Transformational Leadership
(→The Characteristics of Transformational Leaders) |
(→The personality traits of transformational Leaders) |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
[[File:Correlation graph.png|600px|thumb|right|Correlation graph]] | [[File:Correlation graph.png|600px|thumb|right|Correlation graph]] | ||
| − | The effectiveness of transformative leadership largely hinges on the individual leading it — namely their personality. In exploring this connection between personality traits and transformative leadership efficacy, "Personality and Transformational and Transactional Leadership: A Meta Analysis" sheds light on the five traits that contribute to successful transformational leadership. <ref> Bono, J. E., & Judge, T. A. (2004). Personality and Transformational and Transactional Leadership: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(5), 901–910 - https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2004-19456-013</ref> | + | The effectiveness of transformative leadership largely hinges on the individual leading it — namely their personality. In exploring this connection between personality traits and transformative leadership efficacy, "Personality and Transformational and Transactional Leadership: A Meta Analysis" sheds light on the five traits that contribute to successful transformational leadership. <ref name="1"> Bono, J. E., & Judge, T. A. (2004). Personality and Transformational and Transactional Leadership: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(5), 901–910 - https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2004-19456-013</ref> |
The five traits are: | The five traits are: | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
Agreeableness had a positive correlation: 0.17, | Agreeableness had a positive correlation: 0.17, | ||
Conscientiousness had a positive correlation: 0.19, | Conscientiousness had a positive correlation: 0.19, | ||
| − | These results indicate the critical role of personality in shaping a leader's capacity to undertake transformative initiatives successfully. Outgoing leaders who possess high levels of extraversion tend to inspire those around them through their energetic nature whereas low levels of neuroticism help promote emotional stability that instills confidence within teams during challenging times. To select effective transformational leaders, organizations must consider candidates' unique personalities that display qualities conducive to the desired outcome such as inspiring motivation or generating positive change within working environments.<ref | + | These results indicate the critical role of personality in shaping a leader's capacity to undertake transformative initiatives successfully. Outgoing leaders who possess high levels of extraversion tend to inspire those around them through their energetic nature whereas low levels of neuroticism help promote emotional stability that instills confidence within teams during challenging times. To select effective transformational leaders, organizations must consider candidates' unique personalities that display qualities conducive to the desired outcome such as inspiring motivation or generating positive change within working environments.<ref name="1"> |
=== Transformational compared to transactional leadership and laissez-faire leadership === | === Transformational compared to transactional leadership and laissez-faire leadership === | ||
Revision as of 23:23, 9 May 2023
Written by Michael Vinther - s163490
This article will explore transformational Leadership from a project management perspective. Transformational Leadership is a leadership style that focuses on motivating people to reach a common goal. This leadership style actively encourages individuals to take responsibility for their work while striving for personal growth. Unlike traditional leadership models that rely on power dynamics, transformational leadership in project management places the project manager in a role model position. It is no longer sufficient for leaders in today's rapidly evolving business environment merely to manage; they must lead with purpose and inspiration. Transformational Leadership is one such approach that has emerged as an effective way to steer diverse teams toward shared goals through inspiration and motivation. [1] In this refere Specifically, within the realm of project management, transformational leadership helps managers rally their teams around a commonly agreed-upon objective while simultaneously promoting collaboration and encouraging creativity. Challenging assumptions, creating shared visions and offering dedicated support are three critical aspects of transformational leadership - a distinct style from others such as transactional leadership, which often involves exchanging rewards, or laissez-faire leadership, which provides little guidance. When utilized in project management contexts, transformational leadership enables managers to motivate their teams toward achieving shared goals underpinned by concrete visions. Transformational Leadership practices have gained widespread recognition within organizational settings due to their positive impacts on individual job satisfaction and engagement levels. These attributes are closely tied to improved project outcomes as well as enhanced team performance overall. One of the key features that set transformational leaders apart is their ability to provide tailored support for each employee on the team. Leaders focus on identifying individual strengths, weaknesses, and goals so that they can assign work responsibilities that align with staff interests while offering appropriate feedback along the way. Leaders who possess transformational leadership skills are not only able to inspire their teams but also motivate them toward achieving their objectives. Unlike transactional leaders who select rewards or punishments based on performance, transformational leadership shifts the focus towards building sustainable relationships among team members through trust-building activities. By sharing a unified vision for the future, these leaders commit themselves to promoting creativity and innovation in those they lead. By adopting the transformational leadership approach, leaders set themselves up as role models for their teams through mutually respectful relationships based on common values.
Understanding Transformational Leadership
Originally conceptualized by James MacGregor Burns in 1978 and further developed by Bernard Bass in subsequent decades, this leadership style has garnered widespread attention for its use in diverse contexts like project management. Its efficacy was found to lie precisely in instances where it fosters teamwork among team members who take personal responsibility for achieving specific goals. Transformational leadership is a potent approach to cultivating a sense of collaboration, establishing shared goals, and sparking creativity and innovation. Four elements delineate transformational leadership, namely idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individualized consideration. These critical components play a crucial role in how such leaders inspire and motivate their team members toward achieving mutual objectives. Idealized influence corresponds to the ability of the leader to become an embodiment of values and behaviors that they hope others will emulate. In order for organizations to thrive, transformational leaders must embody exceptional ethical standards while achieving their goals. This involves leading by example and motivating team members towards a common goal through inspirational motivation that provides them with a sense of direction.
The Characteristics of Transformational Leaders

Transformational leadership encompasses four fundamental components, often referred to as the "4 I's," which together shape the essence of this leadership style and its impact on followers. These components are: Idealized Influence, Inspirational Motivation, Individualized Consideration, and Intellectual Stimulation, as shown in figure 1. [5]
- Idealized Influence is the first component of transformational leadership, wherein the leader serves by leading by example. By consistently embodying the qualities they seek in their team, the leader "walks the talk" and becomes an admired figure. Their exemplary conduct creates a strong impression on others and builds respect. This admirable quality inspires employees to aspire to be more like their respective leaders while building trust and admiration.
- Individualized Consideration underscores the transformational leader's genuine concern for the individual needs and emotions of their followers. They demonstrate a personal commitment to each member, actively facilitating their self-actualization and growth. By offering individual attention and support, the transformational leader fosters trust and strengthens the bond between the leader and their followers. This mutual trust enables teams to collaborate more effectively, enhancing decision-making processes and promoting a sense of unity and shared purpose.
- Inspirational Motivation is a crucial trait of transformational leaders’ ability to motivate their followers through the articulation and communication of a compelling vision. With this skill, they can communicate an inspiring vision that instills their followers with purpose and enthusiasm. Idealized influence combined with inspirational motivation can be incredibly powerful, leading to exceptional levels of productivity.
- Intellectual Stimulation is the final component of transformational leadership, representing the leader's inclination to challenge their followers to think critically, be innovative, and challenge the current situation. Contrary to the misconception that transformational leaders are "soft," they consistently push their followers to reach higher levels of performance and surpass their own limitations. By encouraging creativity and stimulating intellectual growth, transformational leaders help their followers expand their perspectives and connect the dots, thereby fostering innovation and continuous improvement within the team. They understand the importance of investing time and effort into furthering innovation within their teams.
In summary, transformational leadership encompasses the four fundamental components of Idealized Influence, Inspirational Motivation, Individualized Consideration, and Intellectual Stimulation. This leadership style empowers leaders to lead by example, inspire their followers, cater to individual needs, and encourage intellectual growth. By embracing these components, transformational leaders create a positive and influential environment that fosters trust, unity, innovation, and continuous improvement within their teams.[6]
The personality traits of transformational Leaders
The effectiveness of transformative leadership largely hinges on the individual leading it — namely their personality. In exploring this connection between personality traits and transformative leadership efficacy, "Personality and Transformational and Transactional Leadership: A Meta Analysis" sheds light on the five traits that contribute to successful transformational leadership. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
The five traits are:
Neuroticism characterizes people who typically have unfavorable views about their surroundings and frequently experience profound feelings of fear, guilt, and anger. Researchers show that there is a strong connection neuroticism and both low self-esteem as well as general low confidence.
Extraversion is a personality trait that is characterized by assertiveness, activity level, talkativeness, optimism, and high energy. Notedly the people who show signs of this type also tend to seek excitement as well as social attention. Due to their optimistic outlook on life extroverts make exceptional leaders as they inspire confidence and enthusiasm in others with their positive nature. Moreover, they thrive on change which further contributes to their inclination toward intellectual stimulation.
Openness is a personality trait that is characterized by being generally more creative, introspective, and resourceful while being able to engage in divergent thinking when required. Talking about leadership, having openness is linked with transformational leadership where leaders can inspire others through visionary leadership style alongside their ability to think creatively. They often display inspirational behaviors towards others due to their imaginative nature. This allows them to envision the future of an organization better while contributing towards making a flexible organizational culture that encourages learning, and growth while enabling innovation opportunities among team members.
Agreeableness is a personality trait characterized by people who prioritize maintaining good relationships and feeling empathy and concern for other people while avoiding conflicts. In terms of leadership style individuals scoring high in agreeableness demonstrate specific behaviors centered around personal growth and development. This approach promotes teamwork while fostering loyalty amongst everyone in the group.
Conscientiousness is a personality trait characterized by people having exceptional focus when pursuing set objectives. They tend to exhibit cautious tendencies combined with deliberate actions alongside self-discipline that value organization highly. Conscientious leaders usually exhibit less passive behavior in fulfilling their organizational responsibilities due to their dependability, self-discipline, and willingness to take on leadership roles. While conscientiousness might not necessarily imply visionary thinking or creativity - it still plays a crucial role in effective leadership by emphasizing goal completion & task execution while incorporating attention-to-detail abilities.
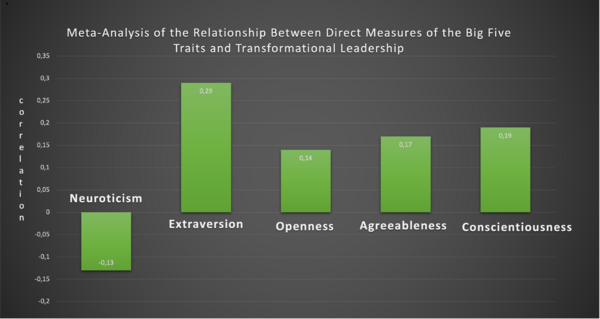
The research indicates correlations between specific personality traits and transformational leadership practices that may hold significance for organizations aiming to implement transformational leadership. The results are displayed in the Correlation graph.
Extraversion had the highest positive correlation: 0.29,
Neuroticism showed a negative correlation: -0.13,
Openness had a positive correlation: 0.14,
Agreeableness had a positive correlation: 0.17,
Conscientiousness had a positive correlation: 0.19,
These results indicate the critical role of personality in shaping a leader's capacity to undertake transformative initiatives successfully. Outgoing leaders who possess high levels of extraversion tend to inspire those around them through their energetic nature whereas low levels of neuroticism help promote emotional stability that instills confidence within teams during challenging times. To select effective transformational leaders, organizations must consider candidates' unique personalities that display qualities conducive to the desired outcome such as inspiring motivation or generating positive change within working environments.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
name cannot be a simple integer. Use a descriptive title
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found