Scenario Planning Strategy
Scenario Planning Strategy is a systematic and methodical way for organisations to define their future actions. It is considered as part of the Strategic management tools, aiming to create a flexible plan, based on which the organisation will benefit in the long term. Scenario planning came to change and enhance the way of thinking in terms of decision making under critical uncertain cirumstances. According to Pierre Wack "Scenarios deal with two worlds; the world of facts and the world of perceptions" [1]. The known and the unknown are mixed and a set of different possible scenarios for a particular issue is formed following people's both subjective and objective thoughts regarding how the social, technical, economic, environmental and political (STEEP) trends are going to affect it. The holistic integrated pictures of the future assist companies to both quantify and qualify their future policies and strategies creating an adaptable planning that mitigates the possible negative impacts on them.
Different types of scenarios exists such as ‘mission scenarios’, ‘issues scenarios’,‘action scenarios' [2] 'crisis scenarios' etc depending on the specific case. There are also different approaches and steps for utilizing scenario planning in businesses. Nowadays, a common thread to identify your possible scenarios is to implement a SWOT analysis or PEST Analysis having in mind the pace of which changes happen in the buisness sector, increasing business critical uncertainties. Although, as in every management tool there are strenghts and weaknesses that managers and businesses should take into account and will be analyzed in the article as well. A specific focus will be made in scenario planning and its liaison with project porgram and portfolio management. The article aims to investigate in what extend this tool can be implemented and what it the process to succeed it. A general overview of scenarios development and the Project program and Portfolio Management context will be presented in order to identify their incorporation.
Contents |
Big Idea
Origin of Scenarios
The first time that scenario planning came into view as a concept was during the Second World War as a technique for military planning, trying to conceive and prepare against, the opponents' actions [2]. The years after, the concept further developed in military intelligence focusing on policy games where different parties involved, were playing different roles under multiple plausible stories, with the view to observe the reaction of persons under different uncertain circumstances. Later, during 1970s, scenario planning revolutionize business sector with its application in Royal Duch Shell. Pierre Wack, was the first who was looking for possible strategies in case an unexpected event is occurred in the Oil market. Through his scenarios, he facilitated the managers of the company to imagine their decision in case each of this scenarios was taken place [2]. When the oil crises broke out in 1973 no one was expecting it and only Shell was effectively prepared to address the issue. A widespread acceptance and an increase in the tools appeal was further reinforced after the terrorist attach in September 11th 2001 in the US [1]. The attack was one of the most tangible examples of the high uncertainties that occur in 21st century along with its tremendous impacts.
Context
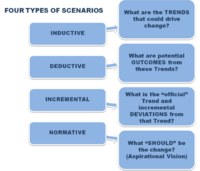
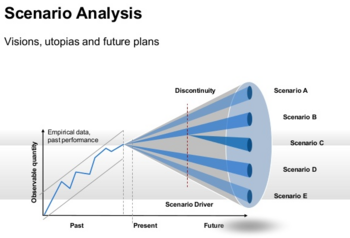
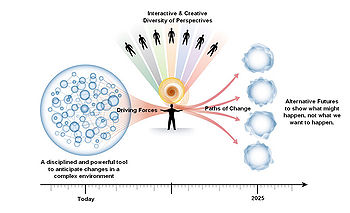
Scenarios
Scenario planning it is not about predicting the most likely future; it is about addressing assorted sets of strategic buisness issues by rehearsing different decisions based on a range of possibilities [4]. Different kind of scenarios exist that is hard to sort them. The categorization of the scenarios, facilitates the communication, comprehension, comparison and further development of the concept [5]. Nonetheless, a consensus hasn't been reached yet and a standardization hasn't been attempted. Examples are presented in Pictures 1, 2 and 3 that show three common approaches of scenario typologies according to the angle and the variants that each one has been developed.
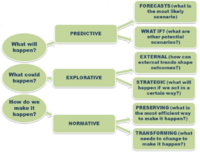
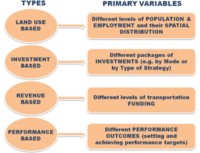
Several approaches have been developed in a theoretical point of view pertaining the creation of scenarios. In practise, each organization choose their own strategy and key principles for a good scenario formation. A general guidance for a successful scenario creation is summarized below [6]:
- The plausibility of scenarios and the rational consistency with the known facts is the first key principle. Apart from being interesting they should be also challenging in respect to organizatios' criteria. It worth to note that even if a wide range of possible scenarios will be determined for a particular issue, as a group should be mutual exclusive and concise.
- During the implementation of scenario planning process, organizations should have the consciousness and insight comprehension that divergence and not convergence drives the industries. Their envisage of the future should crearly shows that.
- Scenarios should not be limited in worst or best-case scenario. Setting constrains is like trying to set boundaries to the evolution of nature. In life, there is not only bad or good perspective, there is also a huge prospect between them. As a result creativity and imagination should play a vital role in the process considering both major changes such as, an extensive economic crisis, recession, natural disaster etc and smaller scale changes.
- The number of the possible scenarios is a matter of interest. Preferably, a description of more than three but less than five scenarios should be developed. This number let the managers to easier handle them without covering only the basic probabilities of worst case, best case and most likely futures.
Project Program and Portfolio Management
Portfolio Management consists of a set of principles and processes that aim to implement and coordinate a group of projects or programs. Portfolio defines the strategy while the management of portfolio creates priorities and ensures the alignment of the projects. It is an investment that in order to be successful, money, man, machines and materials should effectively be managed. According to Cooper et al, portfolio management is "… a dynamic decision process whereby a business’ list of projects is constantly updated and revised. New projects are evaluated, selected, and prioritized; existing projects may be accelerated, killed, or deprioritized; and resources are allocated and reallocated to active projects" Although, nowadays decision making becomes more and more complex as a number of influences should be taken into account [6]. Furthermore, in the already vulnerable environment of social, political, economical, technological and environmental changes, the ncrease of competition came to further impede organizations from coping with uncertainties. Consequently, organizations striving to achieve a proper project balance or optimal portfolio mix due to the ambiguous questions that have to reply [6]. Risk versus reward, maintenance versus growth, and short-term versus long-term projects are only some of their concerns. Scenario planning, as a strategic decision-making tool can utilize these uncertainties and incorporates them into a strategy that will prepare managers to handle the unpredictable driving forces. Scenario planning to be developed, follows the same principles (STEEP trends) for developing scenarios with the one that used for the prioritization and selection of projects within the portfolio management[6].
Application
When scenario planning is applicable
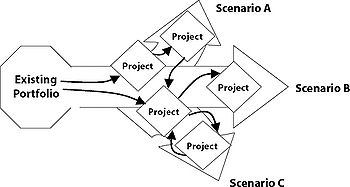
Keeping up with the rapid evolution of technology, the political and social changes and the general unstable business environment, enables scenario planning an inseparable tool in strategic management. Potentials has also been identified in its application in Project, Program and Portfolio management. More specifically, it significantly improves the way that a wide range of business problems are addressed in terms of organization [4].The application of scenario planning is not restricted in specific cases. The tool may finds its application as a learning tool or a networking process, utilizing the collective participation from people with different backround with the view not only to challenge strategic paradigms but also to redefine the borders of the organization [add ref networking]. Although, it is hard to define the exact circumstances under which the tool should be used, the following broaden conditions can be identified:[7] [4]:
- Creation of a more sustainable long-term strategy
- Decision making under uncertain conditions
- Targeting on innovation reinforcement
- Aligning key stakeholders in support of a shared vision
- Large deviation of opinions regarding decision
- The industry has already affected by an important change or is expected to
- Low quality of strategic thinking
In terms of project portfolio management, scenario planning assists in discerning in which projects should invest and allocate resources fitting to the organization's strategic direction [6]. It can be used as the main strategy of developing portfolios[8]. It is about determining a strategic decision based on wide range of possibilities, exploring innovative and unexpected events and scenarios, making business to think out of the box. In other words, scenario planning in project portfolio management plays the role of the project charter in projects [6]. More specifically, it leads the organization, providing guidance pertinent to its projects and the efficient allocation of time, money and resources on them; this is a way to fulfil the primary objective, investing on projects that are more likely to obtain a competitive advantage for the organization[6].
Scenario planning may be also applicable in project management. First, the principle difference need to be discerned between visions and scenarios. For instance, considering a simple model that from Point A you want to go to Point B choosing the most effective way to do so. The common strategy that is followed, is to create a vision of the future, where Point B represents this vision. Tactical and operational tools then will be utilized to define the plan that is required to achieve Point B; the following table (Table 1) shows the general flow. On the other hand, more than one versions of Point B could be assumed due to the uncertainty of the future. As a result the flow in the project plan will be altered[8].
| General flow | Scenario-based flow |
|---|---|
| (project)leader → vision → strategic decisions → implementation | (project)leader → scenarios → strategic decisions → implementation |
In program or project management, scenario planning could be useful when different scenarios between the team members of even the stakeholders need to be discussed in order to clearly define and reveal all the possible aspects [8]. Three major categories that the tool contributes in projects and programs are Preparatory planning, risk management and generation of new ideas (EPM add). On the contrast, many would argue that since scenario planning strategy to be implemented requires a minimum of five years time horizon, its applications in projects, that usualy their life span is less than that limit, will be limited [8].Additionally, as scenario planning contributes at most in primary decision making about the future, it may prove to be unsuitable when the project plan has already determined and approved. However, as it has already discussed, the key principles can add value and advantages in project, program and portfolio management. By definition, projects are prone to use the more tactical perspectives while programs and portfolio the more strategic aspects [8].
How to use the tools
As it has already mentioned, scenario planning is a strategy that consists of multiple plausible scenarios considering a wide spectrum of possibilities, in order to develop robust strategies. The question is how to start using this process in order to fully exploit its opportunities. The engagement of high level executives is required along with experts, researchers and managers. Diversity of knowledge is a necessity in order to examine scenarios in multiple dimensions. Several approaches have been developed standardizing the steps of the implementation process. However, there is no a single recipe that fits in all kind of organizations or industries. A general approach is defined by the following steps [6]:
- Define the Critical Issue
- Identify Critical Decision Factors
- Analyze and Rank Decision Factors by Order of Importance and Uncertainty
- Create Scenarios
- Identify Implications and Interrelationships of Scenarios
- Select Leading Scenario Indicators
- Implement Strategic Plans
Example
Limitations
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 .The Economist, "Scenario planning". Online article [URL: http://www.economist.com/node/12000755] Retrieved on 15 October 2017
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 . Dana Mietzner & Guido Reger"Advantages and disadvantages of scenarioapproaches for strategic foresight",Department of Economics and Social Sciences, University of Potsdam" (2005). [1]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 .VLAD GAVRILOVIC, Renaissance Planning "TOWARDS A TYPOLOGY OF SCENARIO PLANNING" Online article http://www.citiesthatwork.com/blog-renaissance/2014/02/towards-a-typology-of-scenario-planning] Retrieved on 21 October 2017
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 .GBN Global Business Network, Monitor Group "Introduction to Scenario planning" (2008)
- ↑ .Lena Bo¨ rjesona, Mattias Ho¨ jera, Karl-Henrik Dreborgb,Tomas Ekvallc, Go¨ ran Finnvedena. ELSEVIER "Scenario types and techniques: Towards a user’s guide" (2006)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 Dye, L. D. (2002) "Using scenario planning as an aid in project portfolio management" Paper presented at Project Management Institute Annual Seminars & Symposium, San Antonio, TX. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute. [2]
- ↑ Paul J. H. Schoemaker "When and hoe to use scenario planning: a heuristic approach with illustrations" (1991)
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Craddock, W. T. (2009) "What are the roles of scenario planning in project management?"Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2009—EMEA, Amsterdam, North Holland, The Netherlands. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute
Annotated bibliography
- 1. Winch, G. M. (2010), "Managing Construction projects". Second edition
- Summary: