Tuckman's Model for Sustainable Team Development
Developed by Dionysios Dasopoulos
Team development can be described as the process through which a group’s performance is boosted by improving team’s skills and communication. In order for a company to be successful and profitable, it is of vital importance to be capable of achieving teamwork of high standards and effective collaboration throughout the whole organizational structure.
Although every team relies on different theories and strategies in order to continuously improve and develop, researchers have suggested approaches and models that can be implemented and explain how team behaviour and performance are connected and lead to fruitful development adding value across the company[1].
This article mainly investigates Tuckman’s model for team development by classifying the five stages through which teams can thrive, achieve goals and retain coherence over time. Each of the five stages of team development could be presented as a step on the team ladder. Understanding the concept behind the Tuckman's model implementation, boosts the successful project, program and portfolio management as well as the sustainable development of a company.
Contents |
Model Description & Analysis
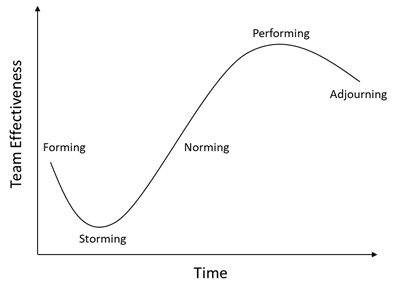
In an ideal business environment, it would be easy for the different teams across the company to perform efficiently and be really productive from the beginning of their collaboration. However, under real circumstances, it is an undoubted fact that team/group members have to be adapted separate business environments in order to perform at high standards achieving effectiveness, a process that requires time. Team efficiency is improved through continuous assessment of milestones aiming to attain targets and achieving project goals. Moreover, it is necessary for the team to breed creativity and keep the morale high especially when strict deadlines must be met and there is a lot of pressure.
The psychologist Bruce W. Tuckman investigated theories about the sustainable team development and he published the model he created regarding group development in 1965. His efforts mainly focused on the five process stages through which team members learn to collaborate with each other effectively avoiding conflicts and act professionally in order to boost company's performance. A thorough analysis of each stage is described below.
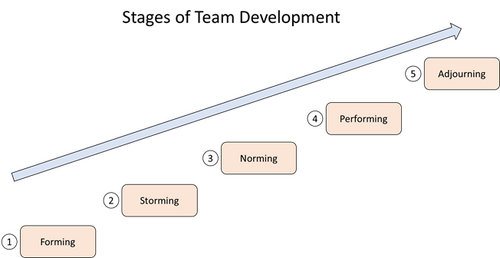
Forming
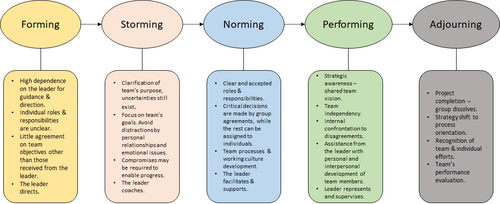
Forming is the initial stage that refers to the first contact of the team members, where an introduction meeting is held. Usually, the meeting agenda includes information about each individual's background, interests, and relative working experience. They also get an update about the project they will be responsible for, addressing potential objectives and goals while simultaneously considering their role in the project team and how they can combine their knowledge and work collaboratively in order to achieve more.
During this initial stage of team development, it is significant for the project manager to precisely present the team goals and provide clear guidance regarding the project implementation as the team is highly dependent on him as they consider him as a source of inspiration and motivation. In conclusion, this stage focuses more on the people than on the project perspective, thus the team probably won’t be able of performing at high standards.[3].
Storming
As the team begins to work together, team members move into the Storming stage. This stage cannot be avoided as every team and especially a new one who has never worked together before, goes through this stage of growing and expanding its activities and area of responsibilities. In the particular stage, team members face challenges of competing with each other in order to gain respect and trust in their capabilities and ideas. It is a common fact that conflicts are often created as different opinions are around the table, regarding the actions that should be done and the optimal way of dealing with all the potential challenges.
As the team builds its skills through this phase, problem-solving and result-oriented strategies are developed under the supervision and contribution of the team leader. Roles and responsibilities are shared across the team while the participants work both independently and collaboratively for the overall team development and success. It is worth mentioning that the Storming stage requires an experienced team manager who is able of facilitating the procedures and organize the team coordination. It is important for him to identify team's strengths and weaknesses so as to combine both in a way that the team will benefit more. Team members should learn to cooperate with each other and listen to the manager's advice trying to create a friendly and well-operating working environment.
Summarizing, this stage process ends when all the aforementioned have been completed with success. Reaching that point, a well-established team collaboration and communication have been created and the team members are ready to take over tasks relative to decision making processes and act more independently. However, it is possible for a team to be incapable of dealing with the upcoming challenges of this stage and therefore group members perform at poor standards with a conflict domination to be obvious leading to difficulties meeting project deadlines and goals[3].
Norming
The Norming stage is defined as the phase where team development dominates aiming to create effective team performance. The current strategy focuses on team goals with the members working collaboratively in order to achieve high performance. A cooperative working culture has already been developed with mutual respect among all the members as the common goal for everyone is to add value to the team and to the company as well. In the norming stage, the team has established a way of internal communication defining the available resources and knowledge that will help to deal with the upcoming challenges. The team members trust each other and they are willing to provide any kind of help in order for the team to progress and grow. Moreover, project implementation is also improving as it is obvious that the whole team performance is also boosted.
In this stage, the team manager has the choice to be less engaged with the operational processes as the team has become more independent and has gain experience in taking over responsibilities. However, this does not mean that he must not be always updated and aligned with the project progress and the potential challenges that need to be addressed. The team leader must be available at any moment, during a project implementation, to provide advice and solutions to the rest team and achieve successful project as well as stakeholder management[3].
Performing
The Performing stage consists of team operation and performance at exceptionally high levels. The main focus area and activities include goals achievement as a well-organised unit where strong relations of trust exist among the team members. It is not easy for a team to reach this stage of team development and therefore the norming stage can be the last one in many cases. Generally, the team performance has been improved at the greatest possible extent and the group members work independently, trying to deliver always on time and meet the project deadlines. It is widely accepted that the team operates and performs without much involvement of the team leader by extended participation in the decision-making processes and having the ability to face new challenges successfully. Obviously, the team leader never stops to be updated about the team progress and coordinate when needed as well as celebrating goal achievements with the rest team to continue keeping the team morale high.
To conclude, it is worth noting that sometimes it is necessary or avoidable for a team to return back to an earlier stage is the circumstances require so. For instance, a deviation from the established working culture and the cooperative spirit can bring the team in front of the challenge of stepping back to the storming stage. Furthermore, a modification to the team structure means that any new colleagues need to be approached from the very beginning leading to repeat of the procedures of the forming stage. Thus, it seems rational that teams needs to move back to earlier stages of team development when noteworthy changes may affect the overall team progress and performance. It is of utmost importance for the team to successfully manage these changes[3].
Adjourning
Τhe Adjourning stage was added later (1975) to Tuckman's model and the initial concept included only the four stages mentioned above. At this stage, the project deliverables are completed and the team members are focusing in different activities and the group breaks up. This stage focuses on a different aspect of the team comparing to the aforementioned stages. This phase is more relevant to the well-being of the people rathen than the managerial perspective of the team development, which was the main area of interest in the previous stages.
The team manager at this stage makes sure that the necessary procedures should be implemented so as the team members follow seperate directions. After a successful passing through the four main stages of team development, it is obvious that the team members have created really trustworthy relations and they communicate effectively. So, despite the fact that they may work in different projects in the future, they continue to communicate with each other and they are willing to provide any kind of help in case it is necessary[3].
Application - Practical Approach[5].
Tuckman's model may has been developed many years ago, but it can be applied in a variety of cases till today. Below, an alternative approach and implementation of Tuckman's model for team development in a non-governmental organisation (community folk team), is described in order to provide insights and knowledge for other community groups development. Briefly, community folk team is a non-profit organisation with main area of focus to improve the life quality in community by performing social activities. The team members are residents from the community who are interested in proacting the organisation and there is also a team leader who is declared by team voting.
- Forming (Objective Identification - Support in Facilities and Personnel)
In the first stage of team development, the initial steps of organizing are conducted. As the team begins to create relationships and cooperative spirit, there is a dominant enthusiasm and motivation to succeed together as a team. However, it seems rational that there is evident lack of coordination, planning and long-term strategy. Specifically, the location of the activities as well as the time cannot yet be guarranted. Therefore, this phase aims to indentify team's expectations and motivate each member to be devoted to team goals and perform at high level.
- Storming (Platform Development - Characteristics Establishment)
Proceeding in the second stage, the objectives of the team become more clear and members are getting more engaged. The expectation of adding value to the community rises and the potentials of improving the team's performance are highlighted. The circumstances of development are clarified and concepts of creating a platform and improving space activities pull team member's interest in order for the community to grow. At this phase, it is also important to start forming the team culture that is higlhy related to the team strategy development.
- Norming (Core Members Training - Innovation Stategy)
During this stage, team members start to create deeper bonds and closer relationships. There is a shift to the team behaviour and at this phase the motivation is directed at providing services that will satisfy others through the successful community operation. A lot of attention is paid to the growth of team spirit as well as to the members' training so as to be close to residents lives. Team becomes mature and the team leader aims to adapt an innovative way of dealing with team challenges, while simultaneously retaining high efficiency.
- Performing (Evaluation Method - Team Performance)
The dominant characteristic of this stage is the enhanced team cohesion and collabotaive spirit that manage to bring the desired results for the organisation and achieve team goals. Particularly, team's performance contributes in creating civilized communities retaining a friendly and quiet reality that provides the necessary services to the residents. The loose groups of the forming stage have been converted into the folk teams with highly developed skills and management abilities.
- Adjourning (Focus on People)
The completion of community folk team management and development can lead to different directions. Some groups can develop and establish an ideal way of addressing and confronting with the residents' challenges. However, sometimes it is possible for the team not to succeed in achieving its goals and that can lead to group dissolution and restructure. At this stage, a clear focus on the people perspective is oriented aiming to deal with potential challenges and improve the human resources management.
Reflections & Conclusion
Tuckman's model describes the process stages through which a team grows and obtains skills and competencies that contribut to achieve goals and be effective. The simple overview of the five stages provides a good understanding of group development and it is a useful tool in training people so as to adjust in team environments and boost their performance. Comprehending Tuckman's model increase the possibilities for a project to be successfully implemented[6].
The specific model is crucial because it also affects and determines the behaviour of the team leader as this behaviour changes through these five stages. In the beginning, it is common that the team leader plays a vital role as it directs and coaches the group members and has high responsibilities regarding the initial group formation and goal setting. However, as the team develops and the members take over more tasks and everyday jobs, the team leader obtains a more remote role as a supervisor and advisor that is always updated regarding the team progress but does not involve so much in the decision-making processes. After the project completion, the team may promote a new leader and the previous one can move on to help another team grow[6].
Anotated Bibliography
- Project Management Institute - Project Management: A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (2017)
This publication (6th edition) has been updated to reflect the latest good practices in project resource management and reflects in principles of team development.
- Jie Zhen - Application of Tuckman's Model in the Community Folk Team Management in Community Education (2017)
The research article presents a practical approach of Tuckman's Model for Team Development.
- Project Management - 5 Stages of Team Development: Tuckman’s Group Development (2020)
The article investigates the five stages that Tuckman developed so as to describe and facilitate the team development & progress.
References
- ↑ Project Management Institute, (2017). Project Management: A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge. [1]. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ↑ Lumen Learning, (2016). Stages of Team Development. [2]. Retrieved 17 February 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 5 Stages of Team Development: Tuckman’s Group Development (2020). [3]. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ↑ Principles of Management, (2014). The Five Stages of Team Development. [4]. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ↑ Jie Zhen, (2017). Application of Tuckman's Model in the Community Folk Team Management in Community Education . [5]. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Alan Chapman, (2017). Tuckman: Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing model. [6]. Retrieved 20 February 2021.