Work Break-down Structure
Contents |
Abstract
Successful project management depends heavily on the ability of project managers to determine the content and scope of project work according to the characteristics of project products (deliverable) and activities. WBS can analyze the project process comprehensively and systematically, and it is also a very effective basic method of project management.
Work breakdown structure (WBS) is a principle of project management that arranges project elements based on the deliverables instead of a schedule activity. which summarizes and defines the whole scope of work of the project, and each descending level represents a more detailed definition of the project work. WBS is always at the center of the planning process, and it is also an important basis for making progress plans, resource requirements, cost budgets, risk management plans, and procurement plans. [1]. WBS is also an important basis for controlling project changes. The key process for building a WBS is to disintegrate the assignments into an amount of light workload and distribute it to every individual who is considered as a participant. [2]
Big ideas
Definition
Work breakdown structure (WBS) is an effective tool in project management and systems engineering which considers deliverables as the key elements of a structure. The structure decomposes the project into different levels and each lower level defines a more detailed project work. The department and staff are divided into groups according to the work packages in WBS.[3]
WBS consist of three key elements. Work is the task that can produce tangible results; breakdown is the hierarchical structure of gradual subdivision and classification; the structure is to organize each part according to a certain pattern.
History
In 1957, the U.S. Navy’s Fleet Ballistic Missile Program occurred a heavy schedule delay. The team tried to solve the problem and developed a form to define tasks and organize activities needed for a project on the basis of deliverables, which became known as PERT (program evaluation and review technique).
Subsequently, the Department of Defense (DOD) and NASA published the first definition of the work breakdown structure process in 1962, then the first official reference in 1968. The Work Breakdown Structures for Defense Materiel Items (MIL-STD-881) became a standard across the DOD, with templates released for specific military applications.
In 1987, the Project Management Institute introduced the work breakdown structures as standard practice to non-military applications. Then the term “work breakdown structure” was officially documented in 1993 for applications in business firms and other organizational projects.
In June 1999, the PMI Standards Program developed the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Practice Standard which summarizes the planning process into three critical steps, scope planning, scope definition, and work breakdown structure development.
Content of WBS
WBS should include project products, project organization, and division of project schedule. The structure focus on the work packages of the project which is the deliverables. The accomplishment of the project is based on the coordination and arrangement of all work packages. Therefore, the work packages that are not included in the WBS do not belong to the scope of the project.
WBS dictionary
For WBS, it is necessary to establish a WBS dictionary to describe each work part. WBS dictionary usually includes information such as work package description, schedule date, cost budget, and personnel allocation. The main application of the WBS dictionary is to define the work in detail to help create the product that will be obtained with the execution of the project. Work Packages represent the list of tasks in order to produce the particular unit of work. When WBS and OBS are used together, a coding system should be established. The coding scheme is the coding system used to uniquely determine each unit of the project work breakdown structure. Costs and resources are allocated to this coding structure. Used correctly, the WBS Dictionary becomes much more than a document that describes the work. It becomes a project kaleidoscope that allows you to look at your project data in an infinite number of ways.
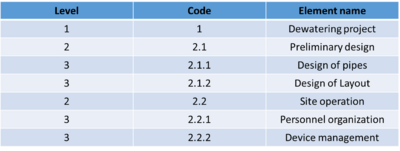
WBS elements
In fact, WBS elements are "nodes" in WBS structure. From the form of expression, they are "boxes" in "organizational chart". These boxes represent independent deliverables with the subordinate or superior relationship. After decades of development, most organizations prefer that the WBS structure be necessarily related to the project objectives and must be oriented to the final product or deliverables, so the WBS element is more suitable to describe the composition of the output product.[4] It is obvious that different organizations and cultures use different methods, procedures and resources to complete the same structure work, but their destination must be the same and meet the specified requirements. On the one hand, by considering every WBS element as a unique deliverable can we control and manage the project most effectively. On the other hand, only by identifying the deliverables can we clarify the methods, procedures and resources used by internal or external organizations to complete the work. The lowest level of element in WBS is called work packages.
Work packages
Work package is a unit of work required to fulfill a specific request. Work packages explicitly express the activity that need to be performed corresponding to the specific work, as well as the start and finish dates of the activity. It is the basis of all project work, and also suitable for a status report. The formats include work package assignment table and work package description report. The basic requirement of establishing work package is to provide sufficient and appropriate management information for project control. Work package is the lowest level project deliverable of WBS, which has the following characteristics:
- Work packages can be assigned to another project manager for planning and execution.
- The work package can be further decomposed into the WBS elements of the subprojects.
- Work package can be further decomposed into activities when making project schedule.
- The work package may be the responsibility of a single department or contractor. When used for subcontracting outside the organization, it is called the commitment package.
- The definition of work package should consider an 80-hour rule or two-week rule which means the completion time of any work package should not exceed 80 hours. At the end of each 80 hours or less, only the accomplishment of the work package is reported. Through this method of regular inspection, the adjustment of the project could be controlled.
Structure type
- Summary WBS
The outline work breakdown structure is a guiding and strategic work breakdown structure. There are only three levels in the decomposition structure
Level 1: the whole system refers to defense equipment projects, such as aircraft system, electronic system, missile system, ordnance system, space system and ground vehicle system.
Level 2: major units of defense equipment projects, such as aircraft, ships, system experiments and data.
Level 3: units subordinate to level 2, such as airframe, propulsion plant, information, service and technical publications.
- Contract WBS
Contract work breakdown structure is a work breakdown structure applicable to specific contract or procurement activities. CWBS summarizes the tasks of the project, determines the relationship among these tasks, the organizational structure and the technical status of the project. It also clarifies the logical constraint framework for the relationship between the performance, technical objectives, progress and cost of the project. The work breakdown structure of the contract shall be consistent with the levels specified in the contract. The contract should indicate at which level of the contract the cost is accumulated. Then the contractor shall have the ability to trace the accumulated cost by extending the level of contract WBS.
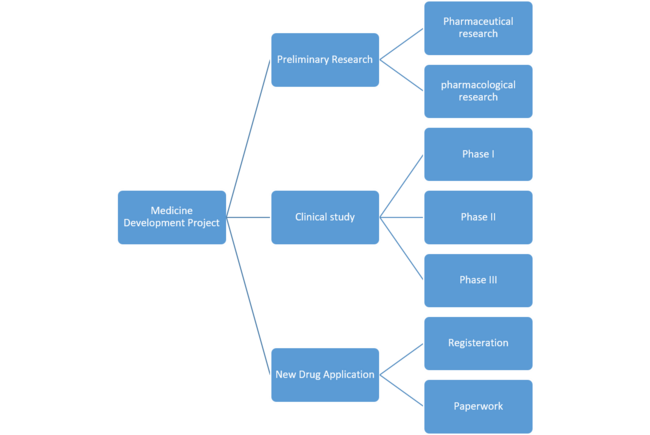
Main uses
WBS has four main uses:
- WBS is a planning and design tool to describe ideas. It helps project managers and project teams to identify and effectively manage project work.
- WBS is a structure design tool that can clearly show the relationship between the work of each project.
- WBS is a planning tool that shows the whole picture of the project and specifies the work that must be done to complete the project.
- WBS defines milestone events, which can report project completion status to senior management and customers as a reporting tool for project status.
WBS is a group of project elements oriented to project deliverables. These elements define and organize the overall scope of work of the project, and the work not included in WBS does not belong to the scope of the project. Each subordinate of WBS represents a more detailed definition and description of project work.
Prevent missing project deliverables. Help project managers focus on project objectives and clarify responsibilities. Establish visual project deliverables to estimate workload and allocate work. Help improve the accuracy of time, cost and resource estimates. Help build a project team and get a commitment from project staff. Define a benchmark for performance measurement and project control. Clear responsibilities to assist communication. Establish a framework for other project planning. Help analyze the initial risks of the project.
Application
Rules of task decomposition
The premise of WBS is to understand the scope and task of the project. Therefore, we need to carefully study the contract and learn the context of the whole project. The role of the system is to simplify a complex project through gradual decomposition. The requirement for decomposition should be distributable and deliverable. The rule of task decomposition could be summarized below.
- Ensure that the responsibility for completing each underlying work package can be clearly assigned to a member, a group of members or an organizational unit, and at the same time, consider making a work detail as easy as possible for a group of people with the same skills to undertake.
- In principle, each task should be decomposed until it cannot be further subdivided.
- Each element in WBS has a specified position and only appear once in the structure.
- One man is nominated as leading manager for each WBS, other group members are considered as participants or assistants.
- The structure is team centered contains top-down and bottom-up communication, everyone only responses to his own superior and subordinate.
- Task decomposition should synchronized with the practical situation of current execution mode.
- According to the principle of 80 hours, the time span of work package should not exceed 2 weeks, otherwise it will bring some difficulties to project control; at the same time, the granularity of control should not be too fine, otherwise it will often affect the enthusiasm of project members
- Each stage of the project life cycle can be regarded as the first layer, and the deliverable of each stage can be regarded as the second layer. If the composition of some deliverable is complex, put the constituent elements of the deliverable in the third layer.
- When decomposing, we should consider that project management itself is also a part of the scope of work, which can be taken as a separate item.
- We can extract some common work in each stage, such as personnel training as an independent detail.
Building process
The process of building a WBS is critical because project managers, project team members and project participants are required to consider all aspects of the project in the work breakdown process. The process of establishing WBS should be as follows:
- Obtain project contract and project scope description.
- Set up a project team, and the project manager leads the project participants to analyze the main tasks of the project and determine the work breakdown mode of the project.
- WBS decomposition, try to refer to the existing template, this can be easy to implement the project breakdown structure, and can reduce the difficulty of work.
- Drawing WBS hierarchy, high-level tasks can be defined as milestone events.
- Decompose the project task into small project elements, take the deliverable as the work package, make sure to detail the project to the level of budget, assign the responsible person, and arrange the schedule.
- Check the correctness of the decomposition, prevent the higher-level project elements from being decomposed, and modify the lower-level project elements that are unnecessary.
- Establish a numbering system to facilitate tracking and inquiry during project development.
- With the development of project tasks, the WBS is constantly updated to ensure that it covers all project elements.
Standard of WBS
In order to test whether WBS decomposition is reasonable and whether all elements of the project are completely decomposed, the following inspection standards can be referred to
- Each WBS element is a work package as deliverable.
- The starting point of each element accurately defined.
- The schedule is reasonable and meets the schedule requirements of the project.
- The status and completion of each project element should be quantified.
- Each project element should not interfere with each other.
- Each WBS element must be documented to ensure that all project team members can accurately understand the scope of work.
- The content of an element in WBS is the sum of all the elements in the next level.
- Project team members should actively participate in WBS decomposition to ensure the consistency of WBS.
- WBS should be able to meet the work content of the project normally according to the scope description and adapt to unpredictable changes at the same time.
Decomposition methods
WBS decomposition is to decompose a complex project into a series of clear and intuitive project work according to a specific method. For the same project, different WBS decomposition directions lead to different decomposition results. There are several ways to decompose WBS.
- Break down according to each stage of the project.
There are different stages in the process of project development, and the tasks of each stage are diverse. Take each stage as a decomposition element until the project is completed.
- According to the functional system.
For an engineering project, WBS decomposition elements can be defined as various functional departments, such as design, manufacturing, marketing and service, while the departments under each department are further decomposed
- According to the product system structure.
According to the structural characteristics of the product, it is decomposed into various elements, such as software package, hardware package, document package and maintenance package
- According to the implementation process.
The top-down method decomposes the project work step by step until it is considered that the project work has been fully decomposed
- According to the time node of the project.
As the final date of customer requirements is determined, the services to be provided should be decomposed one by one from the back to the front, and finally a work structure decomposed by time node is obtained.
Key benefits
(1) It can provide more effective control for work definition.
Generally speaking, good project management has the following principles:
1. Manage through the structural decomposition of facilities;
2. Focus on results: what to achieve, not how to achieve it;
3. Through the work breakdown structure, technology and personnel, system and organization can balance the results;
4. Establish a contract among all departments involved in the project by defining roles, responsibilities and working relationships.
5. Adopt a concise report structure.
Using WBS can meet the first three of the five principles of effective project management, and avoid the misunderstanding of planning, that is, defining work at only one detailed level. Defining work in a structured way ensures better results. Work is defined through the deliverable. As the project moves forward, only the work that is necessary for the production facilities is done, so the plan becomes more fixed. In the changing environment, the work required by the project may change, but no matter how it changes, it must be beneficial to the final result.
(2) Assign work to the appropriate work package (corresponding authorization).
The work package in WBS is natural, because the purpose of WBS is to produce products and assign responsibilities to separate departments of each product or service. If the work is defined at a detailed level and integrated into a work package, then the work package is not natural. The project manager can only be busy telling people some techniques and methods every day instead of letting them complete the work independently.
(3) Easy to find the best level of control.
People's control at a lower level may mean that they spend more time on control than they need to complete the work, while control at a higher level means that some important situations will slip away when we don't pay attention to them. Through WBS, we can find the best level of control. In general, the length of control activities should be consistent with the frequency of control meetings.
(4) Helps to limit risk.
In the above discussion, we limit the scope of planning and control, and do not include high risks. In fact, the decomposition level of WBS is not necessarily fixed, and the lowest level of WBS can be determined according to the level of risk. In a low-risk project, the lowest level of work breakdown can be work package, while in a high-risk project, we can continue to the lowest level of the project.
The work breakdown structure is a very useful tool for project managers in the process of planning and controlling their projects. A complete WBS is prepared to determine the overall objective of the project and the relationship between each individual work (part) and the whole project (whole).
(5) It is the basis of information communication.
In modern large and complex projects, a large number of resources are involved, involving many companies, suppliers, contractors and so on. Sometimes there are high-tech facilities or capital investment from government departments, so the amount of comprehensive information and information communication required is often quite large. These large projects involve huge funds and last for several years, so the project environment envisaged at the beginning of the project will change greatly with the progress of the project, that is, the uncertainty of the early stage of the project that we have mentioned many times [PP1]. This requires all relevant groups to have a common information base, a tool that can be used by relevant groups or users to communicate information from the beginning to the end of the project. These groups include: owners, suppliers, contractors, project managers, designers and relevant government departments. A properly designed work breakdown structure will enable these groups or users to have a more accurate information communication connector and become a common basis for mutual communication. Using the work breakdown structure as the basis to prepare the budget, schedule and describe other aspects of the project can make all personnel or groups related to the project understand the work needed to complete the project and the progress of the project.
(6) It provides an effective means for system synthesis and control. Typical project control system includes different subsystems such as schedule, cost and accounting. To some extent, these subsystems are independent of each other, but the system information transfer between each subsystem is indispensable. These subsystems must be well integrated in order to truly achieve the purpose of project management. The application of work breakdown structure can provide such a means.
In the application of WBS, each subsystem uses it to collect data. These systems receive information on the basis of code dictionary and coding structure which are directly related to WBS. Due to the application of WBS code, all the information entering the system is made through a unified definition method, which can ensure that all the collected data can be compared with the same benchmark, and make project engineers, accountants and other project management personnel refer to the same kind of information with the same meaning, which is obvious for the significance of project control.
For example: one of the typical problems in many projects is that the accounting system and the schedule control system do not adopt the same classification or coding, but it is very important for the effective management of the project to make a unified and appropriate explanation, analysis and prediction of the cost and schedule on the basis of an organized common. In addition, the more common links among subsystems based on WBS, the more beneficial to project control, because it can reduce or eliminate the system differences in analysis.
limitation
WBS is an effective method for comprehensive and systematic analysis of engineering projects, and it is one of the theoretical pillars of project objective system management and process control. However, WBS method also has some defects: all the activities defined by WBS are in the form of work packages, and each work package comes from the upper work package of a higher level. Such subordination makes the relationship between the upper and lower levels prominent, but ignores the relationship between specific activities, which will bring some obstacles to the application of WBS method in engineering projects. Moreover, the success of WBS highly depends on the project manager's comprehension of the project. If the manager does not have full knowledge and understanding of the key problems in a project, the division of WBS elements could be subjective and one-sided which could lead to a negative impact on the project.
Reference
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Standard for Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs, and Projects, Project management institute 2019
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Project Management: A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK guide), 6th Edition (2017)
- ↑ Glossary of Defense Acquisition Acronyms and Terms: Contract Work Breakdown Structure (CWBS). Defense Acquisition University. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ↑ Effective Work Breakdown Structures. Gregory T. Haugan. Management Concepts Press 2001.
Annotated Bibliography
- This book helps readers understand some potential problems that may arise in the Portfolios, Programs, and Projects, and explains in detail how to deal with them. WBS is also a part of this book that explains the basic concept and application of the project.
- This is a standard textbook of project management that provides detailed information. It helps develop your perspective and approach as a project manager and introduces a variety of tools and methods you can use in the application.
- Contract WBS is a developed form of WBS and this book have full knowledge of Contract WBS that could help you become an expert in this field.
- The key factor of a successful WBS is the project manager"s understanding of the project, this book could help to analyze the current situation of a project and how to create a corresponding and effective WBS on it.