Work breakdown structure (WBS)
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
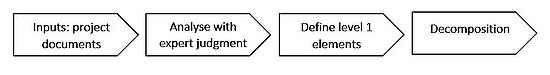
In this section follows a general overview of how to create WBS followed by a more detailed description of key elements. The process of creating WBS can in general be described as shown in Figure 1: [1] [4] | In this section follows a general overview of how to create WBS followed by a more detailed description of key elements. The process of creating WBS can in general be described as shown in Figure 1: [1] [4] | ||
| − | [[File:Figure1wbs.JPG|FIGURE TEXT]] | + | [[File:Figure1wbs.JPG|FIGURE TEXT|550px|middle]] |
Revision as of 21:30, 20 February 2021
Contents |
Abstract
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a method within project management aiming to structure and divide a project into smaller and more manageable components. This will make it easier to organise the work that has to be done in the project, and it will also make it easier to assess the time constrains of the project as well as the total costs. The process of creating WBS is performed once, at the beginning of the project, or at predefined points in the project, and the key benefit of the process is that it provides a framework of what has to be delivered [1]. This will support the project manager by creating an overview of the different steps and sub elements of the project, the work that has to be done, as well as providing an overview of the different resources, costs and time constrains involved in the project, ensuring better control with the project as a whole.
WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of the work that has to be done in the project carried out by the project team to make the required deliverables in order to accomplish the project objectives [1]. This is represented geographically in a hierarchical tree showing the different sub elements of the project work. In the context of the WBS, work refers to work products or deliverables that are the result of activity and not to the activity itself [1]. This means that the hierarchical decomposition of the scope of work represents the actual deliverables throughout the project, e.g., a product, service, or data, and not the activities that lays behind in order to reach these deliverables.
The concept of WBS – why and how to use it
WBS is a planning tool with the purpose of assisting project managers in creating a clear overview of the work within a project. This is done by sub-dividing a project into smaller and more manageable parts, in terms of the creating an overview of the different steps of work that has to be done in order to achieve the overall goal of the project. This provides a better control with the project as a whole, as sub-dividing the project into smaller parts also provides an overview of the different resources, costs and time constrains involved in the project. The Practice Standard for Work Breakdown Structures outlines some of the key benefits from performing WBS as [3]: • Better communication to project sponsors, stakeholders, and team members • More accurate estimation of tasks, risks, timelines, and costs • Increased confidence that 100% of the work is identified and included • A foundation for the control processes within the project.
This means that Work Breakdown Structures are a key component in project management within the planning of the project as it organizes the project’s scope by reflecting the work specified within the project. [3]
Definition of WBS
As with many other concepts in Project Management, there are more than one definition of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
The PMBOK Guide – 6th edition defines WBS as: ‘’The WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. The WBS organizes and defines the total scope of the project fines the total scope of the project and represents the work specified in the current approved project scope statement.’’[1]
PRINCE2 defines WBS as: ‘’A work breakdown structure is a hierarchical breakdown of the entire work that needs to be completed during a plan; in PRINCE2 a work breakdown structure contains only activities’’. [2]
The biggest difference in these two definitions, or approaches to WBS, is that in PRINCE2, a work breakdown structure contains only activities. This is different from the approach in the PMBOK Guide, where ‘’work’’ refers to work products or deliverables that are the result of activity and not to the activity itself [1]. Despite this difference of the definition of WBS, both uses of the terminology agree that project managers need to plan by breaking down the products or outputs of the project first and then break down the activities needed to produce the products [2]. This article mainly assess the approach to WBS as defined in the PMBOK guide.
Tools and techniques
In this section follows a general overview of how to create WBS followed by a more detailed description of key elements. The process of creating WBS can in general be described as shown in Figure 1: [1] [4]