The Role of the Project Sponsor
Contents |
Abstract
A sponsor is the person or group who provides resources and support for the project, and is accountable for enabling success. The sponsor may be external or internal to the project manager's organization [1]. This is a critical role, as is focused on monitoring and controlling the project in a strategic level. It Is very common to associate the term “Project Sponsor” to a disconnect stakeholder from the project. On the contrary, a Project Sponsor can define the difference among success and failure. Moreover, one of the fundamentals reasons why a project fails is the absence of executive sponsorship and management [2]. The Sponsor owns the business case and leads the project through the initiating processes until formally authorized, and plays a significant role in the development of the initial scope and charter [3]. Therefore, it is vital to establish a close relationship between the sponsor and the P3 [glossary 1] to ensure that the business case remains viable and it will deliver the stipulated goal and benefits. There is a lack of understanding of the impact that a Project Sponsor can address on the success of a project. The main goal of this article is defining the role and responsibility and identify the importance of a Project Sponsor in any project.
Introduction
The term “Project Sponsor” appears to have emerged at the end of the 1980s. In 1990, the term appears in the book “Project Leadership by Brines Geddes and Hastings, 1990”[4], defining the project sponsor as the “Project Manager boss”. In 1993, J. Rodney Turner[5] discussed the sponsor as the “owner” of the project, the person who paid for the work and controlled the flow of the money. Turner made the distinction between the sponsor as the owner, and the champion as the project’s advocate Regardless of the precise definition of the role, the term “project sponsor” has come into widespread use in the context of internal projects. On closer examination, it appears that the term and the role are more frequently used in the context of internal projects, projects where both the project owner or client and the project manager and project delivery team are within the same organisation. The term is less widely used where the project is delivered to the client or owner by a separate organisation through a contractual arrangement as is generally the case. The client or owner organisation, may however appoint a project sponsor, responsible, on behalf of the client or owner organisation, for the interface with the contracting organisation delivering the project. This helps to explain the need for a project sponsor. The project sponsor role becomes relevant where there is a need to identify a person responsible for the project on behalf of an organisation and as Kerzner says: Project sponsorship has evolved into the best way that executives can provide support for a project regardless of whether internal or external[6].
The Project Sponsor
Definition and Responsibilities
According to the PMBOK® Guide, a sponsor is the person or group that provides the financial resources, in cash or kind, for the project. When a project is first conceived, the sponsor champions the project. This includes serving as spokesperson to higher level of management to gather support throughout the organization and promote the benefits that the project will bring. The sponsor leads the project through the engagement or selection process until formally authorized, and plays a significant role in the development of the initial scope and charter. For matters that are beyond the control of the project manager, the sponsor serves as an escalation path. The sponsor may also be involved in other important issues such as authorizing changes in scope, phase-end reviews, and go/no-go decisions when risks are particularly high. ref3
In dissecting this definition we can extract the following responsibilities of a sponsor: [7]
- Champion the project
- Lead the project through the engagement or selection process until formally authorized
- Provide a significant role in the development of the initial scope and charter
- Serve as an escalation path
- Authorize changes in scope
- Provide go/no-go decisions.
General Role
The sponsor leads the project through the initiating processes until formally authorized, and plays a significant role in the development of the initial scope and charter. For issues that are beyond the control of the project manager, the sponsor serves as an escalation path [1]. The Project Sponsor Role is responsible for providing good governance for the project. This includes the following: [8]:
- Maintaining a focus on the broader issues on behalf of the project / informing the project manager and team of organizational and environmental changes which might impact the project.
- Establishing connections on behalf of the project, and supporting interfaces between the project team and the winder organization and external environment.
- Advocating on behalf of the project with the senior executive and other key senior stakeholders.
- Clearing pathways so that key resources can be obtained for the project.
- Motivating the project team when times are difficult.
- Objectively criticizing project performance.
- Providing ad hoc support to the project manager and the project team, including mentoring.
- Approving finance.
Role between the Project and the Organisation
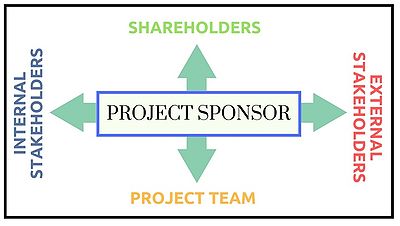
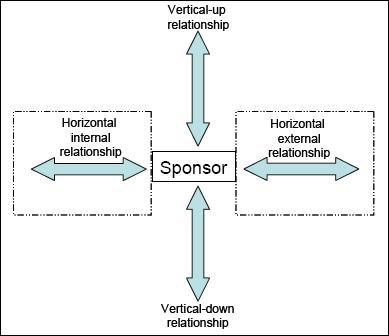
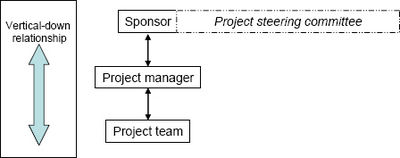
The Project Sponsor often serves as the liaison between the project and the organisation. The sponsor has different responsibilities towards different stakeholders during different phases of the project life-cycle. These responsibilities are what ultimately determine the attributes required by the individual who will act in this role.[9] Figure 1 illustrated the framework (Lechtman, 2005[10]) for describing and analyzing the pivotal role with 360 degree relationships. It is clear that there are four main sets of relationships, namely vertical-up, horizontal internal, horizontal external and vertical-down.
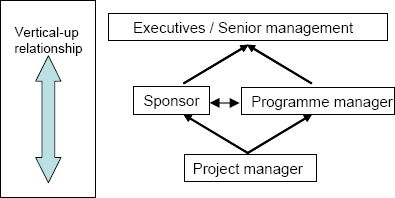
- Vertical-Up Relationship: this section relates to the senior managers, directors and executives. Aligning the project with strategic objectives, ensuring good governance and managing the relationship with senior management (Figure 2). The sponsor is mainly responsible for re-defining the existing way of doing business through innovation and new ideas and is, therefore, the idea originator. This is followed by selling the idea or project to the decision-making body and obtaining the necessary funding for it.(ref6). The project sponsor should understand the greater impact the project will have on the organization now and in the future. Ensuring that governance is maintained on the project through representing the project in governance structures within the organization. This means taking full accountability, responsibility and ownership of the project, ensuring that it is correctly resourced with the right people, that it is funded properly and enjoys the correct priorities. Moreover, this role is expected to solve any senior management conflict that could compromise the evolution of the project.
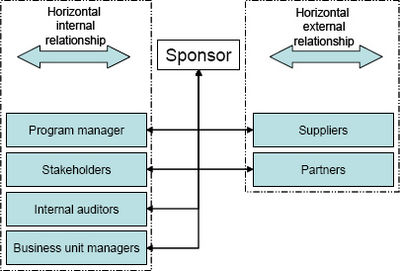
- The Horizontal Relationship: As shown in Figure 3, relates to the different internal stakeholders and business unit managers as well as external relationships with vendors, suppliers and partners. From the internal relationship viewpoint, there is an expectation that the sponsor should understand what is expected from the project from a business perspective. The sponsor must ensure buy-in and cooperation from peers and all other stakeholders. Maintaining a good relationship with peers and stakeholders will assist with removing any obstacles that requires hierarchical power. The external relationship viewpoint, the sponsor should liaise with and acquire support from all third party suppliers and vendors and ensure that all deliverable are appropriate. The sponsor should also ensure that the requirements of external partners, such as a holding company, are addressed through the project. The above can be summarized into two main responsibilities namely to build and maintain relationship with internal and external stakeholders, to facilitate an environment and political climate that is conducive to project success.(ref6)
- The vertical-down relationship: The expectation from the project manager and team is that the sponsor should drive the implementation of the project and facilitate changes to the environment through supporting the change processes. The person in this role should provide leadership in the project and the business and make decisions on what is in the best interests of the organization. The sponsor should work very closely with and give direction to the project manager and team (Figure 4) and ensure the project remains on track by maintaining discipline. From the project team point of view, the sponsor must assemble an efficient team and be involved in the guidance, support and motivation of the team. Regular communication with the team should also take place to obtain their feedback. There are also task-related expectations of the sponsor that include prioritizing project requirements and the timely approval of changes according to the change management process. The sponsor must make decisions where they cannot be made by the team or project manager, and escalate problems that must be resolved.(ref6)
Project Stakeholders & Governance
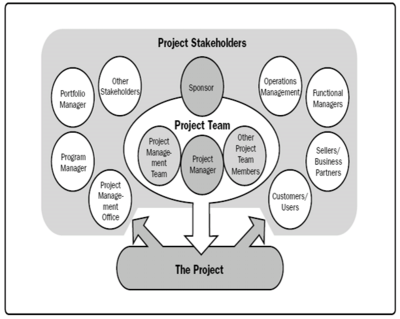
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization who may affect, be affected by, or perceive itself to be affected by a decision, activity, or outcome of a project. Stakeholders may be actively involved in the project or have interests that may be positively or negatively affected by the performance or completion of the project. [1] Project governance—the alignment of the project with stakeholders' needs or objectives—is critical to the successful management of stakeholder engagement and the achievement of organizational objectives. Project governance enables organizations to consistently manage projects and maximize the value of project outcomes and align the projects with business strategy [1]. These two provide the structure that a Project Manager and Sponsor need to address to satisfy all the requirement’s form the stakeholder.
Project Stakeholders
Stakeholders include all members of the project team as well as all interested entities that are internal or external to the organization. The project team identifies internal and external, positive and negative, and performing and advising stakeholders in order to determine the project requirements and the expectations of all parties involved. The project manager should manage the influences of these various stakeholders in relation to the project requirements to ensure a successful outcome(ref3). Figure 6 illustrates the relationship between the project, the project team, and various stakeholders.
Stakeholders have different levels of responsibility and authority when contributing on a project and this change affect the course of the project's life cycle. Identifying stakeholders, understanding their grade of impact on a project, and balancing their demands, requirements, and expectations are critical to the success of the project and failure to do so can lead to delays, cost increases, unexpected issues, and other harmful consequences including project annulment.
Just as stakeholders can positively or adversely impact a project's objectives, a project can be perceived by the stakeholders as having positive or negative results. For example, business leaders from a community who will benefit from an industrial expansion project will see positive economic benefits to the community in the form of additional jobs, supporting infrastructure, and taxes. In the case of stakeholders with positive expectations for the project, their interests are best served by making the project successful. In contrast, the interests of negatively affected stakeholders, such as nearby homeowners or small business owners who may lose property, be forced to relocate, or accept unwanted changes in the local environment, are served by impeding the project's progress. Overlooking negative stakeholder interests can result in an increased likelihood of failures, delays, or other negative consequences to the project.(ref3)
Accordingly to the PMBOK® Guide the following are some examples of project stakeholders:
- Sponsor: The sponsor leads the project through the initiating processes until formally authorized, and plays a significant role in the development of the initial scope and charter.
- Customers and users: Customers are the persons or organizations who will approve and manage the project's product, service, or result. Users are the persons or organizations who will use the project's product, service, or result. Customers and users may be internal or external to the performing organization
- Sellers: vendors, suppliers, or contractors, are external companies that enter into a contractual agreement to provide components or services necessary for the project
- Business partners: Business partners are external organizations that have a special relationship with the enterprise, sometimes attained through a certification process. Business partners provide specialized expertise or fill a specified role such as installation, customization, training, or support.
- Organizational groups: Organizational groups are internal stakeholders who are affected by the activities of the project team. Examples of various business elements of an organization that may be affected by the project include marketing and sales, human resources, legal, finance, operations, manufacturing, and customer service.
- Functional managers: Functional managers are key individuals who play a management role within an administrative or functional area of the business, such as human resources, finance, accounting, or procurement.
- Other stakeholders: Additional stakeholders, such as procurement entities, financial institutions, government regulators, subject matter experts, consultants, and others, may have a financial interest in the project, contribute inputs to the project, or have an interest in the outcome of the project.
Project Sponsor vs Project Manager
Conclusion
Glossary
- ↑ P3: Project, Programm and Portfolio Management.
Bibliography
References- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge PMBOK® Guide, Fifth Edition, 2.2 Project Stakeholders and Governance
- ↑ KPMG New Zealand Project Management Survey 2010
- ↑ A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge PMBOK® Guide, Fifth Edition, 2.2.1 Project Stakeholders
- ↑ Project Leadership, Briner, Wendy, Geddes, Michael, Hastings, Colin. 1990
- ↑ Handbook of Project-based Management: Leading Strategic Change in Organizations, 1993, J. Rodney Turner
- ↑ In Search of Excellence in Project Management: Successful Practices in High Performance Organizations, Harold R. Kerzner, 1998 – Page 471
- ↑ https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/project-sponsorship-collaborative-journey-6210. James, V. M. (2011). Project sponsorship: a collaborative journey. Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2011—North America, Dallas, TX. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute
- ↑ Tools for Complex Projects, CRC Press, 2016. Kaye Remington, Julien Pollack. Role definition, page 125
- ↑ https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/exploring-role-executive-project-sponsor-8107. Labuschagne, L., Cooke-Davies, T., Crawford, L., Hobbs, J. B., & Remington, K. (2006). Exploring the role of the project sponsor. Paper presented at PMI® Global Congress 2006—North America, Seattle, WA. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ Lechtman, E. (2005). A Holistic Framework for Successfully Sponsoring ITProjects