The Stage-Gate Model
(→Applications) |
(→Limitations) |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
==Limitations== | ==Limitations== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The typical Stage-Gate model has some limitations that the new versions have tried to overcome. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Firstly, although the Stage-Gate model was developed after examining the practices of the top innovative firms at the time, it has thereafter been accused of being too linear and rigid to handle innovative and dynamic projects. Also, a disadvantage of the model is that it is not adaptive and flexible enough to meet teh new reality of projects. Moreover, there is a lot of critisism about the decision making points and the criteria used for decision making. Senior management should be available and present to assess the progress of the project, and the financial perspective of the project should not be overweighted for the final decision. | ||
| + | |||
==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
Revision as of 23:57, 22 September 2017
Contents |
Abstract
The stage-gate model is a project management methodology used to drive a project from idea-to-launch in a structured way, including several decision-making points, so called gates, where senior management is involved to take decisions regarding the course of the project.
The stage-gate model was firstly developed by companies as a way to manage the product development process more efficiently. However, the model being intuitively appealing and simple, it was adopted to manage a variety of other projects like process improvements and changes in the processes within companies. Today, it is regarded as a general project management methodology with a wide range of variations.
A phase-gate process, a waterfall process, a front-end loading (FEL), a big design up front (BDUF) are very similar methodologies to the stage-gate model.
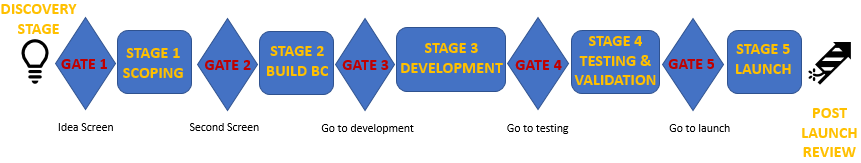
Usually, the model involves from four to seven stages and gates. Each stage is followed by a gate, when certain deliverables are to be submitted and a decision should be taken that leads to the next stage. A typical model is comprised of the following stages and their gates:
Idea – G1 – Preliminary Assessment – G2 – Business Case Development – G3 – Development/Manufacture – G4 – Testing and Validation – G5 – Launch
The stage-gate model mitigates the risk apparent in a new project through the structured process with the senior management support, however sometimes it is regarded as rigid and slow and accused of killing creativity and innovation.
History
The Stage-Gate Model was created in the 1980s by Robert G. Cooper, a now internationally recognized expert in the field of innovation management. The Stage-Gate Model was the result of an extensive research about the new product development (NPD) practices followed by top performing companies, leading innovators and entrepreneurs, published by Robert G.Cooper in 1985.
Robert G.Cooper continued his research activities within new product development and innovation management, which has led to over 120 article publications and ten published books until today. Furthermore, along with his fellow researcher and innovation expert Scott J. Edgett, he founded the Product Developement Institute Inc. in the year 1996 and the Stage-Gate International in the year 2000. Scott J. Edgett has also extensive research activity and expertise in the field of innovation management with more than 60 academic articles and co-authoring of six books. The Product Developement Institute Inc. is helping companies to improve their approach to new product development and portfolio management, while Stage-Gate International is an innovation management consulting company that offers expert advice in companies globally.
As a result of all this research activity and the continuous contact with the industry, the Stage-Gate Model has evolved since 1985. Thus, there are plenty variations of the model, that follow the advances in the field of innovation management and the new needs for more flexibe, adaptive and lately fast-track product development.
It is important to mention that approximately the 80% of the Global 1000 companies had adopted a version of the Stage-Gate model up to 2015.
Typical Model
The initial Stage-Gate Model is comprised of stages and gates in a linear mode, where each stage is followed by a gate. The stages are the phases of the actual work that needs to be executed in a project/ new product development and the gates are points in time when a decision has to be taken about the future of the project/ product. At the gates, the decision is made by the gatekeepers, who are usually from the senior management, since this role requires both a good understanding of the business, as well as the authority to make decisions.
Usually,the typical Stage-Gate model is comprised from four to seven stages and gates as it can be seen in the following picture:
At the gates there are three important elements:
- input
- criteria
- output
The input at each gate is comprised of the deliverables that should be sumbmitted in order for the project to be examined and the decision to be made. Usually, the deliverables at each gate are either set from the beginning, chosen from a predetermined list of deliverables, or have been determined in the previous gate.
The criteria are the elements based on which the project will be examined. The gatekeepers play an initial role in setting the criteria for projects. The range of criteria may be broad but usually the quality of the project is judged in terms of its business case and financial criteria.
The output of the gate is the final decision about the project. It is usually a GO/KILL decision, but sometimes other options exist like HOLD or RECYCLE.
- GO - the project proceeds to the next stage
- KILL - the project is terminated
- HOLD - the project remains on hold
- RECYCLE - the project repeats the current stage
Applications
The Stage-Gate model was developed for new product development (NPD) management and innovation management. However, it was adopted from a variety of companies to manage a variety of projects. This is mainly because the Stage-Gate model is a simple and intuitive model that can be easily modified to include more or less stages and gates and different sets of elements at the gate so as to accommodate the needs of a specific project.
The most common variations of the model that allow also for different applications are the following:
(has not been completed yet)
Limitations
The typical Stage-Gate model has some limitations that the new versions have tried to overcome.
Firstly, although the Stage-Gate model was developed after examining the practices of the top innovative firms at the time, it has thereafter been accused of being too linear and rigid to handle innovative and dynamic projects. Also, a disadvantage of the model is that it is not adaptive and flexible enough to meet teh new reality of projects. Moreover, there is a lot of critisism about the decision making points and the criteria used for decision making. Senior management should be available and present to assess the progress of the project, and the financial perspective of the project should not be overweighted for the final decision.