Hersey and Blanchard's Situational Leadership
The general way of leading people can vary greatly between countries, cultures and industries, and has changed significantly over the last decades. The classic way of leading people was with a centralized decision-making in a top-to-bottom-approach, where management settled upon a direction, in which the people on the floor was commanded to follow. Today the general model of leading has been turned upside down, and now has the bottom-to-top approach, where employees can make decisions themselves, and are now recognized for their competences [1].
As a project manager, one of the key roles when facilitating a project, is to lead a given project team in the desired direction. This is done by utilizing and improving each team members core competences, whilst developing and supporting their weaker points, but this can be quite a challenge. Leadership is an art form, and there are about as many ways of leading people, as there are leaders. One way of doing it, is through an adaptive leadership style, where the style of leadership is dependent on the given situation at the given time. This form of leadership is called 'Situational Leadership' (SL), and proposes four different leadership styles, that each are appropriate at different stages of the team’s development:
- Directing
- Coaching
- Supporting
- Delegating
The stage of development in the team is very dynamic and will change over time. The style of leadership must therefore be adaptive to accommodate these changes [2].
Throughout this article, the history of the SL-framework, the framework itself, and its area of application will be explained. The statements will be supported with relevant examples, and there will furthermore be accounted for the limitations of the SL-framework.
Contents |
About Situational Leadership
When being in charge of a project as a project leader, the work is balanced out onto three main skillsets: 'Technical Project Management', 'Strategic and Business Management' and 'Leadership', as stated in the PMI Talent Triangle[3]. This article focuses on the leading-aspect of being a project leader, and this is done by both managing and leading a project team. The difference between these two words lies in their definitions, which respectively is by "Having executive control or authority"[4] over someone, and to "Show (someone or something) the way to a destination by going in front of or beside them"[5]. Thus, leading and managing are vastly different approaches to running a project, and how these two factors are balanced, defines the style of leadership that is applied. Which style to apply will be dependent on the situation you find yourself in at that moment of time, and will therefore change. You will therefore constantly need to adapt to these changes, and a way of deciding upon the most fitting style, will be determined using SL to assess both the given situation, but also the maturity of the project team members.
The framework of SL was founded in the 1960'es by two American psychologists named Paul Hersey and Kenneth Blanchard. They came up with the theory of SL, which at first was named the "Life cycle theory of leadership" while working on their book called “Management of Organizational Behavior”. This framework is up to this day applied globally with great success among its users, and builds upon common sense, and a belief that leadership is the opposite of one-style-fits-all. A leader applying the situational leadership should adapt to the given circumstances in a team, and manage, lead, guide and support the team members in order to achieve success in a project [6]. This will be elaborated in the following section.
Applications
In order to turn the theory of the SL into practice, one of the most important tools for the project leader is common sense. The reason for the framework to be a globally accepted way of leading people, is due to its simplicity and straight-forward approach to the subject. This framework is applicable when managing projects regardless of the scope, or the line of business, as long as there are project members to lead.
The two dimensions that the project leader is working with in regards to leading the project team members, is illustrated in the figure to the right, and requires an assessment of both the given situation of which the project is carried out in, and the team maturity of which is given by the members.
The style of leadership is shown at the top of the figure to the right, and illustrates a 2x2 matrix giving an overview of the four different leadership styles. These leadership styles are as follows [7]:
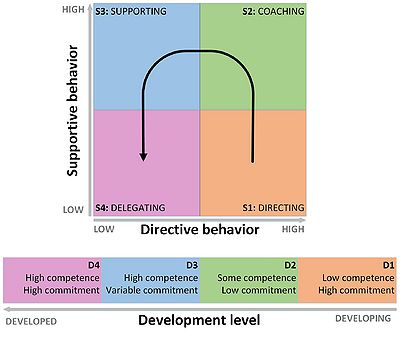
- S1: Directing (originally 'telling'): This style of leadership is in the spirit of classic management, where the project leader decides on how the different tasks involved in a project should be carried out by the project team members. Here the decision-making authority is very centralized, which is why no input from the additional project team members is allowed, and the project tasks is therefore decided upon solely by the project leader. The leadership style is therefore high on directive behavior, but low on supportive behavior.
- S2: Coaching (originally 'selling'): This style of leadership is similar to the S1-style, but also invites the additional project members to participate in the decision-making process. This is typically be carried out in a project meeting where the project leader has set up a work agenda that is discussed, and helps utilize the different competences available among the project members. The leadership style is therefore high on directive, but low on supportive behavior. The leadership style is therefore high on both directive and supportive behavior.
- S3: Supporting (originally 'participating'): In this style of leadership, the decision-making authority is more decentralized, thus requiring a higher level of mutual trust between the leader and the members. Here the project members are making decisions upon the work tasks themselves under supervision from the project leader, and leaves much of the project planning responsibility up to the whole team, rather than the project leader alone. The leadership style is therefore low on directive behavior, but high on supportive behavior.
- S4: Delegating (originally 'telling'): In this style of leadership, the decision-making authority is completely decentralized by delegating the responsibility of directing their own work to the team members. This minimizes the involvement of the project leader, thus setting higher demands for the competences of the project members. The leadership style is therefore low on both directive and supportive behavior.
As is appears from the above-mentioned bullet points, both the S1 and S2 styles has a more result-oriented approach focusing on getting the job done, whereas S3 and S4 are leaning more towards personal development, and working independently. Furthermore, the further you move from S1 towards S4, the requirements for personal competences among the project members are higher, and it is therefore essential to pair the right style of leadership with the development of the team.
The team development (originally maturity) is a more intangible factor to grasp, and has several dimensions to it. In order to make the correct assumptions in regards to the development of the project team, an acquaintance of each member is required to a certain degree. The team development can be both an assessment on which competences the team possess, but to a greater extent the familiarity with the work tasks they need to undertake. Is this a team composed of newly qualified employees with little to no knowledge of the given tasks, or is this experienced members that may even have tried the whole ordeal before? Similarly to the styles of leadership, the development of the team is broken down into four levels [9]:
- D1: In this level of development, the members of the project members lack both the experience, abilities or the confidence to take on the given tasks themselves. As mentioned before, this could typically be newly qualified employees, or inexperienced members of the project team. The members here will typically have a low level of competence, but a high level of commitment to the project.
- D2: In this level of development, the members of the project possesses the experience and abilities to some extent, but lacks the confidence to take on the given tasks themselves. This could be the case with a project team composed of members with more field experience, but who may never have been involved in a similar project before. The members here will typically some of the competences required, but a low level of commitment to the project, due to lack in confidence.
- D3: Here, the project members possesses the required competences in the sense of experience and abilities, and will be able to do the required tasks, but the commitment to the project is varying, and the need for support and encouragement from the project leader will continued be required to some extent.
- D4: Here the project members are completely qualified to the given tasks involved in the project, and has the drive themselves to see them through, and to make decisions on their own. The required project leader involvement will therefore be minimal, and is only present to set general project boundaries, and objectives, thus creating the setting for the execution of the project..
These levels of team development is determining which style of leadership should be applied, and
Limitations
The only requisite for facilitating the framework of SL is to have a project manager that possesses the self-knowledge to his own leading-capabilities, who has the desire to develop and mentor the members of the project, and self-evidently has a wish to be adaptive of the situations himself.
Critically reflect on the tool, when possible, substantiate claims with litterature https://www.leadership-central.com/situational-leadership-theory.html puts the matter of leadership simply.
We note that there is little emphasis, in this model, on the specific attributes of the leader. The qualities or traits of a leader are basically not addressed, otherthanthatheorsheisabletoperceivesituationsandmodifybehaviorin responsetothesesituations.Thefollowingsectionexploresthematterofthe characteristicsofa leader. Essentials of Project and Systems Engineering Management, 3rd Edition (2008) by Howard Eisner page 153-154.
Annotated bibliography
Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject. Summarize and outline the relevance of eact reference to the topic (around 100 words pr. reference). Bibliography is not counted in the suggested 3000 word target length of the article
Refrences
- ↑ Project Management: A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK guide) 6th Edition (2017) by the Project Management Institute (PMI)
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pykuvuA-QFU seen on 2019.02.19 uploaded by EPM
- ↑ https://www.pmi.org/learning/training-development/talent-triangle visited 2019.02.19
- ↑ https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/managing seen on 2019.02.19 by Oxford Dictionaries
- ↑ https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/lead seen on 2019.02.19 by Oxford Dictionaries
- ↑ 'http://blanchard.dk/situationsbestemt-ledelse-II seen on 2019.02.19
- ↑ 'The Human Touch: Personal Skills for Professional Success 2012 by James Cadle, Philippa Thomas, Debra Paul page 70-71
- ↑ 'https://expertprogrammanagement.com/2018/11/situational-leadership-model/ seen on 2019.02.19
- ↑ 'The Human Touch: Personal Skills for Professional Success 2012 by James Cadle, Philippa Thomas, Debra Paul page 70-71