Life Cycle Model
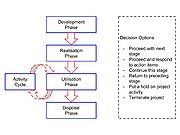
The Life Cycle Model is one of two methodical concepts that build the basis for Systems Engineering. Next to the Problem-Solving concept, which deals with the challenge of developing solutions for project management challenges, the Life Cycle Model aims to structure the life of an engineering system. It can be understood as an overall frame work that defines criteria and expected results for each life cycle phase. This allows for the evaluation of technical systems according to their current life cycle phase. Each phase can be supported by a variety of tools and methods, which are relevant to the project and its content. The model divides the life cycle in four phases, which include development, realisation, utilisation and disposal.
Contents |
Historic Background
The Life Cycle Model can not be clearly attributed to a single author[1]. A range of similar models have been presented by the guide Project Management Book of Knowledge[2] and the Project Management Handbook[3]. This articel is primarily based on the work of Rainer Züst and Peter Troxler[4], who propose the use of the Life Cycle Model in a Systems Engineering context. The content is enriched with further information from the INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook[5].
The Life Cycle Phases
Most of the literature divides the life cycle of an engineering system in-between four to seven stages. While the content of the model and its phases is depended on the targeted system, there are different definitions of each stage. INCOSE for example splits the development stage into three substages which encompass exploratory research, concept and development phase[5], whereas Züst et al.[4] suggest to include all three stages in one development phase. Further differences include wether the support/maintenance phase is excluded of the utilisation phase or, as suggest here, exists as a activity cycle parallel to the utilisation phase. A definition out of the ISO 15288 standards states in this context:
- 6.2.1.3 (a) (5) NOTE The life cycle model comprises one or more stage models, as needed. It is assembled as a sequence of stages that may overlap and/or iterate, as appropriate for the system-of-interest's scope, magnitude, complexity, changing needs and opportunities.[6]
The statement puts the focus correctly on the important fact that no matter which Life Cycle Model is chosen, the user will have to adapt it to the engineering system he/she attempts to structure.
A common feature of any structure in the Life Cycle Model are the decisions gates, which mark the end of one phase and the beginning of another. Primarily the focus is on the quality of the results of a particular phase and the decision wether those results allow to progress forward or if adjustments or even an additional iteration are required. Any project progression without reaching the previous' phases goals may entail increasing risk as the project develops[5].
Development Phase
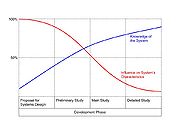
This early phase in the life cycle is crucial for the development of any Engineering System. Here the need for change is established and the decision wether or not to act are taken. Decisions which are taken do need careful consideration as they will typically influence the whole life cycle. The further the development phase progresses the less influence can be taken on the system.[7] The development phase consists of four steps:
- Proposal for systems design
The proposal for systems design originates at the recognition of a need for change. The change may require an improvement of an Engineering System or its new development. A commonly used tool in this stage is the SWOT analysis in order to pinpoint weaknesses or opportunities. Based on an assessment of the need, the decision wether or not to solve the challenge is taken.
- Preliminary study
The preliminary study aims to provide a broad picture of the challenge. It include elements like Stakeholder Analysis and Situation analysis. The target of the preliminary study is a clear problem description and a set of objectives which shall be addressed by a potential solution. Furthermore an overview of risk and uncertainties is established, which for example can be addressed by the application of Risk management strategy. When dealing with complex projects the Causal Loop Diagram might support efforts to achieve further structure within the preliminary study. Concept proposals are developed which are concretised during the main study.
- Main study
The aim of the main study is to specify the concepts in detail. The focus shifts from a broad perspective to the engineering system. The concepts are evaluated against the objectives in order to establish their suitability towards the problem solution and investigates wether issues like stakeholder involvement or critical components within the system are known and dealt with sufficiently.
- Detailed study
Within this phase detailed studies of the subsystems and their interrelation, which lead to detailed information about each sub solution and gives advice towards the implementation of the Engineering System.
Case Example Development Phase
The case company A, experiences unpleasant feedback from their customers on one of their products. The need for change is recognised and the decision to improve the situation is taken (proposal to system design). The company asses the extend of the problem. Internal as well as external factors are included in order to pinpoint the origin of the problems. The key stakeholders are identified and the area of solution defined. The search for solutions trough creative methods leads to the development of concepts, which may be evaluated by using tools such as Cost-Benefit Analysis or an evaluation matrix with a specific set of criteria (preliminary study). The preferred concept is specified and analysed in detail to establish the effect that can be expected to influence the system (main study). Finally each of the systems parts are studied in detail in order to ensure that the concept addresses all issues raised in the first step in a high quality.
Realisation Phase
The realisation phase covers the transition in between the development and utilisation phases. It can be divided in two major steps, which are system realisation and system installation. The system realisation includes task which transform the concept into a tangible system. Examples are the production of machinery or in case of IT and service systems the full documentation of the system. The system is ready to be implemented. The second phase describes the implementation itself. The system is rolled out, which includes the system's installation and the instruction of the customer/end-user.
Case Example Realisation Phase
Company A has developed a concrete concept to deal with its unsatisfied customer and chooses to redesign their existing product. The new product is developed in accordance to the established objectives, defined during the previous phase. Documentation for the new product needs to be released and customers, who are in possession of the previous product get informed about the possibility to upgrade.
Utilisation Phase
The System is in operation and it's performance monitored by a suitable system. Deviations from the expected performance can be grouped into an unintended use of the system by the user or insufficient planning throughout development and realisation phase. Depending on the systems requirements, the use phase is interrupted by activity cycles in order to improve life time and performance of the system.
Case Example Utilisation Phase
Company A has implemented the redesigned product within the system. The monitoring is based on customer feedback. Depending on the significance of the feedback the company can decide whether a third iteration and further improvement of the system is necessary. Smaller changes do not require a whole new Systems Engineering process.
Disposal Phase
The disposal phase describes the decommissioning of a system. The result of this phase is either a complete removal or a radical change of the original system. Ideally the disposal phase is considered during the development phase in order to allow a smooth removal of the system.
Case Example Disposal Phase
Company A continues to receives poor feedback on the redesigned product and decides to upgrade the product one more time. The development of the third generation of the system is interrelated with the disposal of the previous one, as it acts as a successor. Depending on the scale of the upgrade it could either be defined as activity cycle in order to enhance the product or as a complete new life cycle of an engineering system.
Activity Cycles within Individual Life Cycle Phases
Throughout its life cycle any engineering system requires frequent maintenance and updating. Activity cycles are complementary to the four regular phases of the model and target the increase of the life time/product use phase.[8] An example hereof is the servicing or repair of a product: After a certain time in use the product is examined and weak parts exchanged, after which the product re-enters the use phase (e.g. machinery). An other example is the upgrade of a system/product in order to respond to new market developments (e.g. IT software). The activity cycles are iterative and can be repeated as often as required. Usually the activity cycles are organised in separate development and realisation phases. A spare part, for example, does require the same amount of attention like the main system, in oder to ensure that the part will fit in seamlessly. Once the part is integrated in the system, the life cycle of both system and part merge and they usually continue to co-exist throughout the use and disposal phase.
Review of the Life Cycle Model
The Life Cycle Model in a Systems Engineering perspective is a generic model with broad area of application. However, depending on the use-context it does need refinement by the user in order to achieve the best possible result. As focus areas vary in every project, so does the Life Cycle Model need adjustment of the tools and methods, which are used during the four phases of the life cycle to ensure a relevance to the issues that shall be addressed. As noted above a variety of Life Cycle Models have been developed already and every single one does differ by the targeted application. As Systems Engineering itself encompasses a huge variety of products, technical and other systems, it might be reasonable to clarify, which tools can be utilised during which phase and how they can contribute to the specific challenges.
Alternate Use of Life Cycle Model
Life Cycle Models are usually featuring similar phases as described above, but as their use-context and perspectives differ, the content of each phase might be subject to change. Following examples make use of the Life Cycle Model but are not related to Systems Engineering.
- Bonnal, Gourc & Lacoste (2002) define five project management related Life Cycle Models with differing focus e.g. risk, quality or control oriented.[1]
- Life Cycle Model in the context of sustainability. It creates the basis for Life Cycle Sustainability Assessments and Life Cycle Management. Does include the stage of material extraction and is focussed on environment, business and social impacts of a product system.[9]
- Product Life Cycle. The life cycle from a business perspective. It may include issues such as innovation diffusion, maturity of product/market or revenue over time.[10]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bonnal, Pierre, Didier Gourc, and Germain Lacoste. “The Life Cycle of Technical Projects.”. Project Management Journal 33.1 (2002): 12. Print.
- ↑ Institute., Project Management. A Guide To the Project Management Body of Knowledge : PMBOK Guide. Project Management Institute, 2004. Print.
- ↑ King, W. R. and Cleland, D. I. (1997) Life-Cycle Management, in Project Management Handbook, Second Edition (eds D. I. Cleland and W. R. King), John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Züst, Rainer, and Peter Troxler. “No More Muddling Through: Mastering Complex Projects In Engineering and Management”. No More Muddling Through: Mastering Complex Projects in Engineering and Management (2006): 1-185. Web.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 INCOSE. 2012. Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and Activities, version 3.2.2. San Diego, CA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE), INCOSE-TP-2003-002-03.2.2.
- ↑ ISO/IEC 15288:2008
- ↑ Haberfellner R. et al., 2002, Systems Engineering. Daenzer, W. et al. (Publisher). 11. Auflage, Verlag Industrielle Organisation, Zürich.
- ↑ Wimmer W., Züst R., 2002, ECODESIGN PILOT – Product-Investigation, Learn- ing and Optimisation-Tool for Sustainable Product Development with CD- ROM, Kluwer Academic Pubishers, Dordrecht (NL).
- ↑ UNEP-SETAC. Towards Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment. 2011
- ↑ Klepper, S. (1996). Entry, exit, growth, and innovation over the product life cycle. AMERICAN ECONOMIC REVIEW, 86(3), 562-583.