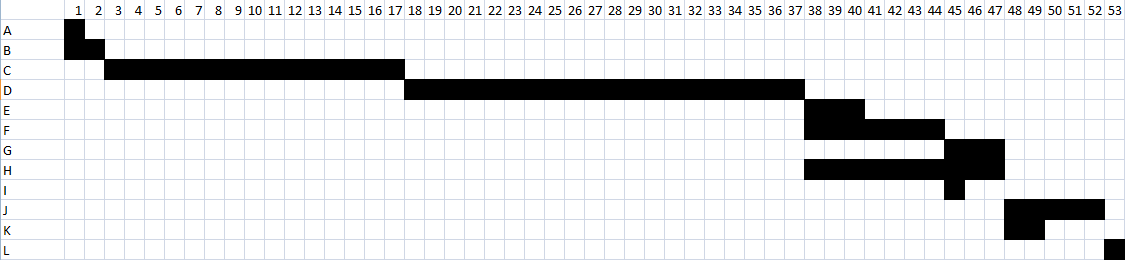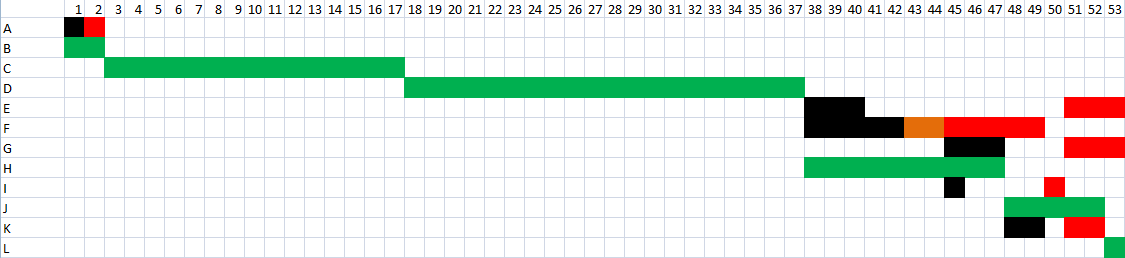The Gantt chart and the usage nowadays
Contents |
Abstract
This abstract has been created on behalf of the course 42433 Advanced Engineering Project, Program and Portfolio Management E15 and the Wiki article that all the students have been enrolled to the course are assigned to write until 29/09/2015. The article has been defined and it should follow the following structure.
- Big Idea: In this chapter a description about Gantt chart will be given. More detail, a chronology about this project management tool and the fields that it is used. In addition to that, the theory that this tool is based on will be described and finally how this theory reflects on the use of Gantt chart
- Application: This is the second chapter of the Wiki article and here it will be explained how to use the Gantt chart. To be more effective the illustration of the methodology, an exercise with the whole solution is going to be provided and explained step by step. Finally in this step, the usage of the tool nowadays and how it has been changed with the passage of time will be explained.
- Limitations: This is the final chapter of the Wiki article and here it will be explained the drawbacks and benefits of using Gantt chart. Moreover wherever it is possible, claims about this critically reflects, are going to be based on the literature.
- Annotated bibliography: This is the literature that the article is based on. All the references (3-10) have to be reported and regarding this, a small abstract per reference should be written in order to explain where each of it has contributed for this article to be written.
Big Idea
Throwback
The first form of the Gantt chart was invented in 1890 and the man behind it was [[1]]. 15 years later, it was the turn of Henry Gantt to develop a new version of this chart which took his name. The popularity of the new type of chart was so intensive in western countries that any other chart similar to this, tended to be associated with Henry Gantt, taking his name.
Methodology
Application
Usage
Example
In order to understand how the theory is applied to practice, it is appropriate to cite a virtual example of project of the Technical University of Denmark. This example does not have any relationship with any events or similarities of reality.
Exercise
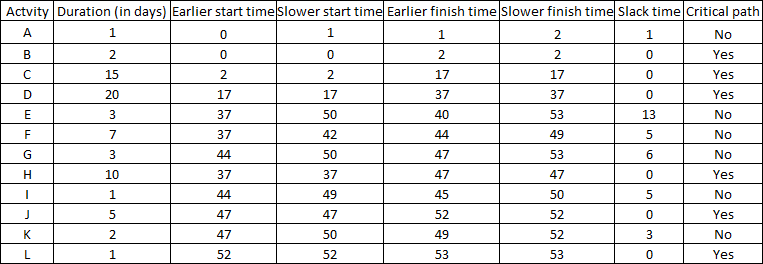
The Organization and Management Department of the Technical University of Denmark organizes one-day conference on the "Electronic commerce". The organizing committee has set out what needs to be done and the challenge is to identify how many days are needed for the preparation of the conference. Also keen to establish a program of the event, which will help it to carry out its target within accepted timeframes and simultaneously will allow it to control all intermediary activities. The table 3.2.1.1 shows the immediately foregoing activities required for the organization of the workshop.
Solution
To manage the timing of the project and in order the critical path to be calculated, the applied method is PERT/CPM. The results of calculations appear in the following table.
It is observed that the activities B, C, D, H J and L are critical and they combine the critical path. These activities must be completed as they initially planned, otherwise the organizing of the workshop will be delayed. The sum of the length of the activities of the critical path is 53 days no matter how much is the earlier or the slower time of expiry of the critical activity L. Therefore, the organizing committee should start the preparations at least 53 days before the scheduled day of the event, so they can carry out all the necessary activities.
In the underneath figure is given the Gantt chart for this project. The duration is in days.
The table above describes the earliest start of each activity. However, there are tasks which can be delayed without affecting the whole process of the project. This figure is lying below. The duration is n days.
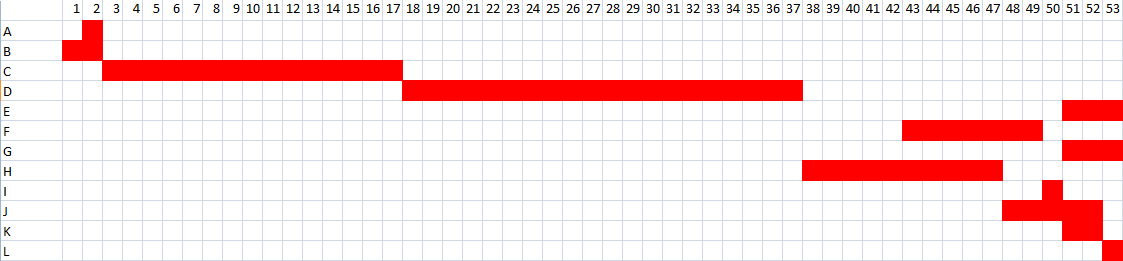
Finally, in order to be understood the difference between the earlier and the slower starting time, a figure with four different colours is given. Black colour is for the earlier start of a task, red colour is for the latest start, orange colour is when the ending of the earlier start matches with the beginning of the slower start of an activity, while the green colour is the critical path where the activity cannot be delayed. This snapshot is given beneath. The duration is in days.
Usage Nowadays
Nevertheless the Gantt charts withstood the test during the passage of time. Changes were made and weaknesses improved. Milestones were added showing specific points in time (mainly six months) during which, tasks have to be completed and indexes showing when a this activity started and when it ended. Over on solid rods, signs are placed indicating the importance of each task (critical controls, revisions). In this case, the units of time are placed by dates. The relations of interdependence of individual operations may be displayed with arrows connecting rods (operations) making by that the Gantt chart a network. However, there are lots of times that it is simpler to have separately the Gantt chart from the relationship network of the project.
Software
Technology is moving with very fast steps and graphs which were displayed manually in the past, have been replaced by programs nowadays. Such programs are the followings:
- Mindview - Gantt chart software
- Smartsheet
- GanttProject
- SmartDraw
Using this kind of software, users' life has been facilitated and in principal, they can save time. In the past, it was very time consuming for managers to draw a project and the whole processes of it. Mainly of changes happened in the original design and the project should be drawn from the beginning.
Limitations
Cons
- Gantt charts do not have great intelligence capabilities, so commonly they are used in less complex projects. That is happening because they are insufficient in project planning, because the interdependencies of individual works are not shown. In other words, it is not evident which tasks should be completed to allow the start of execution of a certain work which is linked with the previous one. Moreover it does not show the effect of a delay or acceleration in some phase of the project.
- Another drawback is the difficulty in the adjustment when changes occur in the period of execution of some actions or activities. In addition to that, there is the difficulty of implementing them in projects with a large number of actions, because of the considerable space required by the portrayal.
- Even there is weakness in the depiction of the interdependencies among the activities of the projects.
- The final disadvantage is the inability for the presentation of critical actions or activities for the successful completion of the entire project.