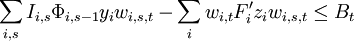Valuation methods in Project Portfolio Optimization - Focus on Real Options
Valuation methods in Project Portfolio Optimization - Focus on Real Options
Contents |
Abstract
Valuation methods are critical supporting tools for any decision in Project Portfolio Management, so as to optimize the project portfolio in terms of expected return for the different values (e.g. money, knowledge, strategic alignment). This article quickly presents general valuation techniques for generic portfolio management (NPV, DCF, see below), but might be more relevant as applied to R&D portfolio selection and optimization.
A project portfolio is optimized by evaluating a multi-objective ranking based on (1) the expected return, (2) the uncertainty, and (3) the strategic fit, while optimizing several budgets allocation:
- Financial budget,
- Technological or knowledge-based budget,
- Budget based on the market uncertainty
- Critical resources allocation budget
R&D portfolios optimization is based on project valuation, and an alternative to classical methods such as NPV (Net Present Valuation) and DCF (Discounted Cash Flow) is the real options valuation.
The core principle is similar to the principle of financial options: holding a decision which is to be made is equivalent to have an option, which can be valued. The only difference is the materiality of the option (‘real’), as opposed to the abstract nature of a financial option.
The real option valuation is based on a mixed set of input data, balanced between the expected return, the expected consumed resources and the different risk factors.
Project Portfolio Optimization in short
Project Portfolio Optimization in short (PPO) <2> Success of a PP = achievement of a sustainable competitive advantage Difficulties - projects may have conflicts in objective. Objectives can be hard to compare, align or match, some are tangible and others intangible<3> - uncertainties associated with project parameters, costs and risks<4> - some projects are highly interdependent<5> Two main factors leading to failure of portfolio to contribute to the implementation of the chosen strategy. First, implementing too many projects, beyond the capacities and abilities of the organization <6> <7> <8> <9> <10> <11> <12> Then, satisfy short-term exigencies may ruin long-term success. Taking a decision and choosing a project implies to tie resource, which may be critical, to this project. Making this decision without considering the opportunity costs may lead to refuse a truly good opportunity or prospect in the future because of lack of resources, the necessary resources to pursue it being tied up in marginal undertakings <18> Critical point is resource allocation, as finite resource available. Therefore, crucial to wisely allocate resources, especially strategic ones, to support the corporate strategy. <19><20><21>
Importance to consider a portfolio as more than the simple collection of several project, as some projects may have interdependences <>, generally in the areas of limited resources consumption, risk balancing and strategy alignment.
Selection and prioritization
Main criteria <13> <14> <7> <4> <5> <10> - alignment with corporate strategy (corporate strategy must be reflected in the project composition of the portfolio and in the resource allocation to projects within the portfolio) - maximizing the value (financial, with metrics such as NPV or ROI, or broader, though weighted scored models for instance) - balancing, particularly balancing risk and return, long and short terms benefits, time to completion. PPM is the “bridge between strategy and operations” <15> <16>
Basic presentation of classical valuation methods, for single projects
NPV, DCF, classical NPV formulas, IRR (internal return rate), ROI, ECV (expected commercial value), EV (earned value)
Src:Book ROV a practitioner guide
Src: doc portfolio management –eve
But these models can underrate some projects, particularly the riskier ones, in dynamic and fast-changing environment <<b>>. Especially for R&D project portfolios, these methods might induce 2 main kinds of errors <<b>>: - Ignorance of the management flexibility, assumption of static cash flow. Does not take into account the possibility to interrupt a project to avoid more losses, for instance in case of technical failure (for instance tests failure, or other technical risks) or any economic risk, such as negative market variations. - Assumption that risk can only decrease the project value
Real Options for projects portfolios
Diagram, tomato garden – cf book et ref book The aim of the real options approach for project selection in PPO is to ensure that the right projects are selected, with the right scope and at the right time, whereas the ‘not right enough’ projects are kept in nurturing until having reached their full potential to become a candidate for the portfolio value and entering the portfolio pipeline (i.e. projects being in development) <17> (portfolio pipeline: http://walkoconsulting.com/walkopress/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/Pipeline.jpg)
Real Options Valuation, a simplified model
From finance to projects
| Input Variable | Financial option | Real option |
| S |
Underlying asset value |
Present value of the project expected incomes |
| X |
Exercise price |
Present value of the project investment costs |
| T |
Time to maturity |
Length of time in which the investment opportunity exists |
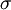
|
Volatility of returns on stock |
Volatility of project cash flows |
| r |
Riskless interest rate |
Riskless interest rate |
5 main kinds of real options <<b>> - Growth option, by adding new products or knowledge (R&D) to the portfolio or the project - Abandon option, which is the option to abandon at any stage of the project - Defer and wait, to reduce uncertainty - Contraction, meaning temporary or permanently suspending - Switch or transition option, for instance changing the product mix (output mix), or the resource mix (input mix)
Generally, the decision to put a research project in a portfolio can be considered as a growth option, which is equivalent to a financial call option <<b>>. The necessary input values can be selected as follows, based on the work of Merck mentioned in Enea, G. & Lo Nigro, G. (2011) <<b>>: - Underlying asset value: expected present value of the cash flows deriving from the commercialization of equivalent products - Exercise price: investment cost at the launch of the project (for instance facilities investment, patent exploitation licenses cost, start-up cost) - Time to expiration: expected completion time of the project - Volatility: for instance, standard deviation of the annual revenues for the concerned industry
This kind of option can be modeled in a closed form, with the Black & Scholes formula for instance <<b>>. As mentioned previously, it is important to consider a research portfolio, and more generally a projects portfolio, as a whole and not only as a collection of individual projects, as there may be interdependencies. Therefore, the modelling of a portfolio is more likely to be done through a compound option, whose value can be estimated with a Geske model. A stochastic optimization model called OptFolio has been developed by Roger & Al <22> and simplified by Enea, G. & Lo Nigro, G. (2011) <<b>> into a model called OptFolio Light, which is presented below. The OptFolio maximizes the overall Real Options Value (ROV) of the portfolio, aiming at identifying the most valuable projects among the whole R&D projects portfolio of a company. It therefore can be used to select the best candidates from a set of R&D projects, those to be injected into the portfolio pipeline. In the original OptFolio, each R&D project process is modeled as a sequence of continuation/abandon (“go/kill”), with these decisions being taken at the beginning of each development phase of the project. Therefore, this is equivalent to financial Bermuda options, which are potions that can only be exercised on predetermined dates. In order to reduce the complexity of the model in OptFolio Light, Enea, G. & Lo Nigro, G. modeled the R&D process as a growth option instead of abandon, or as a sequence of growth options, depending on the number of development phases in the project. The simplified model also assumes that if a project is interrupted at any phase, it is dismissed from the optimal portfolio.
OptFolio Light model
Sets and variables
- Product:
![i \in [\![1;P]\!]](/images/math/1/8/9/189c5abe5aacca80568436dc3df0aabf.png)
- Stage of project development:
![s \in [\![1;S]\!]](/images/math/c/8/5/c8501309e598537833e2c2e252383ae5.png)
- Date, within the maximum time horizon T:
![t \in [\![1;T]\!]](/images/math/5/2/e/52ed75ac7448452a9b90df582f538b31.png)
Parameters:
-
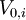 = current value of project
= current value of project 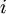 (at
(at 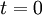 )
)
-
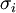 = estimated market volatility for project
= estimated market volatility for project 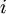
-
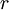 = risk-free interest rate
= risk-free interest rate
-
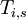 = length of stage
= length of stage 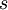 for project
for project 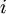
-
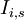 = investment cost of stage
= investment cost of stage 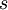 for project
for project 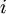
-
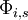 = probability of technical success of stage
= probability of technical success of stage 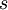 for project
for project 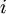
-
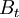 = budget constraint at date
= budget constraint at date 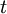 (for instance if the time scale is in year,
(for instance if the time scale is in year, 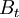 is the budget for year
is the budget for year 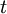 )
)
-
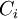 = real options value of project
= real options value of project 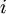
-
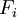 = annual cash flow brought by project
= annual cash flow brought by project 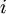
-
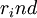 = rate of return in the concerned industry
= rate of return in the concerned industry
-
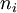 = expected duration of commercialization of the output of the project
= expected duration of commercialization of the output of the project 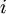
-
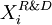 = percentage of cash flows of project
= percentage of cash flows of project 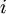 invested in R&D
invested in R&D
-
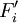 = amount of annual cash flow of project
= amount of annual cash flow of project 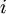 invested in R&D
invested in R&D
The real option value of project 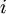 can be calculated accordingly to the number of development stages <<b>>:
can be calculated accordingly to the number of development stages <<b>>:
| Number of development stages | Corresponding formula | |
| 1 stage of development |
Simple investment decision, therefore: |
|
| 2 stages of development |
Black and Scholes formula: where:
| |
| 3 stages of development |
Traditional Geske formula (see <24>) | |
| 4 or more stages |
Extended Geske model, developed by Cassimon & Al (see <23>) |
The value of the uniform cashflow 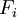 resulting from project
resulting from project 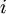 during
during 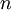 years is calculated with:
years is calculated with:
-
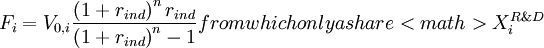 is reinvested in R&D, therefore:
is reinvested in R&D, therefore:
- Failed to parse (lexing error): F’_i = X_{i}^{R\&D} F_i
The decision variables are:
-
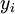 , binary variable which is equal to 1 if the project
, binary variable which is equal to 1 if the project 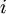 is selected in the portfolio, 0 otherwise;
is selected in the portfolio, 0 otherwise;
-
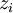 , binary variable which is equal to 1 if part of the cashflow of the project
, binary variable which is equal to 1 if part of the cashflow of the project 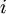 is reinvested in R&D, 0 otherwise; therefore we have a natural constraint
is reinvested in R&D, 0 otherwise; therefore we have a natural constraint 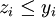 appearing, by definition of the variables.
appearing, by definition of the variables.
-
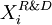 , a continous variable belonging [0;1] and representing the percentage of cash flows of project
, a continous variable belonging [0;1] and representing the percentage of cash flows of project 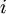 invested in R&D. Samely, by definition, we have
invested in R&D. Samely, by definition, we have 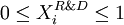
One more constraint is needed, the budget allocation one:
Finally, the complete OptFolio Light model formulation is:
-
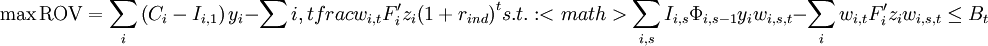
-
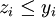
-
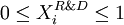
- Failed to parse (syntax error): y_i, z_i \in \left{0;1\right} ; X_{i}^{R\&D} \geq 0 Note on indexing: there is a lag between the decision and its effect, therefore decision in present time (<math> t=0
) will influence the first development stage (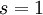 ), and identically for the following decisions and stages.
), and identically for the following decisions and stages.
Extensions
- Fuzzy models - Sensivity analysis (directly reference the two articles on sensivity analysis)
Vocabulary
opportunity cost real option
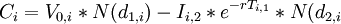
References
/references
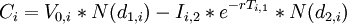
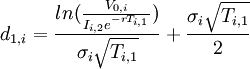
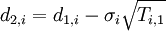
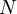 is the cumulative normal distribution function
is the cumulative normal distribution function