Sustainability Issue
Developed by Oriol Solans Ormo
In order to find the solution to a problem, first of all it is needed to accept the problem as true and relevant. Although in previous years the problem of ecological impact was not known, not only the damage to the atmosphere, but also the consequences on society, nowadays, the increase of sustainability in companies’ strategy and goals provide a promising future. In this frame of reference, companies have a key role to play due to their great influence in society thanks to their campaigns based on the idea of satisfying the needs of the customer by means of the product and the whole cluster of things associated with creating, delivering and finally consuming it.
Taking into consideration sustainability requirements, it is needed a change in the field of project management from the perspective of time, budget, and quality to social, environmental, and economic [1]. The change in the paradigm of project management is one of the essentials aspects for which sustainability plays a relevant role. This change is based on moving from predictability and controllability to an environment based on flexibility, opportunity, and complexity. Considering sustainability, it requires a change of mentality from the part of the project manager, for instance, it is not only necessary to provide the expected results but also to assume the responsibility for the long-term growth of organizations and society [2]. In order to find the balance between economic knowledge, social well-being and the rational use of natural resources, sustainable development is necessary and companies are incorporating it into their respective spheres of influence. Sustainability gives to the organization a huge competitive advantage, an improvement in relations with its stakeholders to the organization and contributes to support declining resources.
Contents |
Sustainability
Concept
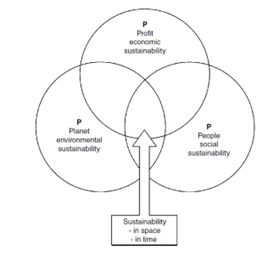
Although sustainability has not sometimes been defined clearly enough among companies, during the recent years many firms have tried to become environmentally friendly. Sustainability has been adopted by many organizations through their mission and their strategy. However, the social and environmental dimensions of sustainability are difficult to incorporate into programs and projects to execute the organization's strategy. Then, it is not enough producing without emitting polluting emissions, it is very necessary that the whole system is reviewed and redesigned to fulfil with the customer requirements and the organization needs in a sustainable manner [6]. In this frame of reference, Elkington developed the concept of Triple Bottom Line which proposed that business goals were inseparable from the societies and environments within which they operate.
This concept englobes the economic, environmental and social goals which are aligned and make an impact on the decision and the actions taken by the organizations. Furthermore, this innovative concept is present in the UN World Business Council for Economic Development (WBSCD) [7]. A group of 150 international companies put into practice the principles of TBL in their business and strategy. Thanks to the application of this concept, they make it possible to address global challenges such as poverty, gender inequality and the depletion of resources. In the WBSCD it is also recommended that, in order to have a greater impact on society, companies become aware of the global challenge that is presented to them and apply the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), not only to go forward in the sustainable impact, but also in improving their business opportunities.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDG)

The 17 Sustainable Development Goals represent the world community's next step for a paradigm shift in understanding sustainability and fighting inequality and tackling climate change in the next 15 years. In the frame of reference in which we find ourselves, the SDGs ask companies to contribute to solve the challenges of sustainable development within a common framework. It should be noted that each SDG offers an opportunity for companies to increase their impact and strengthen their strategy. The implementation of SDG in a company's strategy leads to the opening not only of new and future business opportunities, but also the ability to stabilize markets and society. In addition, the more organizations that use the tool, the collaboration between them will improve as they will use a common language, they will be able to strengthen their relationships with their stakeholders and they will be able to improve the concept of corporate sustainability. Within these objectives, SDG 5 (Gender equality), SDG 8 (Decent work and Economic growth) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) should be highlighted.
Implementation of Sustainability
The objective of the implementation of sustainability in an organization is to improve the success, the resilience capacity of the company in the long term and to acquire new values. Organizational culture is a result of a complex group learning process and it has been defined as “a pattern of shared basic assumptions that the group learned as it solved its problems of external adaptation and internal integration” [9]. However, the culture can only be applied when communication and interaction between individuals evolve.
If it is finally possible to apply this culture, and when it does so robustly, the organization begins to be more effective [9]. It is for this reason that it requires the internal involvement of all individuals to act in accordance with the principles of sustainability. Organizational culture is very important and in fact many studies have shown that failure in change processes can be attributed to the neglect of organizational culture [10].
In order to be successfully implemented, it is necessary that all employees are aware of sustainability values and are prepared to apply them. The best way to successfully achieve this goal lies in the fact that employees must be trained and prepared. Although this transformation is often complicated, it is important to be able to gather knowledge through communication in order to change norms and values related to the environment and socio-economic well-being. Organizations must consider a transformation to chart their path including the inclusive values of sustainability.
Project Management
Overview
Project management can be described as the application of knowledge, a set of processes, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities in order to meet project requirements. It refers to guiding the project work to deliver the intended outcomes specified by the company and within the accepted parameters set by the project [11]. One of the main characteristics of a Project Management is based on the final delivery since it is necessary to come to an end. However, if we talk only about management, it should be noted that it is a continuous process where the objectives are regularly changed and improved. Furthermore, it should be mentioned that a project is carried out to achieve defined and planned objectives, which can be quantified in the form of results or benefits for the organization. If the predefined objectives are accomplished, the project is considered a success according to the agreed criteria and within a specific time frame. The basic elements of each project are the following:
• Time : organization and planning of the schedules in which the work will be carried out in order to fulfil the project's objectives.
• Cost : know the necessary economic amount that is requested to execute the project.
• Quality : assess the level of the objectives achieved and the initial purpose for the development of the project.
The objective of Project Management is to obtain a final product or service that brings a benefit to the organization and that meets the requirements initially marked when the project was defined [12]. When it comes to getting the final result, you need to take into account the control and planning of the tasks necessary to carry it out. Those companies that decide to perform their work with project management lead to guarantee an efficient use of resources, satisfy the needs of the project's stakeholders and enable the desired result of the project to be more successfully achieved.
Stakeholder analysis
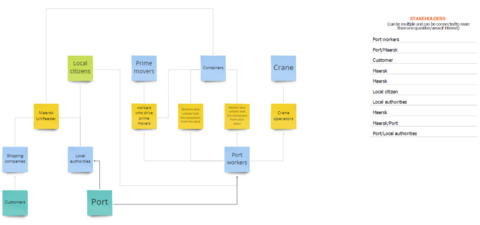
When talking about project management, the idea of who is involved in each of the project's scenarios takes an important relevance. The concept of stakeholder analysis can be described as a method of systematically gathering and analysing quantitative and qualitative information to determine whose interests might be taken into account throughout the project [11]. Projects are performed by people and for people. Each aspect of the project and its management requires the contribution of different stakeholders, who, provide the knowledge and resources to reach the project's objectives. The importance of stakeholders lies in involving all of them in the project [13]. Stakeholder engagement includes the definition of strategies to promote the participation of the different stakeholders. This participation entails working in close collaboration with stakeholders to obtain the required objectives, solve problems, make decisions during the execution of the project and manage the expectations created. Skills such as conflict management, working group leadership and critical thinking are key when it comes to carrying out a project by stakeholders and keeping them involved in the project. If the organization succeeds, it will bring a benefit not only to the company, but also to the stakeholders themselves who are part of the project and have the goal of reaching a successful result. Knowing the relationships between the stakeholders themselves is one of the most important parts in the analysis of the project by an organization, as in this way it allows building new business relationships, enables the organization to develop better in the social and corporate sphere and increases the probability of the project's success by turning stakeholders into protagonists and beneficiaries.
When developing project management, different techniques can be used in order to detect the stakeholders involved in the project and necessary for the organization. In this way, through a Stakeholder Mapping Exercise, it allows those in charge of the project to know who they will be dealing with and how the relationships between the different stakeholders will develop. In addition, for each of the different stakeholders detected, a more in-depth analysis can be carried out using the SWOT analysis.
Project Manager
In this frame of reference, with the goal that projects must executed and completed, project managers need to be actively involved in the organization's project. It is necessary not only to start the project marked by the company, but also to contribute with their experience in project management [14].
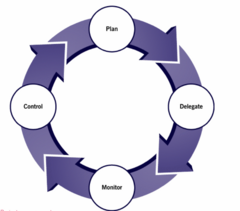
In order to achieve control over something, there must be a plan. It is the project manager who is responsible for planning the sequence of activities to build and execute the project [15]. The ability to delegate activities related to the execution of the project is part of the skills that a project manager must acquire. This skill is important in any form of management but particularly so in project management because it involves the concept of cross-functionality and risks. Project managers generally use Key Performance Indicators (KPI) to monitor progress. Using these measurable values, the objectives of the project can be assessed how effectively they are being carried out. When identifying the areas that need improvement and facilitating the project manager's tasks is when KPIs take on outstanding relevance. The application to the projects of these values is vital to ensure a continued success, to determine the objectives and the path that the project in question must follow. The ability to be able to use your skills when carrying out the various tasks of project management leads to a higher probability of achieving success. Some of these key skills that every project manager must have been:
• Group Leadership : they must be able to communicate and lead their teams and stakeholders effectively and quickly.
• Resolvable : faced with the appearance of different unexpected problems, they must have the ability to solve them clearly and concisely.
• Time Organization : they must have the ability to manage the time spent and know how to delegate tasks correctly to the different members of the project.
Methodology
Despite the importance of sustainability, it is still evident today the lack of applications in a company where this subject can be implemented in project management. The objective of this section is to develop a framework that allows and helps an organization working on different projects to include sustainability as one of the main pillars. The demands of the stakeholders often mark the business strategy and the objectives that must be achieved by the different projects in the short term. However, the inclusion of sustainability when designing and implementing a project can give a big competitive advantage to the company in the long-term projects and will have a positive impact on project performance.
From the perspective of the project, the process to carry out a Project Management and its areas of knowledge must be related to sustainability [16]. It has recently been shown from a panel of experts that sustainability has a positive impact on project performance [16]. This combination when carrying out a project in an organization, leads to a more sustainable project management and positively influences the success of the project. The influence of this management can directly affect sustainable issues, for instance, safety, health, resources used, maintenance and strategic leadership [17]. Because of the positive impact observed in projects when sustainability is included, in order to carry out a successful project it is necessary for the organization to follow certain steps in order to include sustainability.
Next, a methodology is presented to be able to help a company include sustainability in its projects it is working on and in its strategy. This methodology consists of 5 steps: 1) stakeholder analysis, 2) define a strategy map, 3) perform a sustainability analysis, 4) redefine the project and 5) global optimization of projects [6].
• Stakeholder analysis : This first step is based on the analysis of the interested parts including their identification, their interests, categorizing them and investigating their relations between the interested parts. The company should be able to understand the relationships between the different stakeholders involved in the project in order to be able to draw up a Strategic Map.
• Define strategy map : After having carried out the analysis on previous research, when defining the strategy, it is proposed to use the Triple Bottom Line perspective. This perspective, as previously mentioned, includes social, environmental, and economic objectives. The development of this Strategic Map depends on the needs of the organization, that is to say, in order to achieve the defined objectives of the project, it is necessary to study the economic, social and environmental needs where the organization's project will be developed [6].
• Perform sustainability analysis : In this section the main objective is to provide an analysis and a combined assessment of the environment and social relations proposed in the project. On the one hand, the analysis of the different stakeholders involved in the project provide information to indicate the reasons for carrying out the study. On the other hand, the analysis of social and environmental aspects is grouped in the life cycle impact assessment (LCA) and involves the collection of data and procedures to be able to quantify the information of environmental issues associated with the organization's project.
• Redefine the project : In this fourth step of the methodology, it is where the project can be reoriented or redefined. After having analysed the different stakeholders, created the strategy map, and performed the sustainability analysis, it is often necessary to go back to the first stage of the process and discuss which the new objectives for the project of the organisation are. It should be noted that this step may not have to be carried out if those directly and indirectly involved in the project, often the stakeholders analysed, do not consider it appropriate to redefine the project again and, therefore, have to dedicate more time to look for new objectives and establish new relationships between the different stakeholders of the project in question.
• Global optimization of projects : In order to implement strategies, organizations define some alternative projects. Each project contributes to the achievement of different objectives, and some projects may contribute better than others [6]. Each project has costs at the time of its implementation and other costs regarding the environmental and social impact it represents. For this reason, it is necessary to optimize the project by simultaneously evaluating the economic, environmental, and social impacts described in the strategic map. In addition, in this step it is necessary to include issues of sustainability, as optimizing a project also means evaluating the environmental and social problems that can have a long-term impact for the organization.
To illustrate the application methodology, we can consider the following example adapted from an information technology company, Alas Ingenieria [6]. This company provides advanced engineering solutions for executing works, managing information for industrial plants, and offers development and implementation services. Alas Ingenieria recognizes sustainability as an opportunity to conduct its operations more efficiently and with greater robustness.
The first step in the methodology is to conduct a stakeholder analysis, which helps the company identify relevant stakeholders and their respective objectives. This measure enables the company to anticipate significant cost reductions resulting from the efficient use of energy and water. Next, the company performed a general analysis of the economic, social, and environmental areas, taking into account the results of the stakeholder analysis, in order to create a strategy map. The sustainability analysis, as an example, helps to choose the significant impact categories for the work study, such as energy consumption and economic costs. Finally, in the last stages of the methodology, the output data of the project is analysed, and if necessary, changes are made in the previous stages to optimize the company's project. This approach enables the company to achieve its sustainability objectives while simultaneously delivering successful projects.
Benefits
Although the application of the sustainable issue into project management may involve a series of risks at the beginning and meet with the resistance of stakeholders and employees to the change, it entails a series of obvious benefits for the corporation. One of these main benefits is the improvement of the company's reputation in the market and in front of its customers since it allows to demonstrate the commitment to environmental responsibility and the implementation of internal initiatives to change the habits of employees. One of the other prominent benefits is the level of innovation that the company acquires. Facilitating sustainability initiatives allows innovation to be fostered in order to develop new projects and acquire new outputs within the parameters set by the project. In addition, including sustainability in the activities and departments of a company allows to reduce the risk of obtaining the product or service that brings a benefit to the organization and that meets the requirements initially marked when the project is defined.
Limitations
Companies and organizations often face different barriers to implement sustainability in their projects and in their strategy [18]. In order to implement it correctly, it is necessary to change a whole series of processes, internal policies and the direct and transparent involvement of all the people in charge of carrying out the project.
Below are some of the mistakes that lead to limitations for the company and sometimes they do not recognize to overcome:
• There is no clear vision of sustainability
• Lack of information
• Not institutionalizing sustainability
• Reaction of customers and interest groups, if the information disseminated is not correct, or does not contain regulations
• Bad leadership can lead to failure for the company
• Lack of interest from internal and external stakeholders, including lack of support
Annotated Bibliography
Brief explanation of some of the references used in the Wiki-article
- ANALIA SANCHEZ, M., 2015. Integrating sustainability issues into project management. Journal of cleaner production, vol. 96, pp. 319-330. ISSN 0959-6526. DOI 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.087 [6]
- The article presents a framework with the objective to help ensure that an organization is working on the right projects and in the right path in order to attain its business strategy and stakeholder demands. The proposal of this study addresses both the project selection problem and the portfolio tracking phase.
- https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdgs [8]
- The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is a common action to achieve before 2030. This Reference explains the 17 goals and 169 targets, integrated and indivisible, aiming to achieve the universal issues and solve them,as poverty, equality in human rights, in health, education, gender equality. Most of those problems can be solved by a common force and a Global Partnership, facilitating the implementation of the Goals and targets.
- AALTONEN, K. y KUJALA, J., 2010. A project lifecycle perspective on stakeholder influence strategies in global projects. Scandinavian journal of management, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 381-397. ISSN 0956-5221. DOI 10.1016/j.scaman.2010.09.001 [13]
- The paper shows the context for stakeholders and stakeholder behavior related to the project moves through different phases during its lifecycle. It presents a set of propositions that increase the understanding of the potential of stakeholders to influence the project management's decision making during the different phases of the project lifecycle.
- CARVALHO, M.M. y RABECHINI, R., 2017. Can project sustainability management impact project success? An empirical study applying a contingent approach. International journal of project management, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1120-1132. ISSN 0263-7863. DOI 10.1016/j.ijproman.2017.02.018 [16]
- The study aims to propose and to validate a research model on project sustainability management. In addition, it investigates the relation between project sustainability and project success.
References
- ↑ BANADUC, G., MIREA, N. y DRAGHICI, A., 2022. Points of intersection between sustainability and project management. MATEC Web of Conferences, vol. 373, pp. 78-. ISSN 2261-236X. DOI 10.1051/matecconf/202237300078
- ↑ UKAGA, O., 2014. Gilbert Silvius, Ron Schipper, Julia Planko, Jasper van den Brink and Adri Kohler: Sustainability in project management: Grower Publishing Limited, Surrey, England, 2012, ISBN 978-1-4094-3169-5. 2014. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
- ↑ Talbot, J., & Venkataraman, R. (2011). Integration Of Sustainability Principles Into Project Baselines Using A Comprehensive Indicator Set. The international Business & Economics Research Journal , 10 (9), 29.
- ↑ Lecture 1: 42402 – Sustainable Operations and Supply Chain Management. Sustainability and the role of Operations and Supply Chain Management
- ↑ Brundtland, G.B. (1987): Our common future: World Commission on Environment and Development, Oxford University press; p.54.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 ANALIA SANCHEZ, M., 2015. Integrating sustainability issues into project management. Journal of cleaner production, vol. 96, pp. 319-330. ISSN 0959-6526. DOI 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.087
- ↑ https://www.wbcsd.org/
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdgs
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Schein, E. H. (2006). Organizational Culture and Leadership. John Wiley & Sons.
- ↑ Cameron, K. S., & Quinn, R. E. (2011). Diagnosing and changing organizational culture: Based on the competing values framework. John Wiley & Sons..
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2021). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK ® Guide) – 7th Edition and The Standard for Project Management - 1.4 Relationship to PMIStandards+. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI).
- ↑ Lecture 1: 42433: Advanced Project, Program and Portfolio Management.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 AALTONEN, K. y KUJALA, J., 2010. A project lifecycle perspective on stakeholder influence strategies in global projects. Scandinavian journal of management, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 381-397. ISSN 0956-5221. DOI 10.1016/j.scaman.2010.09.001.
- ↑ CUEVAS, R., TORRES-LIMA, P.A. y BODEA, C.-N., 2021. Research on project, programme and portfolio management : integrating sustainability into project management. 1st ed. 2021. Cham, Switzerland: Springer. ISBN 3-030-60139-0
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 AXELOS. Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, The Stationery Office Ltd, 2017. ProQuest Ebook Central, https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/dtudk/detail.action?docID=4863041.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 CARVALHO, M.M. y RABECHINI, R., 2017. Can project sustainability management impact project success? An empirical study applying a contingent approach. International journal of project management, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1120-1132. ISSN 0263-7863. DOI 10.1016/j.ijproman.2017.02.018.
- ↑ Pulaski, M.H., Horman, M.J., 2005. Continuous value enhancement process. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. ASCE 131 (12), 1274–1282.
- ↑ HALLDÓRSDÓTTIR, E. (2014). Limitations of Sustainability Implementation amongst Project Managers. Master of Science Thesis in the Master’s Programme International Project Management, CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, Göteborg, Sweden 2014