Creativity as a Practice in Projects
Contents |
Introduction
Creativity is when something novel and relevant is created. It can be everything from a joke, clay model or food recipe to something more business oriented – new product, process or strategy. Notice that creativity is not only creating something new or unique, but just as important, it should be relevant and appropriate for a given problem or situation [1]. This last notion is what often is referred to as innovation, new ideas that bring value [2]. This article focuses on the topic of creativity used in organizations, and more specifically projects, programs and portfolios. Creativity is what typically fosters the non-standard, imaginative and original solutions to a problem. It is therefore by its nature highly valued by managers and organizations, as it can solve the unsolvable problems and bring competitive advantage.[3]
Advantages and Disadvantages
Below is the most important advantages and disadvantages of working with creativity. The advantages can be divided into team level and organizational level.
Advantages at team level
The following benefits the team, assumed that the creative process is handled professionally and appropriately. Creativity can work as a teambuilding exercise. Creativity is happening on a conceptual level, and therefore everybody is able to participate. As everybody can participate, the team develops, and everybody can see his or her contributions to the progress. Working creatively is also rewarding in itself, since generating ideas is making a feeling of fulfillment. Creative processes is also able to open op the minds of more “closed” analytically team members. Leverage of knowledge and experience is also often a benefit from a cross functional creative team. [4]
Summary:
- Building emotional involvement
- Generating new ideas
- Increasing teaming
- Leveraging and increasing knowledge
- Opening minds
- Stretching the performance of people
Advantages at organizational level
The advantages of the organization is directly linked to competitive advantages. Organizations environment, competitors, markets etc. is experiencing an accelerating rate of change, and thus reacting quickly and working with novel technologies requires a high level of creativity. As the environment is in rapid change, it is also getting increasingly complex, and while complexity requires highly analytical skills, the problem solving requires creative skills. The society is becoming more globalized. Globalization both poses a threat, as well as a new field/option to work with creatively. [5]
Summary:
- Accelerating rates of change
- Rapid technological change
- Increasing complexity of the environment
- Globalization of business competition
- Transition from industrial to knowledge-based society
Disadvantages
The disadvantage of creativity is that it challenges the current situation and progress of the project. A project can take a completely unexpected turn during creative process. Creativity also challenges the authority, by definition you need to neglect authorities when working creatively. Both of the mentioned disadvantages can cause anxiety and dissatisfaction within the project team. From a manager’s viewpoint, creativity can also be a very inefficient way of operating, since it requires a lot of time and most of the experts. And while it is a very costly process, it is, as mentioned earlier, a very unpredictable process and therefore valuable take-away is not guarantied. This last disadvantages is the main reason why creativity is not seen as much in projects as it could be.[6]
Summary: 
- Cause of anxiety
- Challenge authority
- Upset team
- Upsetting the status quo
- Waste of resources
Creativity in project, program and portfolio management
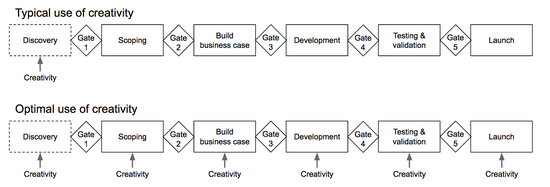
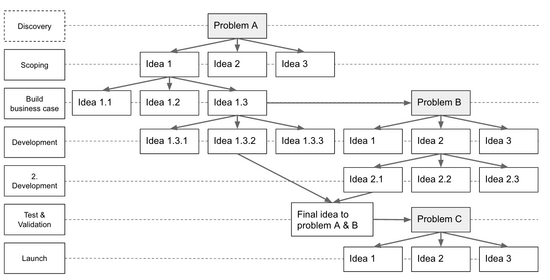
Creativity is often perceived as the initial phase of a project, the idea that sparks a business case. However creativity is happening in all phases of the project, from initial concept to finalization. Therefore the creativity process should be facilitated, and carefully planned for all the phases. See figure 1. An example of why and how creativity is used through all projects phases can be seen in figure 2. The first phase idea generates several ideas for problem A. Then a new round of idea generation commences, however as one of the new ideas is selected, it uncovers Problem B. This converging - diverge approach continues, and even at the last phase, launch, there can still be problems that need to be solved with new ideas. Many projects does like the example in figure 2 face constant changes or arising problems, this is just the typical path of projects. All the ideas seen in figure 2 could be effectively developed through creative processes, since these facilitate open minded, cross-functional, knowledge based ideas.
Specific methods
This section will describe 3 different methods or ways of thinking that can facilitate creativity in a project environment.
Specific goals Many perceive creativity as a limitless, “everything is possible”. However Balder Onarheim found that constrains to creativity is in fact enhancing creativity [7]. Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg who investigated several European companies that had been trying out innovation processes confirms this viewpoint [8]. The more accurate constraints you can add to a problem, the more creative people are when solving it, and the more valuable ideas you get. This gives the project manager the difficult task of establishing clear constraints before any creative process.
Separate the brain The frontal lobe of the brain works as the “sense-making” analytical part of the brain. It has been proven that limited activity in the frontal lobe has caused increased creativity. Initially this was realized as patients suddenly started to paint and be very artistically after the frontal lobe was damaged [9]. This argues that, while being creative, all analytical thought processes should stopped. This requires immense control by the project team and project manager.
Picture cards It has been found that long association connections are facilitating higher quality of creative ideas. The brain develops paths of electrodes as it gets knowledge and experience, however if you need to develop novel ideas you need to take other paths. These other paths are difficult to take without some sort of random inspiration. This has developed the method of picture cards. You pick a random card picturing a person, place or a thing, and from this you try to develop a relevant solution to your problem [10].
References
- ↑ Goleman, Kaufman, and Ray, The Creative Spirit, Plume, 1993
- ↑ Innovations bog
- ↑ Ralph L. Kliem, Creative, Efficient, and Effective Project Management Auerbach Publications 2013
- ↑ James M. Higgins, Innovate or Evaporate, New Management Pub Co 1995
- ↑ James M. Higgins, Innovate or Evaporate, New Management Pub Co 1995
- ↑ Nierenberg, The Art of Creative Thinking, Cornerstone Library, 1982
- ↑ Balder Onarheim, ‘’An Introduction to 'Creativity Constraints’’ Proceedings of The XXIV ISPIM Conference 2013
- ↑ Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg ‘’Innovation as Usual’’, LR Business 2013
- ↑ De Souza Et Al. ‘’Frontal lobe neurology and the creative mind’’, Frontiers in Psychology 2014
- ↑ Balder Onarheims lecture ‘’How to get great ideas’’ the 22 october 2014