The Role of Program Management in an Organisational Change
(→What is change management?) |
(→What is change management?) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
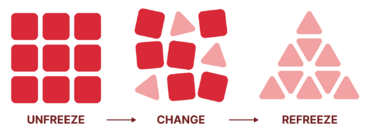
However, the psychologist Kurt Lewin has represented a simplified way of viewing a change process <ref name=hayes>Hayes, J (2010). ''The Theory and Practice of Change Management'', PALGRAVE MACMALLIN, New York</ref>. As illustrated in the Figure 1, the change process is divided into three distinct stages; freeze, change and refreeze. | However, the psychologist Kurt Lewin has represented a simplified way of viewing a change process <ref name=hayes>Hayes, J (2010). ''The Theory and Practice of Change Management'', PALGRAVE MACMALLIN, New York</ref>. As illustrated in the Figure 1, the change process is divided into three distinct stages; freeze, change and refreeze. | ||
| − | [[File:kurt_lewis.png| | + | [[File:kurt_lewis.png|370px|thumb|Figure 1: Kurt Lewin's three step change management process]] |
# '''Unfreeze''': The first stage characterises the starting point of the change process where the organisation prepares for the change. This involves creating awareness about the need for the change, identifying current behaviours and to get people to let go of their old ways of thinking and working <ref>Kotter J. P (1996). ''Leading Change'', Harvard Business School Press, Boston</ref>. | # '''Unfreeze''': The first stage characterises the starting point of the change process where the organisation prepares for the change. This involves creating awareness about the need for the change, identifying current behaviours and to get people to let go of their old ways of thinking and working <ref>Kotter J. P (1996). ''Leading Change'', Harvard Business School Press, Boston</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 17:00, 2 April 2023
Developed by Sebbe Sidenius Bull
Revised by Cirkeline Bräuner
ADD SOURCES
In today's rapidly changing society, organisations are going through changes all the time. This causes, that organisations must be able to adapt to new market conditions, changing customer demands and emerging technology. To remain competitive in a continuously evolving business environment, organisations go through changes such as process optimisation, cost reduction or technology adoption. These are few examples of changes which affect the entire business, and it is therefore crucial that the change is managed in a successful way to avoid harming the business.
Organisational change is a huge alteration for any organisation and can be a dawning task if not managed properly. In the context of project management, organisational change refers to any significant alteration in an organisation that affects the way projects are planned, executed and managed. Project managers must be able to identify the potential impact of organisational changes in their projects and adapt their project management approach accordingly to ensure successful project delivery. (THIS SOUND WIERD) In this regard, program management can serve as an effective tool for managing organisational change. With its comprehensive toolbox of evaluative methods, program management offers a structured approach to assessing each potential change project. This toolbox supports change managers in providing an overview of the change project, ensuring efficient project execution, promoting project alignment, evaluating risks, mapping stakeholders and identifying potential benefits. All of these elements work together to facilitate a more effective and efficient change management process.
This article provides an introduction to what change management is and how it can be related to the four core perspectives of this course; purpose, people, complexity and uncertainty. Afterwards, an introduction to program management is given. Then, the two management fields are combined into one common understand of how program management can be applied in organisational change. Lastly, the benefits and limitations of organisational changes using program management is discussed.
Contents |
Change management
What is change?
"The act or result of something becoming different" or "The process of replacing something with something new or different" [1] are two examples of a definition of what a change is.
A change is simply a variation in the common way of doing things. It refers to any modification, alteration or transformation in something from its previous state to a new state. Changes occur everywhere and is an opportunity to make or become different through new ways of acting. Changes can be temporary or permanent, positive or negative and gradual or sudden. It can be a source of growth and development as well as a source of challenges and difficulties (SOURCE).
Changes are defined as either incremental or radical. An incremental change is a change which happens gradually over time. It involves making small adjustments of an already existing system to improve efficiency, effectiveness and performance. An example of an incremental change is making small step-by-step adjustments in an organisation's strategy. Radical change, on the other hand, is different from incremental change as it involves making a significant change such as introducing a completely new business strategy. Both types of changes can be beneficial for different purposes and choosing the right approach depends on the context [2].
What is change management?
In the section above, the definition of a change is briefly described. This leads on to the next topic, which deals with what change management is from a project management point of view. Unfortunately, there is not a single recipe for applying change management in organisations as the is no one-size-fits-all approach. The process has to be tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of the organisation.
However, the psychologist Kurt Lewin has represented a simplified way of viewing a change process [3]. As illustrated in the Figure 1, the change process is divided into three distinct stages; freeze, change and refreeze.
- Unfreeze: The first stage characterises the starting point of the change process where the organisation prepares for the change. This involves creating awareness about the need for the change, identifying current behaviours and to get people to let go of their old ways of thinking and working [4].
- Change: The second stage involves implementing the change through planning, communication and execution. The objective is to create new ways of thinking and working. During this phase, people must be trained and educated to adopt new methods and behaviours and to overcome any obstacles that may arise [3].
- Refreeze: The third stage addresses making the new change permanent. The objective is to reinforce the new behaviours, ensuring that they become a part of the organisation's culture. During this phase, the focus is on stabilising the new ways of thinking and working, and creating a sense of ownership among employees [3].
Why is organisational change a difficult task?
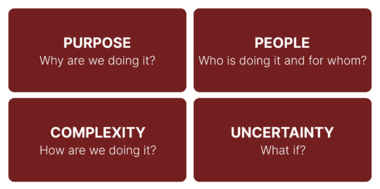
To gain a better understanding of what change management is, it is interesting to view this topic from the point of view of the four core perspectives introduced in the course; purpose, people, complexity and uncertainty [5].
WRITE MORE HERE AND FIGURE OUT IT IT FITS BETTER IN PRORAM MANAGEMENT
- Purpose: Before even starting a change process within an organisation, it is important to clearly define the purpose of the change. Defining the purpose ensures that the goal and objectives of the change are aligned with the organisation's strategy.
- People: People are a necessity to create awareness of the need for the change in the first place. Furthermore, it is also people who are affected by the change and implement it in practice.
- Complexity: A change process can be difficult complex to implement successfully and it is essential to create a plan for how the change should be introduced and implemented.
- Uncertainty: When implementing a new change, there will always be uncertainties and risks involved.
Program management
What is program management?
Application of program management in organisational change
Benefits and limitations
Annotated bibliography
References
- ↑ https://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/definition/english/change_2 Definition of change, last visited 02-03-2023
- ↑ Hodges, J (2016), Managing and Leading People through Organisational Change, Kogan Page, England
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Hayes, J (2010). The Theory and Practice of Change Management, PALGRAVE MACMALLIN, New York
- ↑ Kotter J. P (1996). Leading Change, Harvard Business School Press, Boston
- ↑ https://www.doing-projects.org/perspectives Project management perspectives, last visited 02-03-2023