The double diamond
Developed by Mohammed Hodan Ismail
Abstract
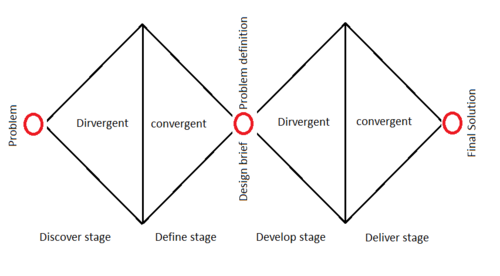
This article describes the management tool called the double diamond which is a design process that has been created by the British design council in 2004. The double diamond tool explores a wide area of the process for a problem-solving mindset, from the initial discovery of the problem to developing a solution.[1] When project managers have a problem to solve, a lot of the time they would move on to a problem-solving phase immediately to solve the specific problem. Which can result to that the solution being temporary or the wrong solution for the given problem. The explanation for the this could be that there haven’t been enough time/resources spend on investigating the actual problem and the right way to approach the root of the problem. [2] The double diamond tool consists of four different phases that’s divided into two Diamonds. In the first diamond we have the problem-solving space, where the first phase is the discover stage where the user must think with a divergent mindset (expanding the problem and the solution space). The next stage is the “Define” stage where the user must think with a convergent mindset, where the user refines the ideas into a possible solution (the focus area). After this the user moves on to the solution space by entering the third stage which is the “Develop” stage where the user diverge on the possible solutions and concepts. And finally, the fourth stage “Deliver” were the ideas gathered from the “Develop” stage is converged on by testing and refining.
Contents |
1.Introduction:
The Double Diamond is management tool on how to work towards a structured design process. That was developed by the British design council in 2004. After a collaboration with some of the world’s leading companies (Alessi, BskyB, Starbucks, Virgin Atlantic Airways, Whirlpool, Xerox, Yahoo! , BT, LEGO, and Microsoft).[3] The aim of the study was to observe how these leading companies approach and operates in the design processes to either their products or services. The criteria for the selected companies for the study was that they needed to represent a variety of sectors and that they could successfully apply the same design processes. The leading company’s way of operating in the design processes to either their products or services had some similarities, In the way their approach/framework was structured. The Double Diamond tool was then invented based on that research. The double diamond tool consists of four different phases: Discover, Define, Develop and Deliver that’s divided into two Diamonds. The four different phases shift between having a divergent and convergent mindset.
2.The problem defining space:
In the first diamond we have the problem defining space where the design process should begin with exploring the problem space. for this to be a success it is important to refrain from having a solution orientated perspective when working in this space, because this may result to that the solution being temporary or the wrong solution for the given problem. In the first phase of the first diamond is the discover stage where the user must think with a divergent mindset (expanding the problem and the solution space). The next stage is the “Define” stage where the user must think with a convergent mindset, where the user narrows down and refines the ideas from the previous stage into a possible solution (the focus area).
3.The problem-solving space:
After the define stage, the user moves from the problem defining space into the problem-solving space with the concepts from previous stage. To the next diamond where the develop stage concentrates on the concepts with again a divergent mindset to explore and work with different solutions concepts. In order to have more options to work with instead of just going with the first solution that appears to be a great solution. After working through the different solutions concepts the user selects the solution concepts that they want to keep working further with to the next step. The deliver stage that marks the end of the second diamond and it’s the final stage in the double diamond. Where the user starts prototyping and testing the solution concepts. The solution concept that fails the testing are discarded and the solution with the best results is chosen.
4.Use of tool:
The Double Diamond is management tool that can be used in almost any design project with a challenge or problem there needs a solution. The Double Diamond as management tool is very flexible and can be made to fit most projects. In a project management perspective, the Double Diamond is a tool that can be used to structure the framework of the project work. To make the project innovative and find the best fitting solution. In an addition traditional project management can be performed in parallel. While it follows the different stages off Double Diamond.
The British design council have presented 25 methods that can be used in the project plan in the four stages of the Double Diamond. But the user shouldn’t feel limited to only use these. The two diamond phases can be seen as management stages [4], where the different stages can be scheduled through a series of milestones. So that the users can review the project progress and approve if the project is ready for the next stage. It is important that the user reviews the current stage, updates the project plan, and look into possible risks. So that the whole process is dynamic and is under constant review throughout the whole time. Sometimes there can be special occasions where the use of an additional diamonds can be required to investigate a concept solution again, before settling down on a solution.
4.1 Discover stage:
In the discover stage the purpose is for the user to explore and gather as much information to diverge on the problem or challenge. This stage allows the user to have a divergent mindset, to be open minded for new concepts and ideas. The framework is to gather information about the users, market or social trends. use and explore all means to have a broad range of information. The more information that’s collected, the more options there is later to work on, to have the best approach to tackle the challenge or problem.[5]
Here are some tools that can be used in the discover stage:
The 5 why’s
The 5 why’s is a simple and effective tool that can be used to discover the root cause of a problem. The tool works by asking a series of why questions, ideally 5 or less but sometimes it requires more. The intention behind it is to use a question to elaborate on the question before and so on. Until the source or root cause of the problem is found.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a simple and well know design thinking technique that most teams use in idea phase. It is a tool that can be used to generate multiple ideas and exploring creative concepts. It is important to being open minded and trying not to be judgmental by other team members ideas, even though if their idea is wild. Just write everything down that comes to mind. Because later on the team can discuss and vote on the ideas.
Desk research, interviews and surveys
These three methods are very useful data collecting method. What makes Desk research a great method for finding information is that much of the secondhand information is available online, but it is important to be aware and critical of the source. Interviews helps with understanding the target groups behaviors and what they think or want, With in-depth questions. The survey method investigates broadly. It maps the relationships being examined with the aim of gaining an overview of general relationships and patterns that are representative of a given area.
4.2 Define stage:
In the define stage the purpose is for the user to converge on the ideas and information that has been gathered from the previous stage, to analyze and make decisions to limit the problem space and focus area. For the define stage the user shifts from a divergent mindset to a convergent one.[6] Here are some tools that can be used in the define stage:
- 1.Focus groups: gather a small group of people and ask them about there ideas about the topic with a facilitator to note down and ask questions.
- 2.Assessment criteria: agree on a set of criteria’s that the ideas can be judged upon.
- 3.Customer journey mapping: to have an visual understanding of key moments
4.3 Develop stage:
In the develop stage the user moves from the problem defining space into the problem-solving space with the concepts from previous stage. The develop stage concentrates on the defined concepts form the previous stage. For the develop stage we shift back to a divergent mindset to explore and work with different solutions concepts for the defined problem or challenge.[7] Here are some tools that can be used in the develop stage:
- 1. A physical prototype: with a physical product unforeseen problem can be identified and solved, its better to test it on a small scale before the final production.
- 2. Service blueprint: with this tool a better understanding of a service and the resources required for the product can be achieve. With service blueprint opportunities and weaknesses can be discovered, for the project managers and organization to act upon.
- 3.Effectiveness vs efficiency: with this tool project managers can weight how effective and efficient the method/solution that they have work on is. The optimal goal is to have a high effectiveness and efficiency, with this tool they could quickly see what method/solution have the most potential.
After working through the different solutions concepts the user selects the solution concepts that they want to keep working further with to the next step
4.4 Deliver stage:
The deliver stage that marks the end of the problem-solving space and it’s the final stage in the double diamond. Where the prototype goes through some more testing and refining before being delivered.[8] Here are some tools that can be used in the deliver stage:
- 1.Phasing: presenting the solution for a small audience, to avoid risk before a full-scale presentation.
- 2.Feedback loops: to receive feedback that can show improvements for future projects.
- 3.Final testing: to validate the quality of the solution/product
- 4.Method banks: make a list of method used in the project, that will be used to improve project for the organization in the future.
5.Limitations:
There are of course some pros and cons with using the Double Diamond as a tool for project management. Double Diamond tool is adaptable to tackle problems for many projects and different levels of a business. It’s a problem-solving tool that can be used to structure the framework of a project. One of the issues with the Double Diamond tool is that the process for using the tool is linear and thus limiting in a context of project that runs an adaptive life cycle. In such cases other frameworks to structure and plan the projects should be used instead like maybe Scrum. In addition, the Double Diamond tool should be supplemented by another project management tool since it there are some areas of project management that are not included in the model. Another limitation is the time management of the Double Diamond tool, there is no timeframe for the different stages, and can there be difficult to know when it is time to move forward to the next stage. The time spent on the different stages could vary depending on the size of the team and project scope. For example, when the project team is gathering information on the problem space when is it enough and when is it time to converge on the ideas from the previous stage. there are no guidelines for that, but it takes experience to master the time management of the Double Diamond tool.
6.Annotated biblographys
[4] A study of the design process - by Design Council- The British design Council has a website that provides a description of the framework of the Double Diamond. It gives a deep and broad understanding of the tool. With and explanation of how and why it was invented.
AXELOS. (2017). Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition (2017th ed.).-A well-known book in project management that often seen as a standard for best guidance on how to manage a project.
Project management institute (2017). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide). (6th edition)-A book for project management that provides guidance on project with characteristics and guidelines.
References
- ↑ "1|[1] A study of the design process - by Design Council.
- ↑ "2[2] Are you solving the right problems? - by Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg.
- ↑ "1|[3] A study of the design process - by Design Council.
- ↑ "Managing Successful Projects | described in chapter 3.4 | AXELOS. (2017). Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition (2017th ed.).
- ↑ "Discover stage | Design Methods Step 1: Discover | by the British Design Council. https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-1-Discover.
- ↑ "Define stage | Design Methods Step 2: Define | by the British Design Council. https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-2-define.
- ↑ "Develop stage | Design Methods Step 3: Develop | by the British Design Council. https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-3-develop.
- ↑ "Deliver stage | Design Methods Step 4: Deliver | by the British Design Council. https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-4-deliver.