to invest in your products? How is the local, national or international affected?
Demographics and psychography: Is there a risk of a change in the target group's age, race, gender, attitudes, values or ways of thinking?
Discussion
PROS
CONS
References
[Book: Business Model Generation]
[https://ivaekst.dk/vaekst/0/6/4/3/swotanalyse] - SWOT-ANALYSE - by IVÆKST
[https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ514327.pdf] - Journal of Vocational and Technical Education By Kirk Swortzel
[https://www.lucidchart.com/pages/what-is-swot-analysis#section_5] - What is a SWOT Analysis
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found