The style of leadership changes throughout the life cycle of a project
Developed by Sophie Bjerg Andersen
Different leaderships styles is necessary to apply when a success for a project wants to be achieved. Leadership is important in all fields of projects espacially in construction process and in construction projects as it is technical demanding and the teams are large and diverse [1].
Different leadership styles will be presented and a description of how the most effective and appropriate leadership can be performed when the goal and the team various. The application and the different characteristics of leadership styles and approaches will be elaborated and discussed regarding the life cycle of a project.
Contents |
Introduction
Leadership is an essential role during a construction project or any other type of project. Construction project is often regarding a lot of different professions on different educational levels which together should reach the same goal – construction e.g. a building. As a leader it is important to be able to motivate and lead in a direction which the led will follow. The characteristic of the leader has therefor an influence on whether the led will follow or not. Research has shown that "leaders" and "managers" are used interchangeably, though they are two different concepts. "Managers" can be characterized as people who among others make short term decisions and solve short term problems. They employ the so called “hard” skills such as e.g. planning and organizing. Whereas the "leader" employ many of the “softer” skills. They among other things direct and guide people, motivate and have a long-range perspective [2]. In relation to this article the main focus will be regarding the role as a leader.
During construction e.g. of a building a lot of uncertainties will appear and therefore it is necessary for the style of leadership to change. Different factors will have influence on which style of leadership there will be necessary to apply as e.g. a high educational level expects greater deference and sensitivity. The styles of leadership has in Winch [3] been divided into four different styles and as the uncertainties in a project decreases another style of leadership, from the one used in the first phase, should be applied.
Leadership
In this section the basics of leadership will be elaborated. The basics of the leadership is important regarding the power of levers to ensure the success of the project. In a business organisation the leadership is required at three distinctive levels. Winch [3] defines them as follow:
- Leadership of the organisation overall
- Leadership of the principal divisions of the organisation
- Leadership of the various units which make up the organisation
As the last level of leadership, which concerns leading a single team, is quit different from the two other levels, the main focus will therefor be at the first two levels.
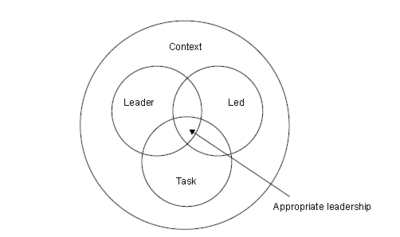
To generate an appropriate leadership three factors influence the appropriate manner of leading and motivate the project coalition, this can be seen of the figure bellow.
Of the figure the three terms: Leader, Task and Led can be seen. The terms refers to the description in Winch [3].
- The capabilities of the leader
- Many successful leaders is likely to have some of the following skill set:
- Analytical and problem solving
- Can set the pace
- Technical skills
- In the resent years of research it has been found that also an emotional skill is necessary for the leader to have.
- The task facing the organisation
- The appropriate way of leading is depending on the situation fx. If the mission is to solve a crisis or to manage steady growth.
- In a construction project different phases requires different styles of leadership.
- The expectations of the led
- The expectation that the led have to the leader. Different groups or teams have different expectation to the led.
- Following factors affects the expectation to the leader:
- Level of education: a higher educational level requires more sensitivity
- Cultural factors: different organizational and national cultures expect different styles in their leader.
- Previous experiences: If the style of leaders perceived to have been successful in the past are more likely to find the favour in the future.
- Perception of the situation: depending on the situation if it is stable or there is a crisis different leadership styles will be expected.
As it can be seen of the figure (to the left) the interaction between the three factors are considered as the zone where the appropriate manner of leader is found.
Styles of leadership
There four different classification of leadership is defined by Winch [3].
- Autocratic: The leader takes the decisions alone or relies on an exclusive circle of advisers
- Paternalistic: The leader takes the decision alone, but takes pains to explain
- Consultative: The leader discusses the issues with the led prior to taking the decision
- Participative: The decision is discussed by the led as a whole
In a contemporary organisation Winch [3] suggest that the two styles of leadership Paternalistic and Consultative are preferable. The style Paternalistic works well in stable situations, where the subordinates do not have a strong desire to participate in the decision making. But by using the leadership style Consultative the subordinates has larger tendency to accept the approach and thereby the leadership.
It is not very common for a leader to contain all the different leadership styles. All leaders at different organizational level "have their own personal leadership styles that determine not only how the lead subordinates but also how they perform" [4]. It is rarely seen that a leader posses all the different styles and when hard decisions have to be made different research has shown the leader tend to revert to their habitual style [3]. Leadership styles does not only vary on the individual level but it is also seen that it vary between countries and cultures.
Contingency models
"Contingency models propose that whether a leader who possesses certain traits or performs certain behaviors is effective depends on, or is contingent on, the situation or context"[4]. As citet the contingency model which will be presented is the Path-goal theory by Robert House, this theory explains different approaches of behavior there can be applied under different circumstances and thereby in among others a construction project.
House´s Path-goal theory
House´s Path-goal theory [5] by Robert House present a theory which is quite similar as the classifications presented by Winch [3]. The House´s Path-goal theory has a premise "that effective leaders motivate subordinates to achieve goals by" [4] clearly identifying the outcome , rewarding subordinates and "clarifying for subordinates the paths leading to the attainment of work goals"[4]. The theory identifies four kinds of leadership behavior that motivate the subordinate.
- Directive behavior: is characterized as a behavior that initiate structure and include; setting goals, assign tasks, show how to complete the tasks, steps to improve performance [4]. "The theory argues that this behavior has the most positive effect when the subordinates' role and task demands are ambiguous and intrinsically satisfying" [6].
- Participative behavior: the behavior is characterized as giving the subordinates a say in the matter and an influence on subjects that affects them. "This behavior is predominant when subordinates are highly personally involved in their work" [6].
- Achievement-oriented behavior: the behavior is characterized as a behavior that motivates the subordinates and set high expectation, so the subordinates can perform on the highest and most challenging level [4]. "Occupations in which the achievement motive were most predominant were technical jobs, sales persons, scientists, engineers, and entrepreneurs" [6].
The life cycle
The life cycle is a description of different phases a project is going through to reach success. The phases are described by Winch [3] as "distinct stages, each with its own challenges and pitfalls and each requiring different skills"
- Phase
- Phase 1 will be characterized as the start-up. The startup has 3 different key task which will be elaborated. The first key task is that it is necessary to build a team that can ensure the success of the project and at the same time a team that can work together. The good collaboration in a team can be started by getting to know each other and thereby the different stresses that can compromise the good collaboration. To maintain the good collaboration within the team communication is the most important tool.When the team is created it is important as a leader to please the team and keep the members of the team inspired and motivated. The second key task in this phase it to review the project. Here the different job specifications are identified and the planing of the project is conducted. In this part of the phase the people who will be affected by the project is beared in mind and included. The third key task is to build up personal credibility with the client and other groups who has an impact on the project e.g designers.
- Phase
- This phase is divided into two; the first part is primarily buying material to perform the project. The second part of the phase is to conduct the project, this will happen alongside the buying process. As the project gradually develop different challenges will appear which will often be handled by dialogue with contractors and/or logistics.During phase 2 the relation with the people who will be affected by the project will still be maintained and also the responsibility of the welfare and the collaboration within the team.
- Phase
- The third phase is characterized as the phase where the focus is on coordination and collaboration. The coordination and the collaboration is between the different contractors and consultants who will have influence on the different phases of the construction. During this phase the contract concerning responsibility, facilities, maintenance, technical difficulties and money will be discussed and an agreement will be found.
- Phase
- The fourth phase is where the project will seems to be finished. The big activities will be determined and only the small contractors will be left. During this phase any financial claims and other mistakes will be dealt with. Furthermore the accounts will be rounded out and all the lose ends will be check both physically and checked by the listing of commissions.
- Phase
- The fifth phase is characterized as the testing phase. This means that the achievement of the fourth phase is tested. The fifth phase will become a success if the project can be concluded as completed.
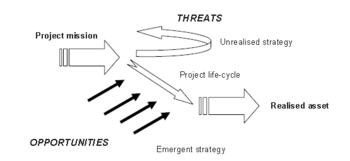
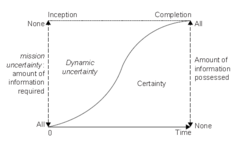
As seen of the two figures bellow (figure 2 and 3); Figure 2 implies that every project has a goal or a mission. This is of course obvious for a construction project as the overall mission or goal is to build the project but during the life cycle of a project the amount of uncertainty differ. Winch describes the term uncertainty as the absence of information required for the decision-making [3]. As seen of the figure to the left ( Figure 3) the amount of uncertainty differs during the construction project and thereby the different phases in regarding the life cycle. Due to these variation of information different approaches of leadership styles should be taken into account. Winch suggested that in the early phases of the life cycle where the project has briefing and design problems a Participative style is most likely to be appropriate. As the project moves towards the phases regarding planning and execution the leadership style is suggested to be an Consultative approach. It is considered that the leadership style Autocratic is an unlikely approach at any phases of the life cycle but it should be beard in mind that evidence has shown that construction managers tend to be at the Autocratic end of the spectrum of leaderships styles [3].
Discussion
Two approaches of appropriate leadership has been presented; Winches theory based on several studies and Robert Houses Path-goal theory. The two theory are at some point quite similar and has some of the same characteristics of the styles of leaderships. They both describes the necessity of flexibility of the characteristics approaches in regarding a project and explains that the approach is depending on the situation, the task and the subordinates. Winch explain the difficulty of switching between the different styles of leadership and the rareness of that, whereas the path-goal theory assumes that the leader is flexible and therefor is able to change the style of leadership when the situation requires it. Both of the theorys also describe a characteristic (respectively the Autocratic and the Direct) that is not very appropriate using to lead the subordinates, but also describes this style or approach as detrimental in some situations, this can e.g be in situations where the subordinates are independent thinkers.
In some minor project it can be the discussed whether a leader is necessary as some studies implies that the subordinates can handle the mission as a group. This is not something that has been elaborated here but i should be taken into account.
Conclusion
In a large project it is necessary to have a leader that has the overview of the project and during the different phases in project different approaches of leadership styles is applied. Many studies shows that the different approaches of leadership is a necessity but the mission and the subordinates have an influence on the approaches. Whether the leader is cable of the flexibility of approaches which the subordinates and the missions requires is something that are still being discussed.
Annotated bibliography
1. Ofori, George; Toor, Shamas-ur-Rehman, "Leadership and Construction Industry Development in Developing Countries.", Universiti Sains Malaysia 2012. The abstract focuses on leadership and the development of the construction industry in developing countries.
2. CIOB, "Leadership in the construction industry", The Chartered Institute of Building, 2008. The report is based on research that has examined the issue from the perspective of managers and directors within the construction industry. The research has among others focus on leadership and the development of these skills.
4. Jones, Gareth R. ; George, Jenniffer M., "Essentials of Contemporary Management. ", McGraw-Hill Education 2015 6th edition. page 326 - 354 This section has focus on different leaderships styles and elaborate different theorys of what effective leadership is and how it can be seen in context.
5. Wikipedia the free encyclopedia, "Path-goal theory". The article describes the heritage of the theory produced by Robert House and describe the different phases in the theory.
Reference
- ↑ [http://web.b.ebscohost.com/abstract?direct=true&profile=ehost&scope=site&authtype=crawler&jrnl=18236499&AN=88053759&h=8b8pAMG8QRUYQKoHdemQUl3GyOue8drTWj4lh6gZCdXx187qfD0w%2bzmEUcmZXuEBuxuHYwvI8iLNESIufmvk%2bA%3d%3d&crl=c&resultNs=AdminWebAuth&resultLocal=ErrCrlNotAuth&crlhashurl=login.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26profile%3dehost%26scope%3dsite%26authtype%3dcrawler%26jrnl%3d18236499%26AN%3d88053759] Ofori
- ↑ Leadership in the construction industry, 2008, The Chartered Institute of Building
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 Managing Construction Project: Infusing the project mission, 2010, Wiley-Blackwell
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Essentials of Contemporary Management, 2015, McGraw-Hill Education, 6th edition
- ↑ [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Path%E2%80%93goal_theory] Robert
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedRobert