Scenario Planning Strategy
(→Context) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
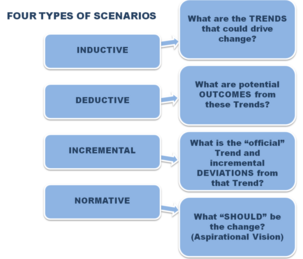
<li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:shell.png|thumb|none|303px|Figure 1: Four types of scenarios by Ged Davis (Shell Oil, 2002)<ref name="typologies">.VLAD GAVRILOVIC, Renaissance Planning "''TOWARDS A TYPOLOGY OF SCENARIO PLANNING''" Online article http://www.citiesthatwork.com/blog-renaissance/2014/02/towards-a-typology-of-scenario-planning] Retrieved on 21 October 2017</ref> (click to zoom)]] </li> | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:shell.png|thumb|none|303px|Figure 1: Four types of scenarios by Ged Davis (Shell Oil, 2002)<ref name="typologies">.VLAD GAVRILOVIC, Renaissance Planning "''TOWARDS A TYPOLOGY OF SCENARIO PLANNING''" Online article http://www.citiesthatwork.com/blog-renaissance/2014/02/towards-a-typology-of-scenario-planning] Retrieved on 21 October 2017</ref> (click to zoom)]] </li> | ||
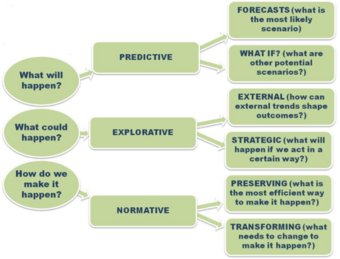
<li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:Sweden.png|thumb|none|340px|Figure 2: Three types of scenarios by Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden (2005)<ref name="typologies"></ref> (click to zoom)]] </li> | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:Sweden.png|thumb|none|340px|Figure 2: Three types of scenarios by Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden (2005)<ref name="typologies"></ref> (click to zoom)]] </li> | ||
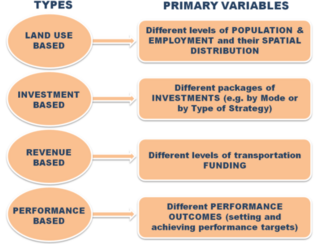
| − | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:map-21.png|thumb|none| | + | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:map-21.png|thumb|none|318px|Figure 3: Types of scenarios by Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), MAP-21 Guidance (2012)<ref name="typologies"></ref> (click to zoom)]]</li> |
</ul></div> | </ul></div> | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 21 September 2017
Scenario Planning Strategy is a systematic and methodical way for organisations to define their future actions. It is considered as part of the Strategic management tools, aiming to create a flexible plan, based on which the organisation will benefit in the long term. Scenario planning came to change and enchance the way of thinking in terms of decision making under critical uncertain cirumstancies. According to Pierre Wack "Scenarios deal with two worlds; the world of facts and the world of perceptions" [1]. The known and the unknown are mixed and a set of different possible scenarios for a particular issue is formed following people's both subjective and objective thoughts regarding how the social, technical, economic, environmental and political (STEEP) trends are going to affect it. The holistic integrated pictures of the future assist companies to both quantify and qualify their future policies and strategies creating an adaptable planning that mitigates the possible negative impacts on them.
Different types of scenarios exists such as ‘mission scenarios’, ‘issues scenarios’,‘action scenarios' [2] 'crisis scenarios' etc depending on the specific case. There are also different approaches and steps for utilizing scennario planning in buisnesses. Nowadays, a common thread to identify your possible scenarios is to implement a SWOT analysis or PEST Analysis having in mind the pace of which changes happen in the buisness sector, increasing buisness critical uncertainties. Although, as in every management tool there are sthernths and weaknesses that managers and buisnesses should take into account and will be analyzed in the article as well.
Contents |
Big Idea
Origin of Scenarios
The first time that scenario planning came into view as a concept was during World War 2, as a technique for military planning, trying to conceive and prepare against the opponents' actions [2]. The years after, the concept further developed in militarry intelligence focusing on policy games where different parties invlonved, were playing different roles under multiple plausible stories, with the view to observe the reaction of persons under different uncertain circumstancies. Later, during 1970s, scenario planning revolutionize buisness sector with its application in Royal Duch Shell. Pierre Wack, was the first who was looking for possible strategies in case an unexpected event occured in the Oil market. Through his scenarios, he facilitated the managers of the company to imagine their decision in case each of this scenarios was taken place [2]. When the oil crises broke out in 1973 no one was expecting it and only Shell was effectively prepared to address the issue.
Context
Scennario planning it is not about predicting the most likely future; it is about addressing assorted sets of strategic buisness issues by rehearsing different decisions based on a range of possibilities [3]. Different kind of scenarios exist that is hard to sort them. The categorization of the scenarios, facilitates the communication, comprehension, comparison and further development of the concept [4]. Nonetheless, a concensus hasn't been reached yet and a standarization hasn't been attemped. The following diagramms show three common approaches of scenario typologies according to the angle and the variants that each one has been developed.
Application
Limitations
References
- ↑ .The Economist, "Scenario planning". Online article [URL: http://www.economist.com/node/12000755] Retrieved on 15 October 2017
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 . Dana Mietzner & Guido Reger"Advantages and disadvantages of scenarioapproaches for strategic foresight",Department of Economics and Social Sciences, University of Potsdam" (2005). [1]
- ↑ .GBN Global Buisness Network, Monitor Group "Introduction to Scenario planning" (2008)
- ↑ .Lena Bo¨ rjesona, Mattias Ho¨ jera, Karl-Henrik Dreborgb,Tomas Ekvallc, Go¨ ran Finnvedena. ELSEVIER "Scenario types and techniques: Towards a user’s guide" (2006)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 .VLAD GAVRILOVIC, Renaissance Planning "TOWARDS A TYPOLOGY OF SCENARIO PLANNING" Online article http://www.citiesthatwork.com/blog-renaissance/2014/02/towards-a-typology-of-scenario-planning] Retrieved on 21 October 2017
Annotated bibliography
- 1. Winch, G. M. (2010), "Managing Construction projects". Second edition
- Summary: