Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
In 1940-50s Abraham Maslow developed the Hierarchy of Needs model and the Hierarchy of Needs theory that remains valid until today. It is used for better understanding human motivation, management training, and personal developments. The Five-levels model of human needs is based on the hierarchical levels within the pyramid and starting from the bottom of the hierarchy the needs are psychological, safety, love and belonging needs, esteem, and self-actualization. Maslow suggested that every person has an individual set of needs and that at the particular moment behavior is driven by the the existence of strongest need. [1]
Nowadays, Maslow’s ideas, surrounding the Hierarchy of Needs concerning the responsibility of employers to provide a workplace environment that encourages and enables employees to fulfill their unique potential (self-actualization), are more relevant than ever. The manager should strive to fulfill the need of subordinates to provide an efficient and well-working workplace. It is also important to ensure a free flow of communication so then employees devote maximal attention towards work.
The article gives an overview of general characteristics of what the Hierarchy of Needs is and what all the separate levels consist of. The next part is explaining the possibility of use Maslow's theory in project, program, and portfolio management but furthermore, it will be focused on project management. Also, it gives examples of improving workplace productivity and achieving the best possible productivity result within the working organization. In the end, the article will mention the criticism, as well as the limitations of Maslow's theory.
Contents |
The Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow was an American Psychologist born in 1908 in Brooklyn. He began his career at Brooklyn College where he became very popular among the students for his unusual combination of confidence in his subject and personal humility. After college, he became chairman of the Department of Psychology at Brandeis University and was also president of the American Psychological Association from 1967 to 1968. After World War II, Maslow begun to question the way psychologists had come to their conclusions, and although he did not completely disagree, he had his own ideas on how to understand the human mind. He called his new discipline humanistic psychology. [2]
Maslow conducted research and studies in many areas, but he is most remembered for his theory of Hierarchy of Needs and the concept of self-actualization. He was thinking in an original way. He urged people to acknowledge their basic needs before addressing higher needs and ultimately self-actualization. He viewed human potential as vastly underestimated and an unexplained territory. [3]
Maslow died on June 8, 1970, due to a heart attack at the age of 62 in Menlo Park, California. [2]
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a motivational theory in psychology compromising a five-tier model of human needs. According to Maslow, we attempt to satisfy stronger motives or needs lower down in the hierarchy before trying to satisfy motives that are higher up. Because the priority of fulfilling basic needs in the hierarchy is a continuing struggle, only a small number of people achieve self-actualization. [4] [5]
The five-stage model by Maslow can be divided into deficiency needs and growth needs. The first four levels are referred to as deficiency needs and the top level is known as growth or being need. The motivation to fulfill deficiency needs will become stronger the longer the duration they are denied. For example, the longer person goes without food, the more hungry they will become. Our activities become habitually directed towards meeting the next set of needs as soon as a deficit need has been acceptably satisfied.
The following part of the article is describing separate levels of the Hierarchy of Needs. The difference between the original and updated Hierarchy of Needs is mentioned as well.
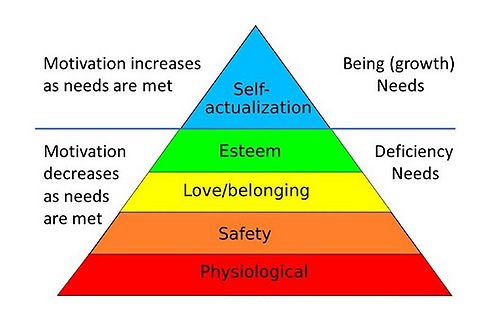
The physiological needs
These include the biological requirements for human survival such as air, food, drink, warmth, minerals to ensure homeostasis in their organisms (protection of the internal balance of the body). [6] The need for shelter and clothes, activity, rest and sleep, and avoidance of pain. One of the most basic needs is a need for physical survival. If the physiological needs are not satisfied the human body cannot function optimally. In Maslow's opinion, all of the other needs become secondary unless the basic ones are fulfilled.[7]
The safety and security needs
Most people want to have order and control in their lives. This need for safety and security contributes largely to behaviors at this level. An example of some of the basic security and safety needs are financial security, health, and wellness or safety against accidents and injury. Looking at it from the negative perspective you become concerned with fears and anxieties.
Together, the safety and physiological levels of the hierarchy make up what is often referred to as basic needs. [7]
The love and belonging needs
The third stage of the hierarchy is social and involves feelings of belongingness. Examples include friendship, intimacy, trust, acceptance, receiving and giving affection, and love. It is also a need to be part of the group – family, friends, work, etc. According to Maslow, except for a few pathological exceptions, all people have a need or desire for a stable and sound self-assessment, self-esteem, and other's respect. [6]
One thing that is also important to differentiate is that love is not synonymous with sex. Sex may be studied as a purely physiological need whereas love needs to involve both giving and receiving love. [7]
The esteem needs
This category Maslow classified into two categories. The first is the need to be appreciated and respected by others related to the reputation of a person, such as status, recognition, and appreciation. [8] The other one is the desire for reputation or respect from others as well as self-respect. [4] Maslow indicated that the need for respect or reputation is most important for children and adolescents and precedes real self-esteem or dignity.
The need for self-actualization
This level is the highest level of the pyramid of needs. It refers to the realization of a person's potential, self-fulfillment, seeking personal growth, and peak experiences. [4] A person should be whatever he or she can be. [7] Self-realization is an effort made by an individual to maximize his own capacity, to develop his skills, and to reach the ideal type of person he really wants to be. [6]
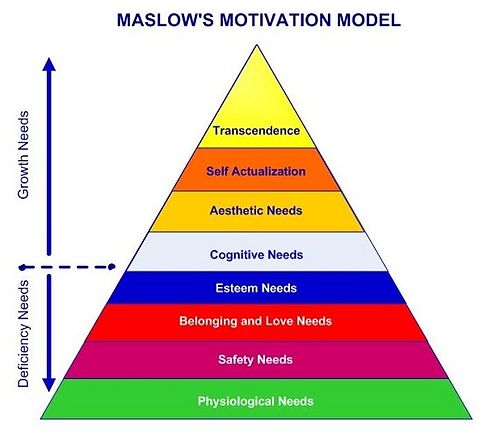
During the 1960s and 1970s, Maslow enriched his original theory with cognitive, aesthetic, and later transcendence needs. The first four levels that are also known as deficiency needs remained unchanged but the growth needs were divided into more levels. [4] Part of cognitive needs are knowledge and understanding, curiosity, exploration, need for meaning, and predictability [4] Aesthetic needs are considered as appreciation and search for beauty, balance, form, etc. [4] The last level of needs is transcendence need that forces a person to be motivated by values that transcend beyond the personal self e.g., mystical experiences and certain experiences with nature, aesthetic experiences, sexual experiences, service to others, the pursuit of science, religious faith, etc.) [4]
Application
Relation to project, program and portfolio management
Theory about Maslows Hierarchy of Needs can be widely applied in different fields of studies and environments. The main purpose and use will remain the same. Although, this article focuses mostly on applying the theory in project management.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs theory is used in management to motivate people in their working environment to make them perform more efficiently and effectively. This theory is considered to be highly effective and is adopted by numerous organizations.
The Leadership of organizations needs to design an environment that induces motivation. There are several ways of doing that as motivation through challenges, control, teamwork, competition, or appreciation.
To accelerate improvement and effectiveness, leaders often focus on prospects through management style, job design, organization events, compensation packages as part of the motivational practices. [9] Good leaders recognize that if they're to build productive and highly successful teams, they need to understand and look after the needs and well-being of team members.[10]
When the worker is employed he is concerned about his basic need of food, water, shelter, and clothes and wants a minimum level of rewards so that the above need is fulfilled.
The manager must enjoy a cordial relationship with employees and ensure the free flow of communication so that employees devote maximum attention to organizational work. By creating workgroups and extending facilities for social interaction so that esteem needs and self-actualization needs, which are intrinsic can be accomplished by workers.
Maslow has laid down that individual has a particular pattern and hierarch of needs, which may not be true. Often, managers instinctively are trying to achieve better motivation for team members using the raise of the salary. Even though the two first levels of the pyramid might be satisfied by increased cash, the rest of the needs will not. There are different types of people working in different environments.
The level of need satisfaction differs from person to person hence the theory cannot be always universally applied. Therefore leaders should realize that they can use a whole range of tools that can be used to built team satisfaction. [10]
The ability to identify your needs and make sure that those needs are fulfilled positively can help to increase the chances of success. When you feel safe, supported, a sense of belonging, and self-actualized, your attitude may also influence those around you in the workplace. Engagement and motivation are often team-based attitudes, so a team of individuals who feel their needs are being met can create a more positive, engaging culture within the workplace. [11]
Needs in the workplace
This paragraph is giving examples of needs from different levels of the pyramid. It can help the project manager to realize the needs of his employees and be able to make the workplace much more productive and efficient.
Psychological needs
- acceptable pay and working conditions
- knowledge about salaries
- the purpose of the project as the whole
- desired outcomes of the project
These easy steps help workers to feel like their basic need has met, they have money, they have a purpose, and know an endpoint (outcome).
For example, if the company does not offer formal meals for all its employees, the leaders can consider placing some fruits, snacks, coffee, etc. in the pantry. Those actions do not require high costs but will provide an environment where employees can feel more attached to the company. [12]
Safety needs
- job security
- clear working role and its description
- health, safety, insurance protection
- realistic expectations from the beginning of work
To satisfy this level, leaders have to ensure employees are working in a safe environment. For example, the office facilities must comply with the property safety legislation. There has been increasing support for working mums with new-born babies in the workplace, in which breastfeeding areas or restrooms for female staff are provided. This helps to give strong support to them as that can also increase their motivation to work.
Social needs
- working in a team
- social facilities, mentoring, coaching
- preferably personal meetings instead of online
These needs should be the ones that everybody can achieve and they must be part of any good project management experience.
Esteem needs
- having a purpose
- recognize contributions to the project
- recognition of achievements
Self-actualization needs
- promotion opportunities, possibilities to grow
- challenging work and job enrichment
As an employee, it is important to assess whether your needs are being met in your current position, they are important and valuable.
Maslow's hierarchy has been seen as highly useful in offering a motivational framework that will get the Generation-Y workers to perform enthusiastically and deliver their best efforts.[12]
Roles and responsibilities of project manager
A Project Manager is a person who is responsible for successfully overseeing a project from start to finish. His responsibilities can range from planning the project, creating a proper timeline, managing the budget to troubleshooting, and being responsible for employee’s wellbeing. He is responsible for leading the team and communicating among workers. [13] He needs to understand the importance of team motivation and the impact it has on project results. [14]
Motivation is a cardinal and a complicated function that managers must perform in organizations for their survival and success.
Daft R.L and Marcic. D (2001:410) defines motivation as the internal and external forces that arouse enthusiasm, desire, purpose, and persistence to pursue a certain course of action. and Mullins L.J (2005:479) also describes motivation as 'the direction and persistence of action. It is concerned with why people choose a particular course of action in preference to others, and why they continue with a chosen action, often over a long period, and in the face of difficulties and problems.[15]
Motivation in employees can be categorized into intrinsic (internal to employees) or extrinsic (external to the employees). Extrinsic motivation is related to tangible rewards such as salary and benefits, security, promotion, work environment, or conditions of work. These rewards are often being determined at the organizational level and often are largely outside of the control of the individual manager. Intrinsic motivation is related to psychological rewards such as a sense of challenge and achievement, receiving appreciation and positive recognition, being treated in a good manner. Those rewards can usually be determined by the action and behaviors of individual managers. [16]
It is important for Project Managers to develop the Project Team. This involves building a team identity and, essentially satisfying those belonging and love needs. If everyone will be happy to be part of the team, then many social needs will be met. [17]
The Maslow Theory of Motivation is a great tool for Project Managers, that can help to keep the team motivated as well as set correct motivational issues.
Limitations and inadequacies
Along with a huge number of supportive views and studies on the hierarchy of needs, the theory has been criticized as well. Looking at the Maslows pyramid of needs from an intuitive perspective, there seems to be a great amount of sense. Although there is only very little evidence to fully support its hierarchical phase [15] and while applying in real life, the theory has its limitation.
Maslow's theory is widely popular both in and out of psychology. Not only fields of business but also education has been particularly influenced by the theory. While popular, Maslow's concept has not been without criticism. Maslow has been criticized for laying down needs in a particular order. Needs don’t follow a hierarchy – Some of the researchers have not been able to substantiate the idea of a needs hierarchy. There are craftsmen, poets, sculptures, painters who have devoted their entire life towards the fulfillment of self-actualization need without having satisfied physical, safety or even social needs. The level of need satisfaction differs from person to person hence the theory cannot be universally applied.
In general, the theory is difficult to test, and especially Maslow's definition of self-actualization is difficult to test scientifically. His research was also based on a very limited sample of individuals, including people he knew as well as biographies of famous individuals that Maslow believed to be self-actualized. [6]
For example, a worker who is a sole income earner for the whole family may feel job security as his most dominant need. Therefore it is possible to deduce that we may not find the needs in the given order and that the strength of a particular need is situation-based The model does not consider the probability of cultural differences and assumes that the same needs apply equally to all human cultures.
Research example on the order of the Hierarchy of Needs
The study was based on the research on the basis of 18 different occupations and to determine the needs of employees in different occupational groups according to the Hierarchy Of Needs Theory, and to compare the needs of employees in different occupational groups to determine and interpret the differences between them if any. This study was carried out on 519 employees from 18 different work occupations. The non-probability criterion sampling method was used and the data obtained were subjected to the reliability and frequency analyses with the SPSS program. As a result of the analyses, 16 of the 18 groups had a different order of needs than that was argued by Maslow in the Hierarchy of Needs. Two of the groups such as bank employees and factor workers were accordant with the original theory.
One of the things that have been determined in the modern workforce, is that the esteem need predominates, and this need comes before the need for safety and social needs. This change can be considered as an effect of increased socialization due to the internet and technological developments in the 21st century. Maslow’s theory from 20 century has been tested with the data obtained from 21 St century workers. The study showed that the idea of the strict order of needs as Maslow had stated, is not valid in our days. Significant differences were found in the orders of needs compared to the theory when the employees were evaluated on a professional basis. [6]
Advantages of the theory
- The theory can be adopted and implemented in an uncomplimented manner and it has a natural appeal
- It has perceptive insight into human nature
- It has relevance in modern-day applications and assists to interpret human behavior and motivation, specifically in the world of business
- It provides an advantageous summary of human needs, which can also be used in product planning, product positioning, product pricing, and also sales channels designs
Disadvantages of the theory
- This method can not be measured empirically, there is no proper method to measure accurately how satisfied a person needs to be to proceed to the next level
- Maslow considered only a narrow segment of the human population
- Some levels, such as self-esteem and security have broadly diverse classifications in cultures around the world
- It brings difficulties for researchers to measure these needs or to generalize them across all human populations
Conclusion
This theory has a huge place in the literature and is a great tool that should be applied by all organizational managers. However, it is important to test, renew and develop the theories designed for humans, whose nature is to change. As the assumption that the order of needs cannot change can be considered the weakest point. It is important to understand the atmosphere of the working organization, take into consideration what is the profession of the employees, and just then apply the tool.
Organizational managers should be very familiar with the characteristics and requirements of the professional group they are in charge of, and instead of applying direct motivation factors, they should analyze the employees, measure their levels of need and develop the necessary strategies accordingly. [6]
Annotated bibliography
- A.H. Maslow, A theory of human Motivation
This book is one of the most popular and famous Maslows publications. It was originally published in the Psychological review in 1943. It gives a detailed description of the hierarchy of needs from a psychological point of view. Part of the book focuses on a very detailed description of the basic needs and how they can be fulfilled.
- A.H. Maslow (1970a), Motivation and personality, New York: Harper & Row
Another publication about understanding the Theory of Needs. In this book, he focuses on explaining how the lack of a safe, nurturing environment not created by parents, will develop in children deep feelings of insecurity.
- A.H. Maslow, Maslow on Management, originally Eupsychian Management: A Journal
In this publication, Maslow argues that eupsychian (the word that he coined and it means moving towards psychological health or self-actualization) management is the ideal model for industrial organizations. Also, he explained how the commitment to work in self-actualizing people's lives and that these most highly evolved persons would assimilate work as part of their personal identity.
- Hierarchy of needs in 21 century: the examination of vocational differences. (Researches on science and art in 21st-century Turkey) Chapter 23. H. Tezkan Uysal, Sibel Aydemir, Emine Genc
This document gives a great overview of Maslow's Theory of Needs as well as gives examples of how the theory can be applied in management. In the end, it provides an interesting example of the research that has been made to better understand each level of the hierarchy and how does it change in regard to different work occupations.
It is available at this website: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321267309_MASLOW'S_HIERARCHY_OF_NEEDS_IN_21ST_CENTURY_THE_EXAMINATION_OF_VOCATIONAL_DIFFERENCES
References
- ↑ https://www.examrace.com/Study-Material/Management/Organizational-Behavior/Organizational-Behavior-Maslow-Theory.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abraham_Maslow
- ↑ Abraham Maslow with Deborah C. Stephens and Gary Heil, Maslow on management
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 https://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html#references
- ↑ https://www.examrace.com/Study-Material/Management/Organizational-Behavior/Organizational-Behavior-Maslow-Theory.html
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Hierarchy of needs in 21 century: the examination of vocational differences. Researches on science and art in 21st-century turkey. Chapter 23. H. Tezkan Uysal, Sibel Aydemir, Emine Genc
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 A theory of human Motivation, A.H. Maslow
- ↑ Motivation and Personality, A.H. Maslow, New York: Harper, 1954
- ↑ https://www.mbahelp24.com/impacts-implication-hierarchy-needs-theory-hr-management/
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newldr_92.htm
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/maslows-hierarchy-of-needs
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Improving workplace productivity: Application of Maslow's Need Theory and Locke's Goal-Setting, Psychology and Psychological Research International Journal
- ↑ https://www.wrike.com/project-management-guide/faq/what-are-the-roles-and-responsibilities-of-a-project-manager-to-be-successful-in-the-job/
- ↑ https://www.project-management-skills.com/maslow-theory-of-motivation.html
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Comparing and contrasting Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Herzberg’s Two Factor (Hygiene and Motivation) Theories, Ilukor Geresom, School of Hygiene-Mbale
- ↑ https://blog.o2employmentservices.com/intrinsic-vs-extrinsic-motivation-employees
- ↑ https://www.velopi.com/insights-and-resources/post/pmi-pmp-free-project-management-resource-hierarchical/