Network Planning in Project Management
EmmaEgelund (Talk | contribs) (→References) |
EmmaEgelund (Talk | contribs) (→CPM/PERT) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
The CPM/PERT method is an ideal method to get an overview of a project planning process and help answering multiple questions that a project manager may have for the process. The procedure described in this section is from <ref name="OR"/>. | The CPM/PERT method is an ideal method to get an overview of a project planning process and help answering multiple questions that a project manager may have for the process. The procedure described in this section is from <ref name="OR"/>. | ||
| − | The method is a combination of the of the well known OR techniques ''Critical Path Method'' (CPM) and the ''Program Evaluation and Review technique'' (PERT). The PERT will graphically visualize the project timeline with all the individual tasks from start to completion of the project. It is used to estimate the duration of each activity, evaluating the the time that is needed in order to complete the project. The method uses the network terminology, where activities are visualized as nodes and arcs describing the precedence relationship between the activities. | + | The method is a combination of the of the well known OR techniques ''Critical Path Method'' (CPM) and the ''Program Evaluation and Review technique'' (PERT). The PERT will graphically visualize the project timeline with all the individual tasks from start to completion of the project. It is used to estimate the duration of each activity, evaluating the the time that is needed in order to complete the project. The method uses the network terminology, where activities are visualized as nodes and arcs describing the precedence relationship between the activities <ref name="PERT/">. |
The critical path can answer how long time the project will take to complete and what the bottlenecks are to be aware of in order to prevent delays of the whole project? The CPM will establish the time length of the project, summing over all the durations of the activities. In a project network from a starting node to an end node, multiple paths can be set up if the activities can be done in sequence with a predecessors and no overlap. Therefor some activities have to wait for other activities to finish before it can start. Those can be activities that are on another path. | The critical path can answer how long time the project will take to complete and what the bottlenecks are to be aware of in order to prevent delays of the whole project? The CPM will establish the time length of the project, summing over all the durations of the activities. In a project network from a starting node to an end node, multiple paths can be set up if the activities can be done in sequence with a predecessors and no overlap. Therefor some activities have to wait for other activities to finish before it can start. Those can be activities that are on another path. | ||
Revision as of 06:57, 9 May 2023
Contents |
Abstract
Planning is a big part of project management, and the success of it is highly dependent on this process. The method Network planning will be used to reduce possible complexity of a project and smoothen the execution of the project planning. A project of a large scale that require coordination of multiple activities is a challenging task for a project manager. Succeeding a project is about simple forms of working and organizing regardless the size of the project [1]. The method will therefore be used as an integration approach where the different activities are separated to get an overview of the process. Understanding the dependencies of the project and setting up millstones is also ideal to motivate the employees involved in the project.
Project networking is investigating a project as sets of interconnected activities with the purpose of assisting in planning, managing, and controlling projects [2]. This article will mainly focus on the most well know network planning techniques: the Critical path method (CPM) and the Program evaluation and review technique (PERT). CPM and PERT was developed in the 1950’s and has since then been used widely in operation research [3]. The goal of the tool is to manage a project, meeting its deadlines with a minimum total cost. The tools will help organising the project, getting an overview of the activities and estimate the total length of the project. There can be multiple paths to the end of the project, but those tools can help the manager find the most effective one. Initially the methods will need three types of information to describe the project: activity, precedence, and time [3]. This will be elaborated in the article followed by a description of the tool, an example of how to use the tool, other alternative planning tools and the limitations of the tool.
This article will elaborate the theory behind network/graphs and the focus on the comparison of different planning tools that are not focused on network planning specifically. The article is based on a project managers point of view and what that person may consider and wonder about when planning a project.
Introduction
In order to manage the complexity of a socio-technical system, such as a project, it is important to consider the following three steps; separating, integrating and adapting. Running a project can be overwhelming and no person is specialised in every little step, therefore it is important to divided the project into different activities. It is then essential for the project that these activities complement each other and contributes to the overall purpose of the project. Lastly the project needs to continuously evolve and respond to changes. The goal of every project is a smooth project execution where deadlines are meet, rework is avoided and every person involved is engaged in the success [4]. To meet this goals and increase the effectiveness, the planning of the project must executed with high priority and professionalism. Network planning is a tool used in project, program and portefolio management in the planning process. The tool is great to give an overview and coordinate the activities in the given project in order to help project managers. Today it is set up as a software package in order to deal with the data and the progress. The two tools that will be described and elaborated in this article is the Critical Path Method (CPM) and the Program Evaluation and Review technique (PERT), which were originally independently developed, but today widely used as two tools merged into one [3]. The tools work great together combining the techniques from both. This is also the case for most softwares, that it uses both tools in one with the purpose of scheduling and monitoring the project planning. In general network planning can study many different kind of problems such as project scheduling, risk analysis, cost minimization or Net Present Value maximization [2] depends on the information that is needed from the project manager. Any delays within a project results in increased costs, which is highly avoidable[4]. The method is supported by the ISO 25000 standards that suggest three main processes for developing the schedule after identifying the activities. First is sequence activities, then estimate activity duration and develop schedule [4].
Following the steps presented by the ISO 25000 standards, some information is needed in order to use network theory for planning a project:
- Activity information: the project must be broken down into individual activities
- Precedence relationships: find immediate predecessor(s) for each activity
- Time information: know/estimate the duration of each activity
Network Theory
The first section will describe the terminology of network planning where two important definitions are described in order for better understanding of the whole article.
Graph Theory
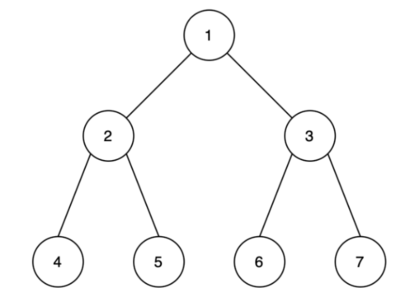
A graph that consists of multiple nodes and arcs, are considered a network. This means that a network consists of nodes that are connected through arcs. In this article the exploration of networks will be centered around project planning, which means that the nodes correspond to the events in the project. The arcs correspond to the connection between the activities and can either be directed or undirected. When an arc is directed, for example for A to B, it means that the network can only go from A to B and not from B to A. An example of a network is illustrated below.
Spanning Tree
Consider a network with a number of nodes n and no initially arcs. By adding one arc at a time between the nodes, a tree will appear. The first arc can be between any of the nodes in the network, but along the way, an arc cannot be placed if it creates a cycle. A network of nodes connected through arcs are referred to as a spanning tree. A network therefore differs between being cyclic or acyclic and a spanning three is acyclic.
A network will always have one or more start node(s) and a finish node/node(s). A project network can be split into two, depending on whether the activity is on the node or on the arc. Those two types are referred to Activity-on-arc (AOA) and Activity-on-node (AON). For the AOA, the node is separating the activities and therefor the arcs show the precedence relationship between the activities on the nodes. The AON is used in the CPM/PERT method, since it is remarkable more simple to construct, understand and revise than the AOA. Therefor this article will forward going only focus on AON, and therefor only activities. In the AOA method, it differs between events and activities, which is elaborated in an article presented in the Annotated Bibliography section.
CPM/PERT
The CPM/PERT method is an ideal method to get an overview of a project planning process and help answering multiple questions that a project manager may have for the process. The procedure described in this section is from [3]. The method is a combination of the of the well known OR techniques Critical Path Method (CPM) and the Program Evaluation and Review technique (PERT). The PERT will graphically visualize the project timeline with all the individual tasks from start to completion of the project. It is used to estimate the duration of each activity, evaluating the the time that is needed in order to complete the project. The method uses the network terminology, where activities are visualized as nodes and arcs describing the precedence relationship between the activities Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
[5]
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found