Porter's Five Forces Framework
Abstract
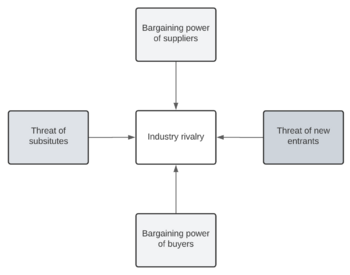
The competitive forces model, also known as Porter’s Five Forces framework, is a method used in industrial organization economics for analyzing the competition in the operating environment of a company. Porter’s Five Forces framework was published by Michael E. Porter of Harvard University in 1979 in Harvard Business Review. [1] Porter developed the model in response to the SWOT analysis, which was considered as rigor and ad hoc. [2] Porter's Five Forces framework consists of five fundamental powers that drive industry competition, namely: bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitutes and complementary goods, threat of new entrants to the market, and internal market competition. [1] Three forces represent horizontal competition: threat of substitutes and complementary goods, threat of new entrants to the market, and internal market competition. Vertical competition is represented by the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers.
The five competitive forces can be assessed to determine the profitability potential of markets and industries for a company. Analysing Porter’s Five Forces can be of great value to companies for exploring and examining market entry opportunities with regards to expanding and evaluating project portfolios – for example, in the field of product and service development. By assessing the entry barriers of industries, managers can make strategic decisions with regards to current and future projects in the company portfolio.
This article is structured as follows. First, each of Porter’s Five Forces is explained in depth, after which the application of the forces in the context of project and portfolio management is described. Besides, limitations with regards to the competitive forces model will be given, and annotated bibliography for further readings is listed.
Contents |
Big idea
Describe the tool, concept or theory and explain its purpose. The section should reflect the current state of the art on the topic
Threat of new entrants
Economies of scale
Product differentiation
Capital requirements
Cost disadvantages
Access to distribution channels
Government policy
Threat of substitutes
Bargaining power of customers
Bargaining power of suppliers
Competitive rivalry
Application
Provide guidance on how to use the tool, concept or theory and when it is applicable.
Limitations
Critically reflect on the tool/concept/theory. When possible, substantiate your claims with literature.
Annotated bibliography
Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject. Summarize and outline the relevance of each reference to the topic. (around 100 words per reference). The bibliography is not counted in the suggested 3000 word target length of the article.