Safety risk management in construction sites
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
It is worth mentioning that nowadays around the world there are companies that offer software that can simplify the lives of project managers, such as CerTus that not only after a few inputs can easily generate accurate risk management models, but also automatically fill out mandatory paperwork regarding health and safety of workers that must be submitted to the local municipality before beginning the construction<ref name="CerTus"/>. | It is worth mentioning that nowadays around the world there are companies that offer software that can simplify the lives of project managers, such as CerTus that not only after a few inputs can easily generate accurate risk management models, but also automatically fill out mandatory paperwork regarding health and safety of workers that must be submitted to the local municipality before beginning the construction<ref name="CerTus"/>. | ||
| − | == Treatment == | + | == Treatment/prevention == |
| + | |||
| + | As already mentioned, after having identified and evaluated the risks, it is vital to eliminate them in order to make the environment as safe as possible. However, quite often many sources of risks can not be eradicated, therefore they must be minimized through different ways. | ||
| + | |||
| + | One of the most effective ways to treat risks is by adopting PPE personal protective equipment<ref name="Ripub"/>, this is probably the one of the most effective steps in guaranteeing safety in a construction site. Workers are in general obligated to wear PPE, however there are times when they need to wear a specific type of equipment only when necessary, such as protective goggles and masks when spray painting or when slicing wood or materials that release harmful particles which might end up in the eyes or be inhaled. Nevertheless, when working on strategies to protect workers, collective protective strategies should always be prioritized over individual ones, such as PPE, since they tend to be passive, meaning that there is no human action required. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here are a few collective details that should be taken into account: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Limit the number of workers who could be exposed to a risk | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Limit the chemical products workers might be exposed to | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Making sure the workplace is as safe as possible | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Try to minimize the amount of time workers are exposed to risks | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Evacuation plans and measures in case of an emergency | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Installing safety signs in places where a risk is not completely eliminated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An aspect that is even more important than treating the risks is prevention, which focusses on preventing a risk from causing an accident in the first place. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Something fundamental when it comes to prevention is to inform the workers about the risks they might encounter in the construction site and prepare/train them on how to behave and tackle them; this can be done thought courses and workshops supervised by the employer<ref name="Ripub"/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Furthermore, all workers should frequently be checked by a professional doctor to make sure they are in good health condition to work efficiently and, if for instance they are not due to long exposure to noises, they should be treated properly and rest until it is necessary. | ||
| + | |||
== Inspections/Maintenance == | == Inspections/Maintenance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | A fundamental aspect of this whole process is related to inspecting and conducting maintenance on all the PPE and other protective equipment or measures taken because if they malfunction or fail to fulfill their purpose, they could put some workers at risk. If some PPEs are defective or broken, they should immediately be fixed and, if it is not possible, they should be replaced with new ones by the employer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is the safety manager’s responsibility to ensure that the measures put in place are effective and continue to be effective during the construction process by inspecting and monitoring the risks constantly<ref name="Martin"/>. | ||
| + | |||
= Limits of the safety risk management process = | = Limits of the safety risk management process = | ||
Revision as of 10:05, 18 February 2023
Building construction sites are some of the most dangerous places to work in where unfortunately roughly 60.000 people lose their life every year around the globe[1] due to the high number of objects, heavy machineries, equipment, tools, moving trucks and so on. Nevertheless, a huge responsibility is placed upon the project manager to ensure that all the potential risks workers might encounter are eliminated and, if not possible, they must be minimized.
Before digging into the concepts, it is relevant to understand what a risk is; according to Macquarie Dictionary, risk is the chance of an adverse event depending on the circumstances and its impact can be measured as the likelihood of a specific unwanted event and its unwanted consequences or loss[2] and it can be identified mathematically as follows 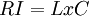 .
.
There are multiple types of risks in a typical construction site that could affect the safety of the workers, such as: vibrations, noises, respiratory, handling of heavy materials, electrocutions and many more. These risks may lead to different types of immediate consequences, from a small injury to even death; however, some complications caused by the constant exposure to one of the risks mentioned above, such as noises, could manifest in months or even years, known as professional illnesses.
Given the importance of such topic, there are a few steps explained in this article that can be followed to guarantee the safety of everybody working in the construction site. The points are the following: identification, assessment, treatment, inspections/maintenance and prevention. It must be said that, regardless of how thorough and accurate the safety risk management may be, some incidents can not be avoided due multiple factors, for instance their unpredictability or also, in certain circumstances, the low level of attention or carelessness of the workers themselves. This process is meant to find the sources of the risks and eliminate or minimize them, but it can not fully solve the issue.
Contents |
Overview of safety risks
A construction site can be a rather chaotic place with plenty of risks that can pose a threat to the health and safety of the workers. Some of the most common risks workers can face in a construction site are[3] :
- Falls from different heights that can involve workers or objects falling onto workers which can cause small injuries, permanent physical disabilities or even death in the worst cases. A few important points to take into consideration are the slipperiness of the floor where workers are operating, the type of shoes they are wearing and also the protection elements around them that could prevent them from falling, for instance the horizontal bars on a scaffolding
- Vibrations, typically caused by construction tools workers have to handle and vehicles. This type of risk does not immediately evolve into an accident, however it can cause professional illnesses in the long run depending on the level of exposure
- Noises, similarly to vibrations, they can be caused by tools and machineries. If not minimized, it can cause issues to the hearing system and in the worst cases, even permanent hearing loss
- Respiratory, this risk depends usually on: the environment in which workers are operating, such as in not well-ventilated closed rooms or the sewer system, the type of products they are using which could be toxic if inhaled, for example spray paints, and also the type on material they are operating on that could pose a threat to their respiratory system, like asbestos
- Handling of heavy materials, this could generate issues to muscles and especially bones such as the spine depending on the methods used to handle the materials and the number of times a worker needs to lift an object
- Electrocution, which can occur when utilizing certain electric tools and can generate fires or even explosions.
Management of safety risks
In this section, the whole process regarding the management of the risks potentially present in a construction site will be explained. This is a process meant to identify and try to eliminate or mitigate as much as possible all the risks that might harm the workers.
Here are the fundamental steps to follow.
Identification
This is a critical part of the process since it lays the foundation for the further steps of risk management. It is a rather complicated topic since it is done before the work begins and therefore it is based on the ability of the project manager to figure out where the risks may arise and in what circumstances[4].
The project manager or whoever is responsible for the safety of the workers should gather as much information as possible regarding similar projects and the accidents and risks that were identified[5]. This is a great way to use past databases that can help spot the sources of risk in today’s construction sites.
Furthermore, communication is vital in many areas, including risk identification; it is suggested to talk to other engineers, project managers or even the workers to see if the can contribute to the process of identifying the risks also replying on their experience in past works[5]. Since many accidents are caused by equipment or tools, it could be useful to verify the instructions of everything the workers will have to use in order to assess the hazards they might encounter[5].
Overall, this firs phase of the safety risk management process replies on the knowledge and experience of the project manager who has to identify the risks or third party individuals who might be involved like the manufacturers of tools or the workers themselves.
Assessment
This is the step in which the risks identified in the previous phase are evaluated and prioritized based on their probability of occurring and the negative effect they might have on the labor force employed in the construction site[4].
Although there are multiple ways to complete this part, two main groups can be defined to assess the risks:
- Qualitative, it is a simple way which consists in evaluating how likely it is that a risk can cause an accident and its potential impact through interviews, brainstorming and checklists[6]; afterwards, the risks are placed in a matrix called risk assessment matrix that illustrates all the risks ranked based on their severity and probability (low, serious/medium and high)[5] as it can be seen in figure 1.
- Quantitative, this is a more complex method that aims at estimating how often a risk can impact the workers and its gravity[6]. There are different ways to assess risks by using method, such as the tree analysis or the Monte Carlo simulation. It is worth mentioning that nowadays around the world there are companies that offer software that can simplify the lives of project managers, such as CerTus that not only after a few inputs can easily generate accurate risk management models, but also automatically fill out mandatory paperwork regarding health and safety of workers that must be submitted to the local municipality before beginning the construction[7].
Treatment/prevention
As already mentioned, after having identified and evaluated the risks, it is vital to eliminate them in order to make the environment as safe as possible. However, quite often many sources of risks can not be eradicated, therefore they must be minimized through different ways.
One of the most effective ways to treat risks is by adopting PPE personal protective equipment[5], this is probably the one of the most effective steps in guaranteeing safety in a construction site. Workers are in general obligated to wear PPE, however there are times when they need to wear a specific type of equipment only when necessary, such as protective goggles and masks when spray painting or when slicing wood or materials that release harmful particles which might end up in the eyes or be inhaled. Nevertheless, when working on strategies to protect workers, collective protective strategies should always be prioritized over individual ones, such as PPE, since they tend to be passive, meaning that there is no human action required.
Here are a few collective details that should be taken into account:
- Limit the number of workers who could be exposed to a risk
- Limit the chemical products workers might be exposed to
- Making sure the workplace is as safe as possible
- Try to minimize the amount of time workers are exposed to risks
- Evacuation plans and measures in case of an emergency
- Installing safety signs in places where a risk is not completely eliminated.
An aspect that is even more important than treating the risks is prevention, which focusses on preventing a risk from causing an accident in the first place.
Something fundamental when it comes to prevention is to inform the workers about the risks they might encounter in the construction site and prepare/train them on how to behave and tackle them; this can be done thought courses and workshops supervised by the employer[5].
Furthermore, all workers should frequently be checked by a professional doctor to make sure they are in good health condition to work efficiently and, if for instance they are not due to long exposure to noises, they should be treated properly and rest until it is necessary.
Inspections/Maintenance
A fundamental aspect of this whole process is related to inspecting and conducting maintenance on all the PPE and other protective equipment or measures taken because if they malfunction or fail to fulfill their purpose, they could put some workers at risk. If some PPEs are defective or broken, they should immediately be fixed and, if it is not possible, they should be replaced with new ones by the employer.
It is the safety manager’s responsibility to ensure that the measures put in place are effective and continue to be effective during the construction process by inspecting and monitoring the risks constantly[4].
Limits of the safety risk management process
Here we will mention some of the limitations or discrepancies that can emerge when using the process described. Can we actually make a construction site 100% safe thanks to the safety risk management tool?
Conclusion
Recap of the whole article.
Annotated bibliography
1) Matej Mihić (2020). "Classification of construction hazards for a universal hazard identification methodology". Research gate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339107995_Classification_of_construction_hazards_for_a_universal_hazard_identification_methodology
2) Anthony Mills (2001). “A systematic approach to risk management for construction”. Emerald Insight. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/02630800110412615/full/html?casa_token=jWz-aT1-efAAAAAA:lmJT0vBRzG_Bq9cGElDnvDB5tVEFMtXJgCZHgv3brjA2U24WqKFpqg4GM3JlMkTS3E-s5hs8zD1wgcbXzeOrQ0J3wf1_q70KR6agbCkPaowsRJPNQw
References
- ↑ Helen Lingard. “Occupational health and safety in the construction industry” (2013). Research Gate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263552916_Occupational_health_and_safety_in_the_construction_industry#:~:text=According%20to%20statistics%2C%20the%20death,worldwide%20every%20year%20%5B5%5D%20.
- ↑ Anthony Mills (2001). “A systematic approach to risk management for construction”. Emerald Insight. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/02630800110412615/full/html?casa_token=jWz-aT1 efAAAAAA:lmJT0vBRzG_Bq9cGElDnvDB5tVEFMtXJgCZHgv3brjA2U24WqKFpqg4GM3JlMkTS3E-s5hs8zD1wgcbXzeOrQ0J3wf1_q70KR6agbCkPaowsRJPNQw
- ↑ European Agency for Safety and Health at Work. “Construction safety risks and prevention” (2014). OSHwiki. https://oshwiki.osha.europa.eu/en/themes/construction-safety-risks-and-prevention
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Martin Schieg (2006). “RISK MANAGEMENT IN CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT”. Tandfonline. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1080/16111699.2006.9636126?needAccess=true&role=button
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Devdatt P Purohit*, Dr.N A Siddiqui, Abhishek Nandan & Dr.Bikarama P Yadav (2018). “Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment in Construction Industry”. Research India Publications. https://www.ripublication.com/ijaer18/ijaerv13n10_56.pdf
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Nerija Banaitiene (2012). “Risk Management: Current Issues and Challenges”. IntechOpen. https://books.google.dk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=6d2dDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA429&dq=construction+risk+management&ots=8SsN0IEQPW&sig=Sn8RJL5zsLH0QXnN1OlntlPami8&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=construction%20risk%20management&f=false
- ↑ CerTus. “Piani di Sicurezza. Acca software. https://www.acca.it/software-piani-sicurezza