The Influence of Psychological Safety in Team Development
(→Overview of Tuckman's Model) |
(→Overview of Tuckman's Model) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
=== Overview of Tuckman's Model === | === Overview of Tuckman's Model === | ||
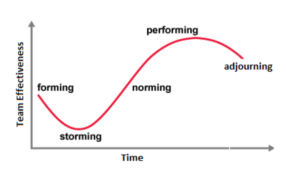
| − | [[File:Five_stages_of_team_development.png|frame|500px|Figure 1. Five Stages of Team Development ()]]In his team development model, Professor Bruce Tuckman distinguishes between interpersonal relations among group members (group structure) and task activity in the different stages of team development. The core identified stages are ''forming'', ''storming'', ''norming'' and ''performing''. After a revisit to the model, a fifth stage was added: ''adjourning''. The following aspects were identified in natural group settings, where tasks were rather impersonal | + | [[File:Five_stages_of_team_development.png|frame|500px|Figure 1. Five Stages of Team Development ()]]In his team development model, Professor Bruce Tuckman distinguishes between interpersonal relations among group members (group structure) and task activity in the different stages of team development. The core identified stages are ''forming'', ''storming'', ''norming'' and ''performing''. After a revisit to the model, a fifth stage was added: ''adjourning'' <ref name="Tuck65">"Tuckman, B. W. (1965). Developmental sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin, 63(6), 384–399. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0022100" <ref/>, <ref name="Tuck77"/>. |
| + | The following aspects were identified in natural group settings, where tasks were rather impersonal. This is usually the case with technical engineering tasks. The characteristics of each stage will be described taking a newly created engineering team as an example. | ||
*Forming: In this phase, the main roles are defined. The leadership role is given by the position, in this case, held by the project manager. Currently, the project manager and other team members have space for testing and understanding the team's boundaries. There is also room for exploring and scoping the task to determine how the team can approach it. | *Forming: In this phase, the main roles are defined. The leadership role is given by the position, in this case, held by the project manager. Currently, the project manager and other team members have space for testing and understanding the team's boundaries. There is also room for exploring and scoping the task to determine how the team can approach it. | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 9 May 2023
The concept of psychological safety was introduced over twenty years ago by Edmonson [1]. It entails the creation of a safe space where the individual members of a team can express their ideas and concerns in the workplace, knowing that they will be listened to and not judged. When Team Psychological Safety (TPS) is achieved, a sense of interpersonal trust is developed among the teammates. The benefits that TPS brings to the overall team performance are such as reducing the fear of taking risks and increasing the innovation potential of a team [2]. Therefore, it is important for a Project Management Office (PMO) to promote psychological safety as a way to seek the best performance of teams. Two main issues for the PMO arise i) how is TPS achieved and; ii) when does it emerge?
The first issue is explored by conducting a literature review with a view to understanding the nature of TPS, as well as the assessments of the same. The latter is addressed by exploring Tuckman’s Model of Team Development. This model is widely recognized and referenced in literature, where five stages are identified are: forming, storming, norming, performing and adjourning. The present work analyzes the aforementioned stages of team development as a function of the development of psychological safety [3]. This study focuses on a newly created team and will address how TPS is sparked and its evolution along the stages of team development. Lastly, new strategies will be proposed for leaders to promote the TPS in newly created teams.
Contents |
Introduction
Large organizations like Google are constantly seeking for optimizing their processes and finding the most efficient way to success. In 2012, they engaged in Project Aristotle, whose goal was to determine what makes a team succeed. The devoted researchers analyzed hundreds of teams within the company and found that, for analogous team structures and expertise, success levels were significantly different. There was no clear pattern to identify the characteristics of the perfect team. The quality of a team is defined by its direct performance and the working relationships (both within the team and externally in the organization). Achieving goals and meeting expectations is a necessary but not sufficient condition for a perfect team. Understanding the relationship between the individual members and their shared culture is key to strive for success. [4]
A change of paradigm occurred when the lead researchers stumbled on the term “psychological safety”. It had been seen that group dynamics had a direct impact on the productivity levels of the teams. When people had the space to express themselves and shared a mutual understanding of the tasks, work was handled better. It became clear how important team leaders were to achieve this safe space. When leaders are direct and clear, they create room for team members to take risks. Conversely, poor leadership and lack of emotional control led to lower performance. [5]
The aforementioned concept of team psychological safety (TPS) refers to the commonly held conviction that there is a safe space for expressing ideas, voicing concerns, making mistakes and giving and receiving feedback without fear of being punished or judged. The term can be thought of as a matter of trust. Although interpersonal trust is an important aspect of psychological safety, the latter term goes above and incorporates the fact that people can be themselves. Members share a common understanding of the norms that define them as a whole rather than them as individuals.
The team leader (project manager) plays an important role in making their team a safe environment. The behaviour of the leader is usually noticeable by the team members and has a direct impact on their perception of psychological safety. When managers are open, supportive and constructive, the team is likely to be perceived as safe. However, when they are rigid, punishing and avoid examining errors, team members tend to avoid speaking up and suppress learning behaviours [1]. As research shows, the term TPS is not usually made explicit. However, team development models are more commonly referred to and looked into by PMs. This work provides an image of how can TPS positively influence team development.
Psychological safety in teams
Benefits
Hereunder, several benefits of team psychological safety are presented in terms of the value they bring to project managers [1], [2].
- Open communication: when members and leaders feel confident in expressing themselves without fearing punishment, they are more likely to communicate openly. This lack of punishment makes team members admit their mistakes faster, giving the leader advantage to act sooner. Moreover, information and knowledge across the team are easily transmitted, which increases the situational awareness of the project manager and the rest of the team.
- Learning behaviour: this perspective relates to the willingness of leveraging previous experience to face new challenges. Being able to fail, allows members individually and the team as a whole to take it as a growth opportunity. However, learning is not exclusive to past actions, seeking feedback and maintaining an open attitude towards new ideas is an important contributor to learning behaviours. Edmondson <"edmon"/> highlights the tight link between learning behaviours and psychological safety. A team leader that encourages learning behaviours will likely see direct results in the degree of safety achieved.
- Increased innovation: is closely linked to the importance of encouraging learning, being able to take risks leads to higher innovation rates. Moreover, teams where psychological safety is a reality tend to have higher levels of critical thinking, which allows members to trust their judgement and identify opportunities. As it has been proved "It [psychological safety] sparks the kind of behaviour that leads to market breakthroughs" <"edmon"/>.
- Employee attitude: a cohesive and psychologically safe team usually leads to a positive attitude towards the team and the workplace. For managers, a positive employee attitude means a higher commitment and performance.
- Improved performance: the main goal for project managers is to deliver results within the established budget and timeframe <"PMBOK2"/>. Searching for ways to improve performance and productivity is a common practice. TPS proves that when teams share a common understanding of the norms and tasks to perform, feel free to voice their ideas and collaborate, important discussions arise. These discussions enrich the development and delivery of the work. The aforementioned learning behaviour has also an indirect effect towards improving performance.
How to create psychological safety
As seen before, psychological safety is based on a set of shared beliefs and norms among team members. As a team leader, the project manager plays a key role in facilitating the creation of this safe space. The project manager has the responsibility of leading by example, keeping open communication, owning mistakes and encouraging the team. Good leadership actions in this line would be [6] ,[7]:
Promoting a transparent culture
The project manager should try to engage in open communication. Sharing one's understanding of situations, thought processes, or decision-making directly impacts the development of the team's inherent norms, fostering an environment of open communication and reflection among team members.
Replacing debate with dialogue
Projects face risks and thus, are subject to unforeseeable events that can disrupt the project plan and resource allocation. These situations can lead to disputes and friction in the team. It is important for project managers to adopt a collaborative role rather than taking an adversarial approach. The end goal of the discussion is to reach a common agreement and find solutions.
Promoting respect
Recognizing the skills and experience that team members bring to the project builds mutual respect. Regardless of the hierarchical structure, empathy and understanding should be shown to all members, acknowledging personal situations. Communication is, again, key to building trust and respect, sharing news early and keeping each other informed of project status and assumptions.
Support the team
The project manager is available and an ally for problem-solving. In this, it is important to engage in active listening to understand the needs of the team and create learning opportunities.
Acknowledge achievements
Celebrating and recognizing the team's progress increases awareness of the real-time status of the project. It also helps in keeping the team motivated for achieving the end goals, to increase engagement and sense of belonging.
Assessing psychological safety
While a team can establish the grounds for Psychological safety, it is an evolving aspect of team culture and as such needs to be measured and monitored periodically. TPS is assessed through reviews with the manager or surveys. During the reviewing process, the team members should not feel pressured into answering positively, transparency and open communication should lead. It is advised to use a neutral tone and allow room for discussions and opinions. Questions should be formulated in a clear manner, like "Do you feel that your contributions are valued within the team?", "How transparent do you feel the culture is?" [7], [8].
Application in new teams
The creation of a new team presents a good opportunity to implement psychological safety, its influence in team development will be followed taking a newly created engineering team as an example. In this team, the management is centralized, where the project manager is accountable for the team formation and task delegation [6].
Implementing psychological safety
The project manager should introduce the concept to the team members, highlighting the benefits and motivation for the establishment of a psychologically safe space. Although TPS is sometimes an inherent belief, explicitly discussing it increases the awareness and understanding of the team. The expectations and desired outcomes of implementing psychological safety should be presented and discussed within the team. It is worth mentioning that achieving TPS is part of a process that requires willingness and patience on the part of the project manager and other team members [1].
Overview of Tuckman's Model
In his team development model, Professor Bruce Tuckman distinguishes between interpersonal relations among group members (group structure) and task activity in the different stages of team development. The core identified stages are forming, storming, norming and performing. After a revisit to the model, a fifth stage was added: adjourning Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tagCite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found