The Work breakdown structure(WBS)
Contents |
Introduction
According to ISO 21500 a project is defined as “ a unique set of processes consisting of coordinated and controlled activities with start and finish dates, undertaken to achieve an objective”. However a project can consist of various variety of different things and become very complex. To be able to simplify the complexity of a project it is important to have a clear scope of what the project is about and what it consists of. The complexity of a project can for example be governed by involvement of different parties or stakeholders, time estimations and cost. The best way of an organized work and smoothly managed project is to break the work down into smaller segments of the bigger pictures. The work breakdown structure model is often used for that [1] .
A well defined project has a clear scope. Breaking the scope down into smaller segments can make a large project more manageable and easier to work with, this is the separating phase. When the separation has been done it is important that each separated segment is integrated so it can work. Even with well organized project, it can change throughout the timeline and it is important to adapt to any evolvement or changes.
Various approaches to project management concepts
In this report the focus is set on the work breakdown structure.
However there are many tools and concepts today that are used and practiced in the field of project management. Here are just few mentioned to give an insight of some useful tools.
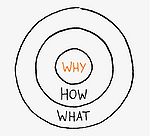
Golden Circle
Golden circle in project management is a concept or a tool where the importance of realizing why to undertake a project or why, doing it in the first place[2]. Simon Sinek gave a TED talk in 2009 which was a huge success, it became the third most popular TED talk of all time [3]. Simone Sinek spoke about what all great leaders and organizations have in common, which is a deep understanding of why they are doing what they are doing. The Golden circle is a circular diagram where fundamental questions are asked, where the most important question “ WHY “ is in the inner diagrams and the questions HOW and WHAT in the outer. Simon developed the tool to help with the realization that there needs to be a clear vision of WHY to undertake a project, otherwise, a well planned project is just a project that has adds no difference or influence to a organizations or the customer. The order in which things need to happen in a project is Vision – Strategy – Tactics, and the golden circle can be used for that [3].
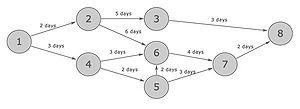
PERT
Program Evaluation Review Technique ( PERT ) is a project management tool, that gives a graphical view of a project´s timeline. PERT is designed in a way to break down individual task in a project for analyzing . It can be used where a large complex project is broken down and each part is used to estimate the time and cost. Mainly it can help a project manager to visualize the tasks that need to be worked on within the scope of a project´s lifetime [5].
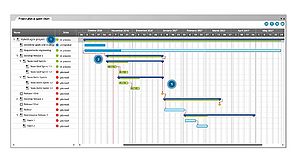
Gantt Chart
Gantt chart is a graph which is structured with two axis, that is the horizontal and vertical axis, where it visually shows the task undertaken over time. It is a helpful tool to show an individual task that needs to be accomplished within a specific date as well of keeping track of the entire project timeline. The vertical axis shows the task that need to be completed, while the horizontal axis is the time[7].
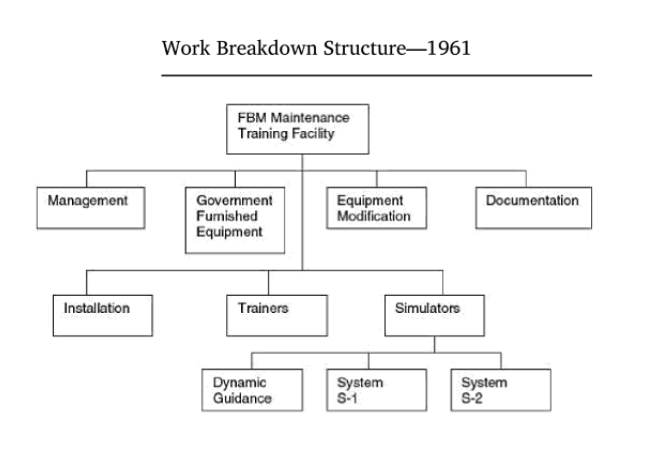
The origin of the WBS
It is hard to imagine that large and complex projects can be conducted with out well organize scope that has been broken down into smaller segments( pices, components). However in 1959 there was a paper published that described a new technique called PERT or “ Program Evaluation and Review Technique”[9]. This new technique was developed for the Program Evaluation Branch of the Special Project Office of the US. Navy. The reason for the development of this technique was because the Special office was concerned about certain plans such as missile guiding systems, weapons and ships[10]. Even though this technique was not specifically described as the WBS it had similar structure and theory as we know the WBS today. It was not until 1961 where the term work breakdown structure became the known term for the model [9]. The department of Defense ( DOD) in cooperation with NASA and aerospace industry created and published a document that had much more detailed use and description which describes the WBS. The model was used much in the coming years primarily for government or military usage. In 1987 WBS was first used by the Project management institute in a non governmental or millatery way and started to be used in businesses and other organizations around 1993. [11].
Concept
Overview
Work breakdown structure is a model that was developed to breakdown the work of a project into smaller pieces to have a more specific and detail scope that is well defined. WBS is often mistaken for the tasks that needs to be done, but that statement is incorrect. It is what is needed to be delivered. The model was specifically designed to assist people that are connected to a project, in a way that the outcome of a project is more visible and clearer. The WBS can be very affective tool and if made right the framework should consist of the entire deliverables of a project [12]. The model itself is structured in a way where the upper part is usually the major deliverables work segment of a project. By dividing the project in the major phases, the project manager can benefit tremendously, it can help him organize and create a specific team that suits each major factor as well as having better overview of the teams and progress. Creating a team can be difficult and can be a key factor in achieving set goals. The lower part of the model usually consists of more detailed parts of each major phase. That is the scope becomes more visible and planning can start in more effective way such as creating timelines and making cost estimation. The top and bottom parts of the WBS are smaller segments of the entire project that combine and work together and create the final outcome of the project.
Who can use the WBS
As stated above in the overview chapter, the U.S Department of Defense used and still uses the WBS. The projects can be of an enormous size and huge complexity as well as smaller sized project. Even though the model is used in complex projects such as the navy or NASA have, the WBS can be used for smaller ones as well. The model is not structured for any specific projects on the contrary, it is designed to function as a tool for projects of any variety. It can for example help construction projects, such as building a house, or software developers designing new software or even a person who has a project connected to themselves in their personal life[1]. The structure and concept of WBS is usually the same despite different industries or projects, the only difference are the deliverables and how they are proceeded. WBS can be effective and efficient, therefore some organizations have standards and pre-made WBS for usage for their employees to save the time in the beginning phases of the creation of the model. The main goal for every project is to succeed, whatever the project is and the WBS can be used for that.
Creating WBS
It can be difficult to realize when or how to create the work breakdown structure even when knowing how to use it. The most important part when creating the projects WBS is to have some initial scope structure of the project that is to be undertaken. A requirements document is important as well, where the goals and purpose are defined. However these things can often be created and evolved while the scope of the project is being defined. It is important to have as much information about the project work in the beginning stages of the project[1]. The WBS is used throughout the duration of the project from the beginning phase to the end phase. Useful structural points of the model to reflect on while a project is ongoing are as stated below:
• Create
• Refine
• Use
• Verify
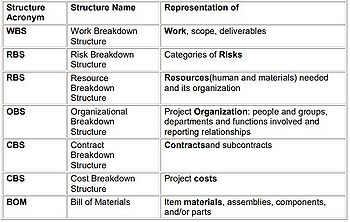
In the creation of the model, the project manager is one of the key members in creating it. However, it is crucial that the project manager and the management team work closely together and involve the stakeholders as well as experts or other personnel that will be working on the project or have experience of similar project to help with the creation of the WBS. There are various ways of how to create and structure a good WBS model. When creating the WBS the project manager needs to be familiar with the concept and the model itself. The reason for that is because there are a lot of models that have very similar structure as the WBS but are not providing the same information and do not serve the same purpose. It is therefore important that all of those who are associated with the WBS have a good knowledge of what it is or at least that they are presented with a “rightly” done model. It is common that people are mistaken of the different models, for example the risk breakdown structure (RBS)[1]. The RBS is used to breakdown different sections of risk in to smaller categories. That is for example, external risk for the larger section and smaller sections can consist of how the external risk can appear in any way. Though the structure and the idea is similar as the WBS it is not the same.
Similar structured and practiced tools are illustrated in the Figure 5:
While creating WBS it can be good to have in mind what is being created. There are different methods of how to create WBS. The most common methods are, top-down, a bottom up, the use of organization-specific WBS guidelines or standards and the use of WBS templates.
Top - down In this approach the WBS is derived in a way where the entire project is decomposed into subproject or smaller task which is the lower part. This approach is based on the characteristics of the project, not on the detailed design element. (CITE). The decomposition keep going in this order where in the end the whole scope has been made in to a manageable segments that can accurately defined and estimated [13].
Bottom – up
This approach as the name implies is approached from the bottom to the top, where the lower part is thought of as the variables or deliverables which are essential to complete the project. This approach often demands much experience from the project manager where the end outcome depends on knowing what is needed to execute the project [13].
WBS guidelines and standards The guidelines and standards are usually an aid for project managers or the personnel which is conducting or creating a WBS. They provide directions and help with the creation and implementation of the WBS. The standards and guidelines are often found in companies that work on high level project management and can be crucial to the one creating WBS. They can consist of teaching material , examples and rules to demonstrate the reader on how to use the model correctly [12].
WBS templates
Templates is a valid way of creating the WBS. Templates is a pre- created structure or an example of the WBS where it helps the creator to realize how to conduct the model and how it can be used. Well defined template can be a great help to an inexperienced person creating a WBS. Organizations can use certain templates for a specific type of projects and adapt them to the work environment they are used of using them in.
100% Rule
Everything that needs to be accomplished by the WBS is defined by the 100% rule.
When creating and organizing a WBS it is critical to follow the 100% rule. The rule is stated and defined as follows:
The 100% rule (Haugan, 2002, p 17) is a core characteristic of the WBS. This rule states that the WBS includes 100% of the work defined by the project scope and captures ALL deliverables—internal, external, and interim—in terms of work to be completed, including project management. The 100% rule is one of the most important principles guiding the development, decomposition and evaluation of the WBS. The rule applies at all levels within the hierarchy: the sum of the work at the ‘‘child’’ level must equal100% of the work represented by the ‘‘parent’’ and the WBS should not include any work that falls outside the actual scope of the project, that is, it cannot include more than 100% of the work. It is important to remember that the 100% rule also applies at the activity level. The work represented by the activities in each work package must add up to 100% of the work necessary to complete the work package.
By using the rule as stated above, it allows a project manager to have a good overview of each branch of the WBS and good vision of the entire project.
Benefits of using WBS
After creating a well organizes WBS, the benefits will be comprehensive. The benefits are substantial and by using the WBS a project is more likely to run smoothly and goals achieved. The deliverables are defined and the work required is organized. It can help realizing a scope creep or risk where deliverables may be badly defined, this can safe both time and money. The entire scope becomes more visual by a well structured WBS. Timeline of a project can be supervised and if some deliverables in a project seems to be falling behind the model can help project managers realizing that. In any project it is crucial to se progress and have some motivation, WBS can be used to show control points and milestones which can boost a moral in complex projects, as well it helps a projects team to brainstorm and can help with the tam to feel invested in the planning[14].
Limitations
Even thought the WBS has a lot of benefits that can help with the variety of projects and make complex projects more understandable, the model can have some limitations. The deliverables are not made in any specific fixed order, which can be confusing in making of the model. There can sometimes be similar deliverables that have been broken down in smaller sections for the WBS but because of their similarity they can often be combined in “one” deliverable where it can be hard to distinguish between them. In many projects the scope can varies from day to day and there for the WBS needs to evolve as rapidly as the changes otherwise the model itself would not be showing the right visualization of the project and the scope can be incorrect[15].
Example
It has been stated above that creating WBS can help with cost planning and timelines. There is a great example of WBS used in a construction project in Iceland. The project was about building a new warehouse for Icelandic post, where the project manager created a WBS and was able to estimate the timeline and created a Gantt chart that was used in the project. The idea was to keep the WBS simple but as affective as possible. The project manager created six major phases where each phase had a subphase.
The original WBS can bee seen in Figure 6:
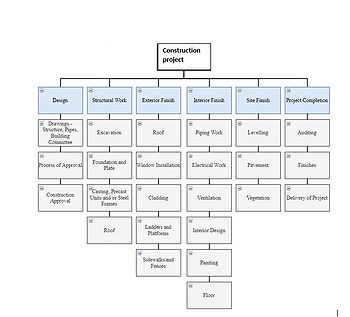
The construction project was not highly complex however the project manager stated “ By creating the WBS the project became easier to grasp and furthermore it made the creation of the Gantt chart easier. The project would have been impossible to work on without pre planning and the WBS as well as the Gantt chart to follow, that said, a fairly simple project becomes even more simple by the usage of these tools which makes everyone’s work more fun and productive.”
The Gantt Chart created with the critical path can be seen below:

References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 L. Buchtik, Secrets to mastering the WBS in real-world projects, (Project Management Institute, 2010),.
- ↑ L.The Golden Circle — Why Do You Do What You Do?, (https://achardypm.medium.com/the-golden-circle-why-do-you-do-what-you-do-e01dbb2ff0c2), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 The Golden Circle for Project Success-start with why? , (https://ianjseath.wordpress.com/2016/06/13/the-golden-circle-for-project-success-start-with-why/ .), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ Figure 1, (https://www.pngkey.com/detail/u2t4t4u2w7o0o0u2_simon-sineks-golden-circle-simon-sinek-golden-circle/), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) Chart, (https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/pert-chart.asp#:~:text=A%20PERT%20chart%20is%20a,of%20a%20project%20for%20analysis.), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ Figure 2, (https://www.projectengineer.net/how-to-draw-a-pert-chart-2/), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ What is a Gantt Chart?, (https://www.projectmanager.com/gantt-chart), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ Figure 3, (https://www.microtool.de/en/knowledge-base/what-is-a-gantt-chart/), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 G.T.Haugan, "Effective Work Breakdown Structures",(Berret-Koehler Publishers, Inc. 2001 ).
- ↑ "Application of technique for research and development program evaluation",(http://mech.vub.ac.be/teaching/info/Ontwerpmethodologie/Appendix%20les%202%20PERT.pdf/), Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ " Getting Started with work breakdown structure(WBS)",(”https://www.smartsheet.com/getting-started-work-breakdown-structures-wbs#:~:text=The%20term%20%E2%80%9Cwork%20breakdown%20structure,Structure%20(WBS)%20Practice%20Standard/), Accessed: 2021-2-18.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Practce Standard for Work Breakdown Structure- second Edition",(Project Management Institute, Inc. 2006),.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Top-down or Bottom-up?",(https://project-management.com/work-breakdown-structure-wbs-top-down-or-bottom-up/) Accessed: 2021-2-28.
- ↑ , "WBS benefits",(https://uwaterloo.ca/ist-project-management-office/methodologies/project-management/planning/work-breakdown-structure/wbs-benefits ) Accessed:2021-2-27.
- ↑ "DISADVANTAGES OF WORK BREAKDOWN STRUCTURE",(https://checkykey.com/disadvantages-of-work-breakdown-structure ) Accessed: 2021-2-27.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Gantt & WBS ",(VSO-CONSULTING),Created 2018.