Time management by CPM and 4D-Planning
Developed by Ismael Karayem
When having a project, it is known that there is a start and an end date. Between those two dates, different deadlines should be achieved to get a satisfied result before the end date is reached. Therefore it will mean that a project depends a lot on the parameter time. When one of the parameters is time, then it is known that the natural follower is cost. Therefore to reach the deadlines with a satisfied and a economical pleased result, it is necessary to have a written well-organized plan. Especially the part of writing a plan down is necessary, since research had shown that, when goals are written down the rate of reach them is increased. What to do for time management and which tools can be used?
To plan in a good manner, there have been used many techniques and many different schedule-schemes have been developed. One very useful and old method for time management, especially when the case has a lot of dependencies, is The Critical Path Method (CPM). The CPM had been used in many construction cases and it is still applied but since the world changes in innovation other methods are required. One of the newer methods is the 4D-Planning. The 4D-Planning is making use of the 3D construction model and the time schedule which is linked to it, that gives 4D-Planning.The methods CPM and 4D-Planning will be explained, while the methods will be seen from a historical perspective. The methods application and limitation will be reviewed.
Contents |
Critical path method (CPM)
History
After the Second World War the situation over the world was still strained. The tense was especially between the world’s two superpowers namely the United States of America and the Soviet Union. This tense between these superpower countries is in the history defined as the Cold War. During that period both countries had a high priority on development and armament. One of the development phases in the 1950s was the US navy’s Polaris missile program. That program was not going as planned and the time schedule was delayed. Therefore the solution proposal for the program was to divide the project into tasks and then connecting the tasks in relation to the dependency of each other. The estimation of duration for each task was written and by that a schedule could give the duration, the critical task(s), the allowed delay time for each task and the critical path through the whole program. At the same time an American chemical company called El DuPont de Nemours Company had delay problems. The chemical company and the US navy cooperated in the 1950s to develop a system to manage the delay. The US navy called their solution for "Program evaluation review technique" (PERT), while the chemical company called it "The Critical path method" (CPM). The systems are almost similar but there are some differences. Among and other the difference is in time estimation. The CPM has a fixed time which is estimated once, while the PERT is a method where uncertainties for the activities planning, organizing, coordinating and controlling are estimated. The development of the method had shown its importance, since the management world got a tool that could manage projects that have many dependencies in a smart way and showing the critical path of the project. Today the method is widely used and implemented in software like Microsoft Project. [1] [2]
Method
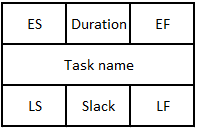
The method of CPM is to produce a network that defines all the tasks and the task dependency in a chronological order. For making that network of tasks, the manager has to list up all the tasks, the tasks presidencies and the duration of each task. Such a list can be seen under 1.3 Example. When the list is ready, the manager will start setting up a network. The network will content of tables which is seen at figure 1. The tables will be logically connected together by arrows, which will be in relation to the dependency of the tasks.
The manager will now be able to fulfill the tables in the network. The tables contents of:
| Title | Explanation |
|---|---|
| ES | The earliest start of the task |
| Duration | The duration of the task |
| EF | The earliest finish of the task |
| LS | The latest start of the task |
| Slack | The delay |
| LF | The latest finish of the task |
To fulfill the table, the manager will make use of the task's duration, the dependency, forward pass and backward pass. The forward pass gives the absolute earliest finish time and that happens by calculation from the first task, through the network and to the last task. The backward pass gives the possible latest finish time without exceeding the time limit and the slack. By the slack the manager will be able to know how much a task can be delayed, without exceeding the time limit for the project. The forward pass is calculated by starting from the first task, though the network and until the last task. For the backward pass it is the opposite way, which should be calculated from the last task, through the network and to the first task. After each table is filled out in the network, the manager can get a visualized overview over the project. It is possible for the manager to see where it is possible to get a time delay in executing the different tasks and an insight in the most critical path across the project will be available, which is an advantage for the whole project.[3] [4]
Example
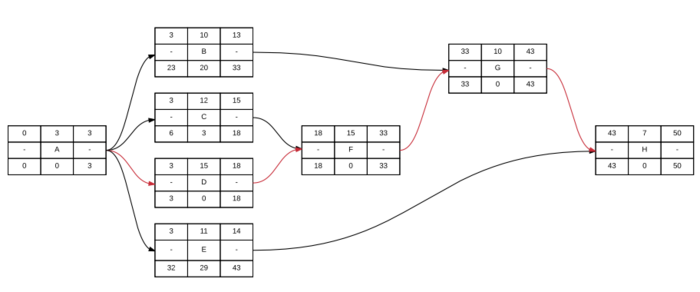
To better understand the critical path method an example is created. The example is given for a small construction project, which gives the advantages to have a simple network and to easier understand the principle. The first step is to create a table where all task, their precedences and duration is listed up. That table is shown below.
| Task | Precendences | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| A | - | 3 |
| B | A | 10 |
| C | A | 12 |
| D | A | 15 |
| E | A | 11 |
| F | C,D | 15 |
| G | B,G | 10 |
| H | E,G | 7 |
When having that information, the network can be created by the logical system and the duration of time can be noted. Applying the forward and backward pass will give a finished network, where the critical path is possible to spot on figure 2. The critical path is highlighted with red colored arrows.
For additional information of how the network was filled out a video has been made. The forward- and the backward pass are applied and explained. The self-developed video can be seen here:
4D-Planning
History
The world's industry could only make use of the paper and the pen to sketch the construction model for a project. The sketches were typically made in 2D. In some cases a 3D drawing was created with details like shadows, which was used for making the sketch more dynamic. Even that some cases did get a 3D drawing, which was very complex, it had the limitations in compare to today’s 3D model where the user can move, turn and zoom in the model. The process to make a drawing, was very time consuming and especially when there should be made some changes at the drawing, the drawing process needed to be changed. The change from the paper and pen should be to something that gave flexibility. The flexibility was able to be reached by making use of the computer, which today is known as Computer Aided Design (CAD). One of the first innovative CAD software’s that was developed was by Ivan Sutherland in the 1960's, which was called Sketchpad. The Sketchpad was very innovative at that time, since the designer was able to for example duplicate the drawings. Even though that Sketchpad was an innovative program there was still space and need for upgrades. The upgrades were to develop a software that could handle to design a 3D-model. In 1987 the industry did get the software that could handle to design 3D-models. The software was called Pro/Engineer. Today the industry has many different programs for the purpose. At the same time in 1987 when the first 3D modelling software was developed, there was thinking about connecting the 3D model to the time schedule, which gave the 4D model. It were Bechtel in cooperation with Hitachi that were thinking to developed a software named CAE/4D that could work with a 4D model. Today the method is used and the industry has software like Synchro available for the purpose. [5] [6]
Method
Since all companies today are using IT-tools as a support, then the 4D-planning is a bigger reality to apply and it is much easier to make use of in comparison to the first years, where the computer was developed. When having a construction project, then the designers/engineers are going to sketch up the full 3D model which they will make use of to carry out the project. By taking the 3D model and insert it in software like Synchro, it is possible to add the time schedule. The time schedule can contents of planning each single subject that is in the model assembly. By the end an amination can be created where the time is seen to run, and while the 3D modelled is built up as planned. [7]
Example
To get a visual insight of 4D-planning video 2 is used. It is possible to see how the 3D model changes depending on the jobs that are planned in the time schedule. The 4D model is made in the software Synchro which is mentioned as a possible software earlier in the rapport.
Application
Critical path method
The critical path method had been and is still a technique, which is applied a lot in time management. The method has especially the advantages when many task dependencies occur, since it gives the knowledge about the flexibility in delaying a task without delaying the whole project. The method can also take advantages in that it is implemented in many different software’s, which makes it easier and faster to calculate the finish time(s) and the delay. By having the software the method also gives the opportunity to easily build the task network, which gives the visual overview according to the task dependency in the project. [4]
4D-Planning
The 4D-planning is still a newer tool in the world of time management but with a large potential of application. The method is better applied for bigger complex projects, since it can be time consuming with developing a 3D model and also link it to a time scheme being for example the critical path method. There are also strongly advantages with the method, since it is seen that by the method the safety, communication and shared understanding of the construction process is improved. By also having that type of system it can be easier for the manager at the site to visual showing the craftsmen which part there should be worked on and when it is planned to be finished.[7]
Connection between CPM and 4D-Planning
The typical way of making a schedule is by having bar charts with fixed times but when connecting the CPM with the 4D-planning, the manager can get information about the flexibility in delaying a task. The information about the possible delay gives the opportunity for a manager to for example better manage the storage space for the tasks, by that the needed materials are always at the site at the needed date and if the storage space is limited, then the manager will know which materials that can be delayed without disturbing the project. By having the 4D the task dependency from CPM is easily checked since it is visualised. The visualisation can also be used to show the collision between the tasks.
Limitation
Critical path method
Even though that the method has many advantages, then there are also some disadvantages, which can limit the application of using the method. The critical path method can easily be calculated by hand calculation but if any calculation is wrong or a task duration or some dependency changes, especially one of the early calculated ones, then it is necessary to start all over from start. Luckily there have been developed many different types of software’s that can handle the calculations, which solve the mentioned issues but it gives that limitation that a computer is necessary. The computer and the computer power that is needed to solve and analyse the network can be a expensive thing which give some limits. Another aspect that can limit the use of the method is that it needs a very specific and detailed approach, which can be a big problem for a manager since the time for the planning process can be limited. [8]
4D-Planning
The 4D-planning is a very smart tool but also very time consuming to develop, which makes it more applicable for bigger complex projects. Therefore it will in many cases not be profitable for small noncomplex construction projects. The method needs a software, which make the dependency on IT-tools very necessary. The dependency for the software will also mean that there will be expenses which can be expensive. Furthermore since the tool is new, it has that problem, that it is few people that are comfortable with the tool. From the start point it is a method with less experience and when the tool is used very limited and by few it will mean that the experience at that area is slowly developed, which can give long view before it is fully implemented by the industry. The age of the tool gives also that issue that there is no standardization at the area yet, which can be hard to use it without a frame.[8]
Connection between CPM and 4D-Planning
The connection of the methods has many advantages but according to the needed time to apply them, it can be a problem for a company to spend the required resources. Furthermore both system needs software and computer power which is a cost.
References
- ↑ Harvey M. Sapolsky,The polaris system development, Harvard University Press (1972).
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_path_method. Visited 19-06-2017
- ↑ Earl B. Anderson & R. Stanton Hales, Critical path method applied to research project planning: Fire economics evaluation system (FEES), United States Department of agriculture.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 https://www.smartsheet.com/critical-path-method. Visited 19-06-2017
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/4D_BIM. Visited 19-06-2017
- ↑ http://www.cadazz.com/cad-software-history.htm. Visited 19-06-2017
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Julie Jupp, 4D BIM for environmental planning and management, Elsevier.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Winch, Graham M. (2010 2.edition), Managing Construction Projects, Wiley-Blackwell.
Annotated bibliography
- 1. Reference: This reference is used to get inspiration to the topic. Graham's book covers a lot of topics due to management in construction projects.
- 2. Reference: This reference is used to get knowledge about the Polaris program and to double check the history for the CPM with other sources.
- 3. Reference: This reference is used to get get a quick overview about CPM and to double check facts and history with other sources.
- 4. Reference: This reference is used to get an understanding about how to apply the CPM.
- 5. Reference: This reference is used to get an understanding about how to apply the CPM and to see the opinion of the users of the method.
- 6. Reference: This reference is used to get a quick overview about 4D-planning and to double check facts and history with other sources.
- 7. Reference: This reference is used to get a historical perspective about 3D modeling and 4D-planning and to double check the history with other sources.
- 8. Reference: This reference is used to get knowledge about the method and the application.