The Role of Program Management in an Organisational Change
Developed by Sebbe Sidenius Bull
Revised by Cirkeline Bräuner
ADD REFERENCES, AND PURPOSE/PEOPLE/COMPLEXITY/UNCERTAINCY
In today's rapidly changing society, organisations are going through changes all the time. This causes, that organisations must be able to adapt to new market conditions, changing customer demands and emerging technology. To remain competitive, many organisations go through changes such as process optimisation, cost reduction or technology adoption. These are few examples of changes which affect the entire business, and it is therefore crucial that the change is managed in a successful way to not harm the business.
Organisational change is a huge alteration for any organisation and can be a dawning task if not managed properly. In the context of project management, organisational change refers to any significant alteration in an organisation that affects the way projects are planned, executed, and managed. Project managers must be able to identify the potential impact of organisational changes in their projects and adapt their project management approach accordingly to ensure successful project delivery. In this regard, program management can serve as an effective tool for managing organisational change. With its comprehensive toolbox of evaluative methods, program management offers a structured approach to assessing each potential change project. This toolbox supports change managers in providing an overview of the change project, ensuring efficient project execution, promoting project alignment, evaluating risks, mapping stakeholders and identifying potential benefits. All of these elements work together to facilitate a more effective and efficient change management process.
This article provides an introduction to what change management is and why it is a difficult task to manage. Afterwards, an introduction to program management is given. Then, the two management fields are combined into one common understand of how program management can be applied in organisational change. Lastly, the benefits and limitations of organisational changes using program management is discussed.
Contents |
Change management
What is a change?
What is change management?"
Unfortunately, there is not a single recipe for applying change management in organisations as the subject is simply too complex. However, all organisational change process can be described through the following simple four-step process:
- Assess the need for change: Recognise that there is a problem and identify the source of the problem.
- Decide on the change to make: Decide what the organisation's ideal future state would be and identify obstacles to change.
- Implement the change: Introduce and manage change and decide whether change will occur top down or bottom up.
- Evaluate the change: Compare performance and use benchmarking.
MAKE A BETTER CONNECTION HERE
CHANGE LEWINS MODEL
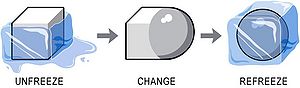
One of the most simplified way of viewing the change process is through Kurt Lewin's three-step change process [1]. As illustrated in the figure, the change process is divided into three distinct stages; freeze, move and refreeze.
- Unfreeze: The first stage characterises the starting point of the change process where the organisation prepares for the change. This involves creating awareness about the need for the change, identifying current behaviours and to get people to let go of their old ways of thinking and working [2].
- Change: The second stage involves implementing through planning, communication and execution. The objective is to create new ways of thinking and working. During this phase, people must be trained and educated to adopt new methods and behaviours and to overcome any obstacles that may arise [3].
- Refreeze: The third stage addresses making the new change permanent. The objective is to reinforce the new behaviours, ensuring that they become a part of the organisation's culture. During this phase, the focus is on stabilising the new ways of thinking and working, and creating a sense of ownership among employees [4].
References
- ↑ [Hayes John (2010). The Theory and Practice of Change Management. 3rd ed. New York: PALGRAVE MACMALLIN. 29.]
- ↑ [Kotter J.P. (1996) Leading Change, BOSTON, Harvard Business School Press]
- ↑ [Hayes John (2010). The Theory and Practice of Change Management. 3rd ed. New York: PALGRAVE MACMALLIN. 26.]
- ↑ [Hayes John (2010). The Theory and Practice of Change Management. 3rd ed. New York: PALGRAVE MACMALLIN. 27.]