Reflective practice
Written by Teis Johannesen
Contents |
Introduction
Reflective practice is the skill of being able to monitor and evaluate one’s own behaviour and practice critically as a learning experience. By distancing oneself towards one’s own performance an increased awareness of relevancy and scope is gained. This knowledge is important as real-life situations are often messy and uninterpretable at first glance, which makes the application of systematic approaches challenging. By being in constant conversation with the context, one’s past experiences and behaviour understanding can be achieved and theories become applicable once again. Therefore it’s a crucial competence to any professional dealing with high levels of complexity or uncertainty.
By utilizing reflective practice, one moves from otherwise inexplainable professional artistry to repeatable, developable rationale. This is achieved by utilizing a constant cycle of experimentation and reflection. While drawing upon the present and past situations solutions and decisions unique to the experienced context, can be created. Through this kind of active inquiry, the professional will then move tacit knowledge, otherwise indescribable, towards conscious thought processes.
Preface
While being an important skill for every position, like mentioned, it’s most critical in situations of high uncertainty. Traditionally developed and used in medical science and arts it's fundamentally applicable to any position where the context provides complexity beyond systematic approaches. The article will also use the term designer in a broader sense, referring to a creator. This creation could be that of a system, a product, a medical procedure, a plan or simply knowledge or understanding.
This article will cover the fundamental theory of reflective practice, its history and its application in current occupations
Big idea
Reflective practice refers to the idea of conversating with the problem faced, its context, past experiences and oneself when designing.
Theory
What is:
Professional artistry
Professional artistry is the display of immediate understanding and response from a professional when faced with a challenge in practice. What differs professional artistry from the usual systemic approach that we all perform every day, is its high level of autonomy. The use of professional artistry shown by professionals deeply invested in their field can sometimes be unconscious. A somewhat deeper integrated connection within the thought processes. Like riding a bicycle, the act may be explained in detail, but its execution requires very little conscious thinking. This artistry is enabled by what is often referred to as embodied or tacit knowledge[2].
Reflection-in/on-action
Like a conversation, any interaction with a complex system, like a person, is to some extent unpredictable. In the same sense, reflective practice aims to tackle high uncertainty situations with a constant shift between experimentation and investigation. But as with language, that which is communicated conveys more than its factuality. It conveys contextual information like rules, culture, history and expression. With the knowledge of this context, we are able to decipher and shape our next inquiry. Comparing what is observed with previous experiences or collectively accumulated knowledge taught through education, we are able to steer the direction of exploration. Through reflection either in the faced situation or after, the professional can abstract her findings, compare with her repertoire of knowledge and compose an answer to this unique problem. [4]
- Knowing-in-action(Schön)/tacit knowledge(Michael Polanyi)
History
While the term ‘’reflective practice’’ is relatively new, it is built upon theories and ideas dating long before the ’70-’80s, when it was popularized. Donald Schön himself refers to Meno, a Socratic dialogue between Plato and Socrates, that touches upon the mysteries associated with searching for something one does not know what is.[1][5] Similarly it’s argued that the ability to develop logic through inquiry of the unknown, is an inherent part of being human. What has allowed us to develop beyond other species is the competence to imagine future scenarios of change. It has allowed us to prepare for winters, establish social structures and develop systems of inventions. Furthermore, it is argued that our inquiry will always be based on logic determined and stated by the people before us as it is deeply integrated into our cultured upbringing. [4]
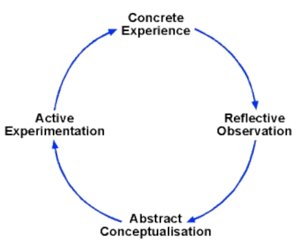
The idea of cycled experiential learning, like that presented by D. A. Kolb and R. E. Fry, and later expanded upon by G. Gibbs, gives the theory of obtaining knowledge through reflection a systematic approach.[3] [6] By presenting stages of experimentation, observation, reflection and application its users where now able to accurately and systematically describe their thought-process in situations of exploration.
Inherent tie to education (Taught systematic approaches that don't work in complex real-life practices)
Limitations
While reflective practice is an instrumental tool for life-long learning, it is not without its limitations. An uncritical utilization of the approach does not naturally lead to an advancement in practice or the development of better solutions. Generally, reflective practice lends itself to the capabilities of the designer. This requires either the professional to be well-informed about the domain in which he presents himself, self-critical towards his own prejudice or portray only small derivations from his observations.
When the designer lack knowledge about the context he’s presented with, he must invent his own understanding of its mechanics. In this situation, he has very little existing knowledge to draw upon. This has the potential to present different challenges for the designer. Without an understanding, he has no point of reference, whether it’s used to compare and evaluate or in planning what to focus on. He also doesn’t draw upon the accumulated knowledge generated among like-minded professionals. Tested theories, approaches and standards are potentially left behind. While a lacking pre-understanding isn’t purely negative, as it incites innovation, it can have great consequences in fields of high technicality, like medicine or construction.
Without a self-critical approach to one’s reflections, reflective practice might lead to self-indulging and strengthening of biases. Without self-doubt, the approach can lead to a less communicative process of rationalizing existing behaviour or practice. Similarly, without being critical of context the professional might herself to what can be immediately changed and disregarding the system or culture that lead up to this point.[7]
Lastly, compared to systematic applications of science it is time consuming. It incites introspective reflection that, if used self-critically, questions one’s own approaches. In time-sensitive situations like that often met by a fireman or doctor, this might have crucial consequences. This is why a systematic and rigorous application of tested theory is still taught in many fields. By leaning on years of dedicated research, the professional can tackle common situations with low uncertainty, with little reliance on the designers own capabilities[7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Educating the Reflective Practitioner, D. A. Schön. (1987)
- ↑ The Tacit Dimension, L. Schrijver. (2021)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Toward an applied theory of experiential learning. In C. Cooper (ed.), Theories of group processes, D. A. Kolb & R. E. Fry. (1975)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Logic, The Theory of Inquiry, J. Dewey (1938)
- ↑ The Meno, Plato, (W.K.C. Guthrie, trans.) (1956)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Learning by Doing, A Guide to Teaching and Learning Methods, G. Gibbs(1988)
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Reflecting on ‘Reflective practice’ in PBPL paper 52, L. Finlay(2008)