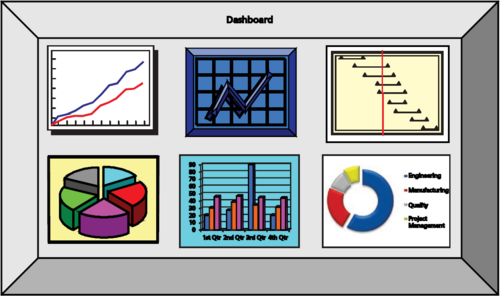
Project Dashboards
(→Why are Dashboards useful?) |
(→Why are Dashboards useful?) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
Dashboards are becoming increasingly useful in most applied contexts since information is becoming more and more digitalized, reliable, and vast. There are a plethora of potential benefits of adopting dashboard depending on the context and application. The following are some of the main general ones (Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, p. 205): | Dashboards are becoming increasingly useful in most applied contexts since information is becoming more and more digitalized, reliable, and vast. There are a plethora of potential benefits of adopting dashboard depending on the context and application. The following are some of the main general ones (Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, p. 205): | ||
| − | [[File: Dashboard_benefits.png | | + | [[File: Dashboard_benefits.png |330px|thumb|right|top|Figure 2: Main benefits of adopting dashboards]] |
:*'''High-level visibility and understanding''' | :*'''High-level visibility and understanding''' | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 25 February 2021
Contents |
Abstract
Since the advent of the computer, the world has steadily become more and more data driven. Today, data is a business key asset to any organization that takes advantage of its potential. Data has also become increasingly valuable within the field of project, program, and portfolio management, since advancements in software and tools have made project data collection and management significantly more seamless - leading to an ever-increasing amount of project data being collected throughout the course of a project. This vast amount of project data holds a great value potential if properly utilized.
Monitoring and controlling is one of the main pillars of a successfully conducted project (PMBOK, p.23). If the project-work and its progression is not monitored then any deviations from the plan will not be detected, meaning that project control and corrective actions become near impossible to manage. Imaging driving a car without a dashboard; without the critical information at a glance – like speed, fuel level, motor temperature, etc. – it becomes very difficult to operate the vehicle. The scenario is similar in a project management context; without critical project-related information at a glance, it can become difficult for the project manager to drive/control the project optimally. For this reason, it is of great importance that project managers ensure effective project monitoring, and a great way to do this is by adopting project dashboards as a tool [1].
This article will explain what dashboards are, their purpose, and why they can be extremely valuable to a project manager. Furthermore, the article will explain practical and technical application of dashboards in project management. Lastly, the pitfalls and limitations related to the adoption project dashboards will be presented.
The Big Idea
What are Dashboards?
It is commonly thought that origin of the dashboard comes from the wooden board that carriage makers attached to the front of horse carriages to prevent mud and rocks from being splashed (or “dashed”) onto drivers and their passengers by the horses that pulled them (https://www.thehogring.com/2012/11/25/where-did-the-term-dashboard-come-from/). Since then, dashboard evolved to become a key feature of e.g. the automobile in the form of a physical instrument panel that display critical information to the driver. This article will not focus on these physical instrument panel dashboards, but instead on digital dashboards that display key information needed to achieve objectives in a business or project-related context. These types of dashboards are commonly referred to as Business Intelligence (BI) Dashboards.
BI dashboards were first properly introduced in the 1980s, as corporations became increasingly data driven and digitalized. While the idea and the vision of the BI dashboard was very sound, the practical application was rarely successful until in the late 1990s, when more effective data warehousing and business intelligence methodologies meant that data had become more reliable and accessible. Since then, the dashboard has become increasingly practical and effective as corporations become increasingly data driven; leading to a surge in its popularity (Stephen Few, Information Dashboard Design, p. 23).
There is a fair degree of diversity in products that can be categorized as ‘dashboards’, and therefore it can be difficult to pin it down to a definitive definition. One definition, that appeared in Intelligent Enterprise magazine, is the following:
- “A dashboard is a visual display of the most important information needed to achieve one or more objectives; consolidated and arranged on a single screen so the information can be monitored at a glance.” (Stephen Few, "Dashboard Confusion", Intelligent Enterprise, March 20, 2004)
Effective dashboards communicate critical information in a clear and concise way in order to help its users achieve the intended objectives. The following are some of the most salient features of a good dashboard:
- Dashboards are visual displays
- A dashboard wants to communicate information with great efficiency and richness; so that the user can quickly and easily extract the correct and most important meaning from it. This is often achieved by adopting a more graphical emphasis in the display, while using text and numbers as supplementation.
- Dashboards display information needed to achieve specific objectives
- A dashboard should only communicate information that is related to achieving the objectives that it is intended to monitor. Any information that is not critical to achieving the objectives will only draw focus away from the most important information, while also making the dashboard unnecessarily convoluted. Therefore, it is important to be selective with the data that is displayed on a dashboard.
- Dashboards are used to monitor information at a glance
- A significant feature of a dashboard is that it should convey critical information at a glance. Therefore, the information it displays needs to be specific, clear, and concise. A dashboard should only display information that is key in achieving the objectives, which often can be measured quantitatively in the form of KPIs (reference). The information displayed on a dashboard is therefore often a set of KPIs. Since more specific details related to the KPIs cannot be monitored at a glance, they should not be included in a dashboard – it is very important to keep this distinction clear.
Overall, a dashboard gathers key information on the progression of achieving the objectives that it monitors. It often does this by monitoring a set of KPIs, hereby communicating the most important aspects that contribute to the achieving of the objectives. By monitoring these KPIs, a dashboard highlights any worrying trends that are occurring, and thus enables the users to address the related issues immediately.
Why are Dashboards useful?
Dashboards are becoming increasingly useful in most applied contexts since information is becoming more and more digitalized, reliable, and vast. There are a plethora of potential benefits of adopting dashboard depending on the context and application. The following are some of the main general ones (Project Management Metrics, KPIs, and Dashboards, p. 205):
- High-level visibility and understanding
- Dashboards provide great high-level visibility and understanding on the overall performance regarding certain goals. Often, different contributors to the goals will be blindsided by the perspective of their own contribution without realizing the context of all contributors – often leading to misalignment and other issues. Gaining a higher-level understanding of the goal using dashboards can help alleviate this.
- Ability to identify and correct negative trends
- One of the main purposes and benefits of dashboards is to give the user the ability to identify and correct negative trends in the KPIs that are monitored.
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Having clear KPIs monitor goals and objectives, means that issues regarding productivity and efficiency become easier to identify and address. While dashboards do not increase productivity and efficiency by themselves, they provide great opportunities to do so.
- Stronger collaboration and goal alignment
- When done correctly, dashboards can facilitate stronger collaboration and goal alignment – both internally and across different functions and departments. Having unbiased KPIs that monitor performance regarding certain goals allows every contributor to assess and align their work accordingly.
- Better decision making based on data
- When adopting dashboards, it naturally requires high data integrity and precision. This facilitates the opportunity to have decision making take basis in data analyses, which leads to less biased, well-founded, and more data driven decisions.
Overall, dashboards provide a higher-level understanding of the performance regarding the goals they monitor. This provides great opportunity for identifying and correcting negative trends and increasing productivity and efficiency. Furthermore, dashboards can provide stronger collaboration and goal alignment internally and across different functions and departments. Lastly, dashboards promote a higher data integrity and precision, leading to opportunities to achieve more data driven decisions.
Dashboards in Project Management
Dashboards are useful in any context where one needs a simplified overview of work that requires complex coordination, and this is not only the case within business management – it is also the case within project management. Projects have become increasingly large and complex which has meant that it is often near impossible for at project manager to maintain overview and understanding of all aspects and functions that contribute to the project objectives. Therefore, most project management methodologies, such as PMI and PRINCE2, put great focus on monitoring and controlling processes to help project managers overcome this challenge. Project Dashboards can and have been used to assist these processes by monitoring performance on any KPI that represents the progress of a certain project- or knowledge area goal. Most of the discussion from this point will take basis in the PMBOK methodology by PMI (reference) since this methodology includes all main aspects of project management while also remaining broadly applicable.
All knowledge areas in PMBOK include monitoring and controlling processes. Therefore, project dashboards can seemingly be useful in all project knowledge areas since all of these areas are complex and therefore generally benefit from a performance overview at a glance. Project dashboards can be used to monitor anything from cost overruns within the project cost management knowledge area to time schedule delays within the project schedule management knowledge area, and so on – seemingly, it is only ones imagination that sets the boundaries.
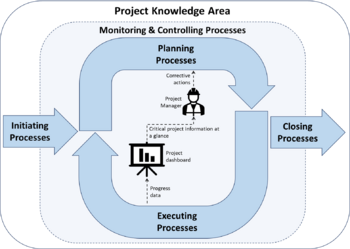
Figure 3 is a general example of how project dashboards can be integrated into the project management framework. In this example the progress of executing processes is being monitored on a dashboard. Then, using insights from the critical information at a glance, the project manager decides to make corrective actions to account for these.
Types of Project Dashboards
Application
Why are Project Dashboards useful to Project Managers?
Here I will relate dashboards to the context of project management, with main focus on the PMI standard. I will outline how dashboard can play a part in the Project Management Process Group, Monitoring and Controlling, and with basis in this explain its usefulness.
How to adopt Project Dashboards?
Here I will explain how a project manager can apply project dashboards.
Practical Application
Here I will explain some of the practicalities when adopting project dashboards. It will take basis in the ‘How to adopt Project Dashboards?’ section but explain it in the context of APPPM. I will also take basis in methodologies for efficient project reporting.
Technical Application
Here I will explain some of the technical aspects of the application:
- System and data requirements
- Project Management Software, coupled with dashboard software
- API utilization
- Levels of technical application
The Pitfalls of Project Dashboards
Here I will explain the main pitfalls of adopting project dashboards:
- Garbage in – garbage out
- Lack of support
- Lack of alignment
- Maintaining dashboard relevancy
Limitations
Here I will explain some of the limitations of adopting Project Dashboards:
- Requires IT skills
- Data must be digital
- Requires maturity
- "Merely" highlights issues